Talmai, father of Maacah
King of Geshur. His daughter Maacah (מַעֲכָה) was a wife to the king David of Israel, mother of Tamar and Absalom (2 Samuel 3:3). After slaying Amnon (for the rape of Tamar), Absalom fled to Talmai in Geshur for three years.
Talmai ( /ˈtælmaɪ/ , TAL-my; Hebrew : תלמי 'my furrows') is a name in the Bible referring to a number of minor people. Its Aramaic version was associated with the Greek Ptolemy (see that article for the list of corresponding names and surnames), and is the origin of Bartholomew.
Talmai, Ahiman and Sheshai were Nephilim, three giant sons of Anak whom Caleb and the spies saw in Mount Hebron (Book of Numbers 13:22) when they went in to explore the land. They were afterwards driven out and slain (Joshua 15:14; Judges 1:10).
King of Geshur. His daughter Maacah (מַעֲכָה) was a wife to the king David of Israel, mother of Tamar and Absalom (2 Samuel 3:3). After slaying Amnon (for the rape of Tamar), Absalom fled to Talmai in Geshur for three years.

Absalom was an Israelite prince. Born to David and Maacah, who was from Geshur, he was the only full sibling of Tamar. He is described in the Hebrew Bible as being exceptionally beautiful, as is his sister. In the narrative of 2 Samuel 13, his sister Tamar takes refuge at his house after she is raped by their paternal half-brother Amnon ; David is angered by the incident, but does nothing, as Amnon is his heir apparent. Infuriated by the rape and David's inaction, Absalom assassinates Amnon and subsequently flees to Geshur, which is ruled by his and Tamar's maternal grandfather Talmai.

Amnon was, in the Hebrew Bible, the oldest son of King David and his second wife, Ahinoam of Jezreel. He was born in Hebron during his father's reign in Judah. He was the heir apparent to the throne of Israel until he was assassinated by his half-brother Absalom to avenge the rape of Absalom's sister Tamar.

The Book of Samuel is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books in the Old Testament. The book is part of the Deuteronomistic history, a series of books that constitute a theological history of the Israelites and that aim to explain God's law for Israel under the guidance of the prophets.

David was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament.
Ammihud is the name of several Hebrew Bible figures:
Narratives featuring incest can be found in the Hebrew Bible, which contains mentions of various types of sexual relationships. It also lays out rules and regulations with regard to prohibited degree of kinship. These prohibitions are found predominantly in Leviticus 18:7–18 and 20:11–21, but also in Deuteronomy.
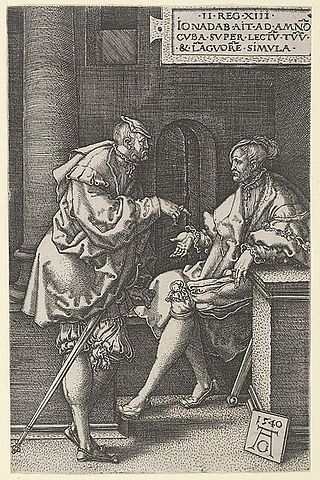
Jonadab is a figure in the Hebrew Bible, appearing in 2 Samuel 13. He is described in verse 3 as the son of Shimeah, who was the brother of David, making Jonadab a cousin to Amnon as well as his friend. He is called "very wise", usually translated as "very shrewd" (NIV) or "very crafty" (ESV).

King David is a 1985 American Biblical epic film about the life of David, the second King of the Kingdom of Israel, as recounted in the Hebrew Bible. The film is directed by Bruce Beresford, written by Andrew Birkin and James Costigan, and stars Richard Gere in the title role. The ensemble cast includes Edward Woodward, Alice Krige, Denis Quilley, Cherie Lunghi, Hurd Hatfield, John Castle, Jean-Marc Barr, Christopher Malcolm, and Gina Bellman.

