
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from Latin: sedere, lit. 'to sit'. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. The art of conducting and resisting sieges is called siege warfare, siegecraft, or poliorcetics.

A Roman siege tower or breaching tower is a specialized siege engine, constructed to protect assailants and ladders while approaching the defensive walls of a fortification. The tower was often rectangular with four wheels with its height roughly equal to that of the wall or sometimes higher to allow archers to stand on top of the tower and shoot arrows into the fortification. Because the towers were wooden and thus flammable, they had to have some non-flammable covering of iron or fresh animal skins.

A glacis in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More generally, a glacis is any slope, natural or artificial, which fulfils the above requirements. The etymology of this French word suggests a slope made dangerous with ice, hence the relationship with glacier.

A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates for access to the city. From ancient to modern times, they were used to enclose settlements. Generally, these are referred to as city walls or town walls, although there were also walls, such as the Great Wall of China, Walls of Benin, Hadrian's Wall, Anastasian Wall, and the Atlantic Wall, which extended far beyond the borders of a city and were used to enclose regions or mark territorial boundaries. In mountainous terrain, defensive walls such as letzis were used in combination with castles to seal valleys from potential attack. Beyond their defensive utility, many walls also had important symbolic functions – representing the status and independence of the communities they embraced.

A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin fortis ("strong") and facere.

A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while others have wheels to enable advancing up to the enemy fortification. There are many distinct types, such as siege towers that allow foot soldiers to scale walls and attack the defenders, battering rams that damage walls or gates, and large ranged weapons that attack from a distance by launching projectiles. Some complex siege engines were combinations of these types.

A parapet is a barrier that is an upward extension of a wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian parapetto. Where extending above a roof, a parapet may simply be the portion of an exterior wall that continues above the edge line of the roof surface, or may be a continuation of a vertical feature beneath the roof such as a fire wall or party wall. Parapets were originally used to defend buildings from military attack, but today they are primarily used as guard rails, to conceal rooftop equipment, reduce wind loads on the roof, and to prevent the spread of fires. In the Bible the Hebrews are obligated to build a parapet on the roof of their houses to prevent people falling.

A machicolation is a floor opening between the supporting corbels of a battlement, through which stones or other material, such as boiling water, hot sand, quicklime or boiling cooking oil, could be dropped on attackers at the base of a defensive wall. A smaller version found on smaller structures is called a box-machicolation.

Scree is a collection of broken rock fragments at the base of a cliff or other steep rocky mass that has accumulated through periodic rockfall. Landforms associated with these materials are often called talus deposits. Talus deposits typically have a concave upwards form, where the maximum inclination corresponds to the angle of repose of the mean debris particle size. The exact definition of scree in the primary literature is somewhat relaxed, and it often overlaps with both talus and colluvium.

Escalade is the act of scaling defensive walls or ramparts with the aid of ladders. Escalade was a prominent feature of sieges in ancient and medieval warfare, and though it is no longer common in modern warfare, escalade technologies are still developed and used in certain tactical applications.

Coping is the capping or covering of a wall. A splayed or wedge coping is one that slopes in a single direction; a saddle coping slopes to either side of a central high point.

Ellerman is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It lies within the outer blanket of ejecta that surrounds the Mare Orientale impact basin, and is located to the west of the Montes Cordillera mountain range. To the northwest of Ellerman is the larger crater Gerasimovich.
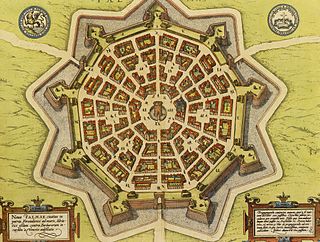
A bastion fort or trace italienne is a fortification in a style that evolved during the early modern period of gunpowder when the cannon came to dominate the battlefield. It was first seen in the mid-fifteenth century in Italy. Some types, especially when combined with ravelins and other outworks, resembled the related star fort of the same era.
This page is a glossary of architecture.

A scarp and a counterscarp are the inner and outer sides, respectively, of a ditch or moat used in fortifications. Attackers must descend the counterscarp and ascend the scarp. In permanent fortifications the scarp and counterscarp may be encased in stone. In less permanent fortifications, the counterscarp may be lined with paling fence set at an angle so as to give no cover to the attackers but to make advancing and retreating more difficult.

Investment is the military process of surrounding an enemy fort with armed forces to prevent entry or escape. It serves both to cut communications with the outside world and to prevent supplies and reinforcements from being introduced.

Sapping is a term used in siege operations to describe the digging of a covered trench to approach a besieged place without danger from the enemy's fire. The purpose of the sap is usually to advance a besieging army's position towards an attacked fortification. It is excavated by specialised military units, whose members are often called sappers.

In architecture, batter is a receding slope of a wall, structure, or earthwork. A wall sloping in the opposite direction is said to overhang. When used in fortifications it may be called a talus.


















