
Anubis, also known as Inpu, Inpw, Jnpw, or Anpu in Ancient Egyptian, is the god of funerary rites, protector of graves, and guide to the underworld, in ancient Egyptian religion, usually depicted as a canine or a man with a canine head.

Nephthys or Nebet-Het in ancient Egyptian was a goddess in ancient Egyptian religion. A member of the Great Ennead of Heliopolis in Egyptian mythology, she was a daughter of Nut and Geb. Nephthys was typically paired with her sister Isis in funerary rites because of their role as protectors of the mummy and the god Osiris and as the sister-wife of Set.

QV66 is the tomb of Nefertari, the Great Wife of Pharaoh Ramesses II, in Egypt's Valley of the Queens. It was discovered by Ernesto Schiaparelli in 1904. Nefertari, which means "beautiful companion", was Ramesses II's favorite wife; he went out of his way to make this obvious, referring to her as "the one for whom the sun shines" in his writings, built the Temple of Hathor to idolize her as a deity, and commissioned portraiture wall paintings. In the Valley of the Queens, Nefertari's tomb once held the mummified body and representative symbolisms of her, consistent with most Egyptian tombs of the period. Now, everything had been looted except for two thirds of the 5,200 square feet of wall paintings. For what still remains, these wall paintings characterized Nefertari's character. Her face received particular attention to emphasize her beauty, especially the shape of her eyes, the blush of her cheeks, and her eyebrows. Some paintings were full of lines and color of red, blue, yellow, and green that portrayed exquisite directions to navigating through the afterlife to paradise.

Tomb KV9 in Egypt's Valley of the Kings was originally constructed by Pharaoh Ramesses V. He was interred here, but his uncle, Ramesses VI, later reused the tomb as his own. The architectural layout is typical of the 20th Dynasty – the Ramesside period – and is much simpler than that of Ramesses III's tomb (KV11). The workmen accidentally broke into KV12 as they dug one of the corridors. In 2020, the Egyptian Tourism Authority released a full 3D model of the tomb with detailed photography, available online.

Henutmehyt was the name of a Theban priestess of ancient Egypt, who lived during the 19th Dynasty, around 1250 BC. The excessive use of gold, and the high quality and detail of her coffins indicates that Henutmehyt was a wealthy woman.

TT1 is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Sennedjem and members of his family in Deir el-Medina, on the west bank of the Nile opposite Luxor. The funerary complex consists of three pyramid-shaped chapels dedicated to, from south to north, Sennedjem's father or brother, Sennedjem himself, and Sennedjem's son Khonsu. Of the three shafts associated with the chapels, only the shaft in front of Sennedjem's chapel was unrobbed. It leads to a series of underground rooms, including the extensively decorated burial chamber.
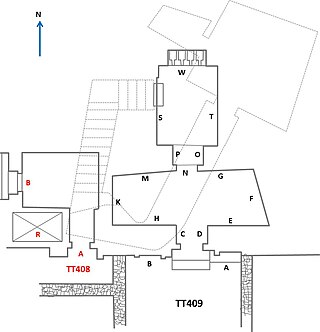
The Theban Tomb TT409 is located in El-Assasif, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian Samut called Kyky, who was Accountant of Cattle of the Amun domain, during the reign of Ramesses II during the Nineteenth Dynasty.
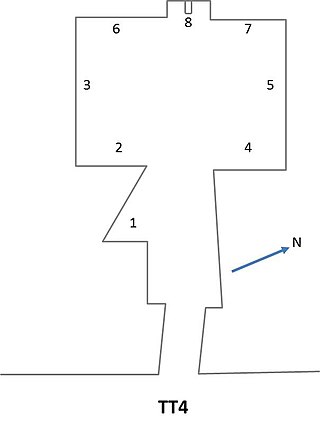
The Theban Tomb TT4 is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian artisan named Qen.

Theban Tomb TT2 is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Khabekhnet and his family in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor.

Theban Tomb TT51 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Userhat, who was First Prophet of Sethi I during the 19th Dynasty.
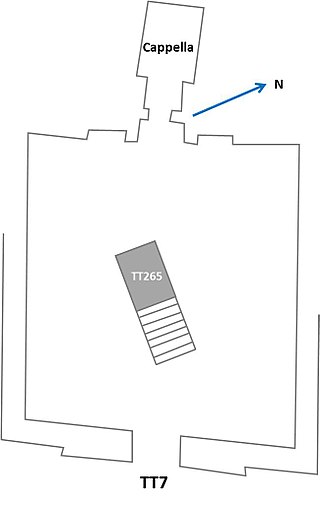
The Theban Tomb TT7 is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian artisan named Ramose, who lived during the 19th Dynasty, during the reign of Ramesses II.

Tyti was an ancient Egyptian queen of the 20th Dynasty. A wife and sister of Ramesses III and possibly the mother of Ramesses IV.

The Theban Tomb TT17 is located in Dra Abu el-Naga, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian noble named Nebamun, who lived during the 18th Dynasty, during the reign of Amenhotep II. Nebamun was a scribe and a physician to the King.
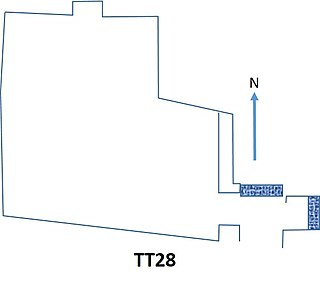
The Theban Tomb TT28 is located in El-Assasif. It forms part of the Theban Necropolis, situated on the west bank of the Nile opposite Luxor. The tomb is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official, Hori.
The Theban Tomb TT48 is located in El-Khokha, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. TT48 was the burial place of the ancient Egyptian named Amenemhat called Surer, who was a Chief Steward, At the head of the King, Overseer of the Cattle of Amun. Amenemhat called Surer dates to the time of Amenhotep III from the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. He was a son of Ith-taui, who was an overseer of the cattle of Amun and the lady Mut-tuy.

The Theban Tomb TT133 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna.

The Theban Tomb TT138 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor.

The Theban Tomb TT212 is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor.

The Theban Tomb TT214 is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor.

QV75 is the tomb of Henutmire, likely the daughter and Great Wife of Ramesses II, in Egypt's Valley of the Queens. It was mentioned by Champollion and Lepsius.