Nathan was the youngest son among four or five children born to King David and Bathsheba in Jerusalem if names were written in order in the Bible. He was a younger brother of Shammuah and Shobab, and Solomon who was the second oldest child of Bathsheba. The first son died before he could be named.
Maacah is a non-gender-specific personal name used in the Bible to refer to a number of people.

Geshur was a territory in the ancient Levant mentioned in the early books of the Hebrew Bible and possibly in several other ancient sources, located in the region of the modern-day Golan Heights. Some scholars suggest it was established as an independent city-state from the middle of the tenth century BCE, maintaining its autonomy for about a century until it was annexed in the third quarter of the ninth century by Hazael, the king of Aram-Damascus.
Tamar is a female name of Hebrew origin, meaning "date", "date palm" or just "palm tree". There are three characters in the Bible with this name. The pronunciation of Tamar depends on each so-named person's language, culture, and idiolectic preference; typical pronunciation in the original Hebrew is ; typical pronunciations in English are and. Variants include Tamary and "Tamara".

Geshur is an Israeli settlement organized as a kibbutz on the ridge of the southern Golan Heights. The international community considers Israeli settlements in the Golan Heights illegal under international law, but the Israeli government disputes this. In 2022 it had a population of 321.

Tamar was an Israelite princess. Born to David and Maacah, who was from Geshur, she was the only full sibling of Absalom. She is described in the Hebrew Bible as being exceptionally beautiful, as is her brother. In the narrative of 2 Samuel 13, she is raped by her paternal half-brother Amnon before fleeing with torn robes to Absalom's house; David is angered by the incident, but does nothing, as Amnon is his heir apparent. Absalom, infuriated by the rape and David's inaction, keeps Tamar in his care and later assassinates Amnon to avenge her, subsequently fleeing to Geshur, which is ruled by his and Tamar's maternal grandfather Talmai. Three years later, he returns to Israel and leads an armed revolt against the House of David, but is killed by David's nephew and army commander Joab during the Battle of the Wood of Ephraim. Tamar is described as being left "a desolate women in her brother's house" and the sole guardian of her orphaned niece, who is also named Tamar.

The sons of King David are mentioned both as a group and individually several times in the biblical accounts of the reigns both of David and his successor Solomon.

According to 2 Samuel, the Battle of the Wood of Ephraim was a military conflict between the rebel forces of the formerly exiled Israelite prince Absalom against the royal forces of his father King David during a short-lived revolt.

2 Samuel 13 is the thirteenth chapter of the Second Book of Samuel in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible or the second part of Books of Samuel in the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish tradition the book was attributed to the prophet Samuel, with additions by the prophets Gad and Nathan, but modern scholars view it as a composition of a number of independent texts of various ages from c. 630–540 BCE. This chapter contains the account of David's reign in Jerusalem. This is within a section comprising 2 Samuel 9–20 and continued to 1 Kings 1–2 which deal with the power struggles among David's sons to succeed David's throne until 'the kingdom was established in the hand of Solomon'.

2 Samuel 3 is the third chapter of the Second Book of Samuel in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible or the second part of Books of Samuel in the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish tradition the book was attributed to the prophet Samuel, with additions by the prophets Gad and Nathan, but modern scholars view it as a composition of a number of independent texts of various ages from c. 630–540 BCE. This chapter contains the account of David's reign in Hebron. This is within a section comprising 1 Samuel 16 to 2 Samuel 5 which records the rise of David as the king of Israel, and a section comprising 2 Samuel 2–8 which deals with the period when David set up his kingdom.

2 Samuel 14 is the fourteenth chapter of the Second Book of Samuel in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible or the second part of Books of Samuel in the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish tradition the book was attributed to the prophet Samuel, with additions by the prophets Gad and Nathan, but modern scholars view it as a composition of a number of independent texts of various ages from c. 630–540 BCE. This chapter contains the account of David's reign in Jerusalem. This is within a section comprising 2 Samuel 9–20 and continued to 1 Kings 1–2 which deal with the power struggles among David's sons to succeed David's throne until 'the kingdom was established in the hand of Solomon'.