Related Research Articles

A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2022, supercomputers have existed which can perform over 1018 FLOPS, so called exascale supercomputers. For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers.

Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is a federally funded research and development center in Livermore, California, United States. Originally established in 1952, the laboratory now is sponsored by the United States Department of Energy and administered privately by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC.
Floating point operations per second is a measure of computer performance in computing, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations.

Blue Gene was an IBM project aimed at designing supercomputers that can reach operating speeds in the petaFLOPS (PFLOPS) range, with relatively low power consumption.

Sandia National Laboratories (SNL), also known as Sandia, is one of three research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). Headquartered in Kirtland Air Force Base in Albuquerque, New Mexico, it has a second principal facility next to Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in Livermore, California, and a test facility in Waimea, Kauai, Hawaii. Sandia is owned by the U.S. federal government but privately managed and operated by National Technology and Engineering Solutions of Sandia, a wholly owned subsidiary of Honeywell International.
Cray Inc., a subsidiary of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, is an American supercomputer manufacturer headquartered in Seattle, Washington. It also manufactures systems for data storage and analytics. Several Cray supercomputer systems are listed in the TOP500, which ranks the most powerful supercomputers in the world.

The Advanced Simulation and Computing Program (ASC) is a super-computing program run by the National Nuclear Security Administration, in order to simulate, test, and maintain the United States nuclear stockpile. The program was created in 1995 in order to support the Stockpile Stewardship Program. The goal of the initiative is to extend the lifetime of the current aging stockpile.

The National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC) is a high-performance computing (supercomputer) research facility that was founded in 1974. The National User Facility is operated by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory for the United States Department of Energy Office of Science.

PGI was a company that produced a set of commercially available Fortran, C and C++ compilers for high-performance computing systems. On July 29, 2013, Nvidia acquired The Portland Group, Inc. As of August 5, 2020, the "PGI Compilers and Tools" technology is a part of the Nvidia HPC SDK product available as a free download from Nvidia.

The TOP500 project ranks and details the 500 most powerful non-distributed computer systems in the world. The project was started in 1993 and publishes an updated list of the supercomputers twice a year. The first of these updates always coincides with the International Supercomputing Conference in June, and the second is presented at the ACM/IEEE Supercomputing Conference in November. The project aims to provide a reliable basis for tracking and detecting trends in high-performance computing and bases rankings on HPL benchmarks, a portable implementation of the high-performance LINPACK benchmark written in Fortran for distributed-memory computers.

IBM Sequoia was a petascale Blue Gene/Q supercomputer constructed by IBM for the National Nuclear Security Administration as part of the Advanced Simulation and Computing Program (ASC). It was delivered to the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) in 2011 and was fully deployed in June 2012. Sequoia was dismantled in 2020, its last position on the top500.org list was #22 in the November 2019 list.

Exascale computing refers to computing systems capable of calculating at least 1018 IEEE 754 Double Precision (64-bit) operations (multiplications and/or additions) per second (exaFLOPS)"; it is a measure of supercomputer performance.
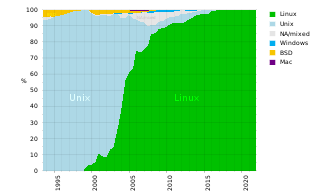
A supercomputer operating system is an operating system intended for supercomputers. Since the end of the 20th century, supercomputer operating systems have undergone major transformations, as fundamental changes have occurred in supercomputer architecture. While early operating systems were custom tailored to each supercomputer to gain speed, the trend has been moving away from in-house operating systems and toward some form of Linux, with it running all the supercomputers on the TOP500 list in November 2017. In 2021, top 10 computers run for instance Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), or some variant of it or other Linux distribution e.g. Ubuntu.

Appro was a developer of supercomputing supporting High Performance Computing (HPC) markets focused on medium- to large-scale deployments. Appro was based in Milpitas, California with a computing center in Houston, Texas, and a manufacturing and support subsidiary in South Korea and Japan.

PSSC Labs is a California-based company that provides supercomputing solutions in the United States and internationally. Its products include "high-performance" servers, clusters, workstations, and RAID storage systems for scientific research, government and military, entertainment content creators, developers, and private clouds. The company has implemented clustering software from NASA Goddard's Beowulf project in its supercomputers designed for bioinformatics, medical imaging, computational chemistry and other scientific applications.

AMD Instinct is AMD's brand of data center GPUs. It replaced AMD's FirePro S brand in 2016. Compared to the Radeon brand of mainstream consumer/gamer products, the Instinct product line is intended to accelerate deep learning, artificial neural network, and high-performance computing/GPGPU applications.

Hewlett Packard Enterprise Frontier, or OLCF-5, is the world's first exascale supercomputer. It is hosted at the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF) in Tennessee, United States and became operational in 2022. As of November 2024, Frontier is the second fastest supercomputer in the world. It is based on the Cray EX and is the successor to Summit (OLCF-4). Frontier achieved an Rmax of 1.102 exaFLOPS, which is 1.102 quintillion floating-point operations per second, using AMD CPUs and GPUs.

ROCm is an Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) software stack for graphics processing unit (GPU) programming. ROCm spans several domains: general-purpose computing on graphics processing units (GPGPU), high performance computing (HPC), heterogeneous computing. It offers several programming models: HIP, OpenMP, and OpenCL.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise El Capitan, is an exascale supercomputer, hosted at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in Livermore, United States and becoming operational in 2024. It is based on the Cray EX Shasta architecture. El Capitan displaced Frontier as the world's fastest supercomputer in the 64th edition of the Top500. El Capitan is the third exascale system deployed by the United States and its primary purpose is to support the stockpile stewardship program of the US National Nuclear Security Administration.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 de Supinski, Bronis R. (August 29, 2019). The LLNL Near and Long Term Vision for Large-Scale Systems (PDF) (Report). Retrieved August 28, 2022.
- 1 2 "TOSS: Speeding Up Commodity Cluster Computing". Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory . Retrieved August 28, 2022.
- ↑ León, Edgar A.; D'Hooge, Trent; Hanford, Nathan; Karlin, Ian; Pankajakshan, Ramesh; Foraker, Jim; Chambreau, Chris; Leininger, Matthew L. (November 2020). TOSS-2020: a commodity software stack for HPC. SC '20: Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis. Atlanta, Georgia. pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-1-7281-9998-6. OCLC 1223541587 – via IEEE.
- ↑ Morgan, Timothy Prickett (November 26, 2018). "One Linux stack to rule HPC and AI". NextPlatform.com. Retrieved August 28, 2022.
- ↑ Степин, Алексей (June 23, 2022). "2-Эфлопс cуперкомпьютер El Capitan получит новейшие APU AMD MI300" [2-Eflops El Capitan supercomputer will receive the latest AMD MI300 APUs]. ServerNews.ru (in Russian). Retrieved August 29, 2022.
В El Capitan лаборатория перейдет от использования проприетарного системного и управляющего ПО к собственному стеку NNSA Tri-Lab Operating System Stack (TOSS).
[At El Capitan, the laboratory will move from using proprietary system and management software to its own NNSA Tri-Lab Operating System Stack (TOSS).] - ↑ Feldman, Michael (June 18, 2018). "Sandia to Install First Petascale Supercomputer Powered by ARM Processors". Top500 . Retrieved August 29, 2022.
- ↑ "Migration to TOSS Operating System". NASA . July 20, 2022. Retrieved August 28, 2022.