
The Almoravid dynasty was a Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus, starting in the 1050s and lasting until its fall to the Almohads in 1147.

Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also called by their endonym Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arabs in the Arab migrations to the Maghreb. Their main connections are identified by their usage of Berber languages, most of them mutually unintelligible, which are part of the Afroasiatic language family. They are indigenous to the Maghreb region of North Africa, where they live in scattered communities across parts of Morocco, Algeria, Libya, and to a lesser extent Tunisia, Mauritania, northern Mali and northern Niger. Smaller Berber communities are also found in Burkina Faso and Egypt's Siwa Oasis.
The Abbadid dynasty or Abbadids was an Arab dynasty from the tribe of Banu Lakhm of al-Hirah, which ruled the Taifa of Seville in al-Andalus following the fall of the Caliphate of Cordoba in 1031. After the collapse, they were the most powerful Taifa and before long absorbed most of the others. Abbadid rule lasted from about 1023 until 1091, but during the short period of its existence it exhibited singular energy and typified its time.

The taifas were the independent Muslim principalities and kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula, referred to by Muslims as al-Andalus, that emerged from the decline and fall of the Umayyad Caliphate of Córdoba between 1009 and 1031. They were a recurring feature of al-Andalus history.

Abu ʿAmr ʿAbbad II al-Muʿtadid, a member of the Abbadid dynasty, was the second independent emir of Seville in Al-Andalus. His father, Abu al-Qasim Muhammad ibn Abbad, had established the Taifa of Seville, and Abbad became its emir when Abu al-Qasim died in 1042. He initially had amicable relations with his neighbour Ferdinand I, Count of Castile and King of León, and tolerated the Christian faith in his own lands. Among other acts of friendship, he authorized the transfer of Saint Isidore's relics from Seville to the Basilica of San Isidoro in León.

Al-Mu'tamid Muhammad ibn Abbad al-Lakhmi, also known as Abbad III, was the third and last ruler of the Taifa of Seville in Al-Andalus, as well as a renowned poet. He was the final ruler of the Arab Abbadid dynasty of Seville, before being deposed by the Almoravids in 1091.

The Sanhaja were once one of the largest Berber tribal confederations, along with the Zanata and Masmuda confederations. Many tribes in Algeria, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Senegal, Tunisia and Western Sahara bore and still carry this ethnonym, especially in its Berber form.
This is a timeline of notable events during the period of Muslim presence in Iberia, starting with the Umayyad conquest in the 8th century.
The Banu Ifran or Ifranids, were a Zenata Berber tribe prominent in the history of pre-Islamic and early Islamic North Africa. In the 8th century, they established a kingdom in the central Maghreb, with Tlemcen as its capital.

The Taifa of Seville was an Arab kingdom which was ruled by the Abbadid dynasty. It was established in 1023 and lasted until 1091, in what is today southern Spain and Portugal. It gained independence from the Caliphate of Cordoba and it expanded the territory it ruled in the mid-11th century. The emerging power of Castile led Seville to ask military assistance from the Almoravids, who then occupied Seville.

The Taifa of Granada or Zirid Kingdom of Granada was a Muslim kingdom that was formed in al-Andalus in 1013 following the deposition of Caliph Hisham II in 1009. The kingdom was centered on Granada, its capital, and it also extended its control to Málaga for a period. Four kings succeeded each other during its nearly 80 years of existence, all of them belonging to an offshoot of the Zirid dynasty of North Africa, a Sanhaja Berber clan. The Taifa of Granada was considered to be the wealthiest out of all of the taifa kingdoms. It was eventually conquered by the Almoravids in 1090, putting an end to Zirid rule in Granada.

The Taifa of Arcos was a Berber medieval taifa kingdom that existed in two periods; first from 1011 to 1068. Ruled by the Zanata Berber family of the Banū Jizrūn. From 1068 until 1091 it was under the forcible control of Seville, by Abbad II al-Mu'tadid. It regained its independence from 1143 to 1145 when it was finally conquered by the Almohad Caliphate.

The Taifa of Málaga was an Andalusī Islamic taifa kingdom located in what is now southern Spain. It existed during four distinct time periods: from 1026 to 1057, 1073 to 1090, 1145 to 1153, and 1229 to 1239, when the polity was finally conquered by the Emirate of Granada.

The Taifa of Morón was a medieval Berber taifa kingdom that existed from around 1010 to 1066. From 1066 until 1091 it was under the forcible control of Seville, by Abbad II al-Mu'tadid.

The Taifa of Silves was an Arab taifa kingdom that existed in what is now southern Portugal for two distinct periods: from 1027 to 1063, and again from 1145 to 1150, when it was finally conquered by the Almohad Caliphate.
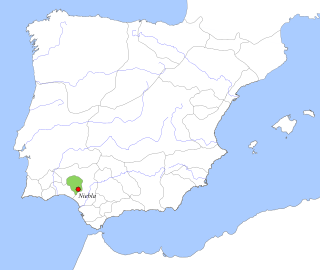
The Taifa of Niebla was an Arab taifa kingdom that existed during three distinct time periods: from 1023 to 1053, from 1145 to 1150 and from 1234 to 1262.
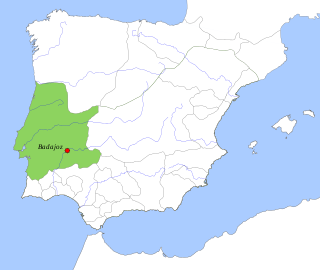
The Taifa of Badajoz was a medieval Islamic Moorish kingdom located in what is now parts of Portugal and Spain. It was centred on the city of Badajoz which exists today as the first city of Extremadura, in Spain.
Zawi ibn Ziri as-Sanhaji or Al-Mansur Zawi ibn Ziri ibn Manad as-Sanhaji, was a chief in the Berber Sanhaja tribe. He arrived in Spain in 1000 (391) during the reign of Almanzor. He took part in the rebellion against the Caliphate of Córdoba and settled in the Cora of Elvira with followers from his Sanhaja tribe. He founded the Taifa of Granada, and founded the Zirid dynasty of Granada as its first Emir, reigning from 1013 to 1019.














