
Thrombin is a serine protease, an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the F2 gene. Prothrombin is proteolytically cleaved to form thrombin in the clotting process. Thrombin in turn acts as a serine protease that converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble strands of fibrin, as well as catalyzing many other coagulation-related reactions.
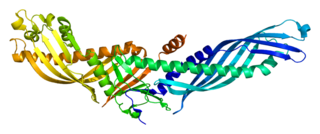
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), also called plasma lipid transfer protein, is a plasma protein that facilitates the transport of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides between the lipoproteins. It collects triglycerides from very-low-density (VLDL) or low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and exchanges them for cholesteryl esters from high-density lipoproteins (HDL), and vice versa. Most of the time, however, CETP does a heteroexchange, trading a triglyceride for a cholesteryl ester or a cholesteryl ester for a triglyceride.

Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein also known as 5-lipoxygenase activating protein, or FLAP, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ALOX5AP gene.

Mannan-binding lectin serine protease 1 also known as mannose-associated serine protease 1 (MASP-1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MASP1 gene.

Mannan-binding lectin serine protease 2 also known as mannose-binding protein-associated serine protease 2 (MASP-2) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MASP2 gene.

Cathepsin G is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTSG gene. It is one of the three serine proteases of the chymotrypsin family that are stored in the azurophil granules, and also a member of the peptidase S1 protein family. Cathepsin G plays an important role in eliminating intracellular pathogens and breaking down tissues at inflammatory sites, as well as in anti-inflammatory response.

Lipoprotein(a) is a lipoprotein subclass. Genetic studies and numerous epidemiologic studies have identified Lp(a) as a risk factor for atherosclerotic diseases such as coronary heart disease and stroke.

Integrin, alpha E (ITGAE) also known as CD103 is an integrin protein that in human is encoded by the ITGAE gene. CD103 binds integrin beta 7 to form the complete heterodimeric integrin molecule αEβ7, which has no distinct name. The αEβ7 complex is often referred to as "CD103" though this appellation strictly refers only to the αE chain. Note that the β7 subunit can bind with other integrin α chains, such as α4 (CD49d).

Taste receptor type 2 member 50 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAS2R50 gene.

Hyaluronan-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HABP2 gene.

Transmembrane protease, serine 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TMPRSS2 gene.

Probable serine carboxypeptidase CPVL is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CPVL gene. The "CPVL" gene is expressed mainly in monocytes and macrophages, and it is located in the endoplasmatic reticulum and in the endosomal/lysosomal compartment. The distribution of CPVL suggests that the enzyme may be involved in antigen processing and the secretory pathway. Besides those macrophages-rich tissues, the heart and kidney also express high levels of CPVL mRNA.The enzyme is similar to the carboxypeptidases CATHA and SCPEP1, but no direct confirmation of the enzymatic activity was obtained so far. The exact function of this protein, however, has not been determined.

Corin, also called atrial natriuretic peptide-converting enzyme, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CORIN gene.

Serpin A9 also known as centerin or GCET1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SERPINA9 gene located on chromosome 14q32.1. Serpin A9 is a member of the serpin family of serine protease inhibitors.

Myosin-15 also known as myosin, heavy chain 15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYH15 gene.

Vesicle transport through interaction with t-SNAREs homolog 1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VTI1A gene.

Kinesin family member 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF6 gene. This gene encodes a member of the kinesin family of proteins. Members of this family are part of a multisubunit complex that functions as a microtubule motor in intracellular organelle transport.

Dmx-like 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DMXL2 gene.

Transmembrane and coiled-coil domain 6, TMCO6, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMCO6 gene with aliases of PRO1580, HQ1580 or FLJ39769.1.

Cancer susceptibility 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CASC1 gene.






















