
Bagpipes are a woodwind instrument using enclosed reeds fed from a constant reservoir of air in the form of a bag. The Great Highland bagpipes are well known, but people have played bagpipes for centuries throughout large parts of Europe, Northern Africa, Western Asia, around the Persian Gulf and northern parts of South Asia.

The uilleann pipes are the characteristic national bagpipe of Ireland. Earlier known in English as "union pipes", their current name is a partial translation of the Irish language terms píobaí uilleann, from their method of inflation. There is no historical record of the name or use of the term uilleann pipes before the 20th century. It was an invention of Grattan Flood and the name stuck. People mistook the term 'union' to refer to the 1800 Act of Union; this is incorrect as Breandán Breathnach points out that a poem published in 1796 uses the term 'union'.

The chanter is the part of the bagpipe upon which the player creates the melody. It consists of a number of finger-holes, and in its simpler forms looks similar to a recorder. On more elaborate bagpipes, such as the Northumbrian bagpipes or the Uilleann pipes, it also may have a number of keys, to increase the instrument's range and/or the number of keys it can play in. Like the rest of the bagpipe, they are often decorated with a variety of substances, including metal (silver/nickel/gold/brass), bone, ivory, or plastic mountings.

The Galician gaita is the traditional instrument of Galicia and northern Portugal.

The shawm is a conical bore, double-reed woodwind instrument made in Europe from the 12th century to the present day. It achieved its peak of popularity during the medieval and Renaissance periods, after which it was gradually eclipsed by the oboe family of descendant instruments in classical music. It is likely to have come to Western Europe from the Eastern Mediterranean around the time of the Crusades. Double-reed instruments similar to the shawm were long present in Southern Europe and the East, for instance the ancient Greek, and later Byzantine, aulos, the Persian sorna, and the Armenian duduk.
Northwest Iberian folk music is a traditional highly distinctive folk style, located along Spain's north-west Atlantic coast, mostly Galicia and Asturias, that has some similarities with the neighbouring area of Cantabria. The music is characterized by the use of bagpipes.
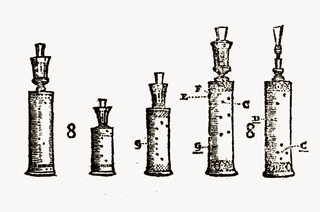
The rackett, raggett, cervelas, or sausage bassoon is a Renaissance-era double reed wind instrument, introduced late in the sixteenth century and already superseded by bassoons at the end of the seventeenth century.

A bagpipe practice chanter is a double-reed woodwind instrument, principally used as an adjunct to the Great Highland bagpipe. As its name implies, the practice chanter serves as a practice instrument: firstly for learning to finger the different melody notes of bagpipe music, and to practice new music.

A rauschpfeife is a capped conical reed musical instrument of the woodwind family, used in Europe in the 16th and 17th centuries. In common with the crumhorn and cornamuse, it is a wooden double-reed instrument with the reed enclosed in a windcap. The player blows into a slot in the top of the windcap to produce the sound.

The kortholt is a musical instrument of the woodwind family, used in the Renaissance period.

The bassanello was a Renaissance double reed woodwind instrument which was described in 1619 by Michael Praetorius in his Syntagma Musicum II:
The guan is a Chinese double reed wind instrument. The northern Chinese version is called guanzi or bili and the Cantonese version is called houguan. It is classified as a bamboo instrument in the Ba Yin system. Unlike other instruments in the double-reed family of woodwinds which mostly have conical bores, such as the Chinese suona or the Western oboe, the guan has a cylindrical bore, giving its distinctive mellow, yet piercing buzz-like timbre.

The kuzhal is a traditional double reed wind instrument used in the south Indian state of Kerala. It is similar in construction to a nagaswaram or a large shehnai, and has a very shrill and penetrating tone.

The piffero or piffaro is a double-reed musical instrument of the oboe family with a conical bore . It is used to play music in the tradition of the Quattro Province, an area of mountains and valleys in the north-west Italian Apennines which includes parts of the four provinces of Alessandria, Genoa, Piacenza and Pavia. It is also played throughout Southern Italy with different fingering styles dictated by local tradition.

The bombard is a contemporary conical-bore double-reed instrument widely used to play traditional Breton music. The bombard is a woodwind instrument, and a member of the shawm family. Like most shawms, it has a broad and very powerful sound, vaguely resembling a trumpet. It is played as other shawms are played, with the double reed placed between the lips. The second octave is 'over-blown'; achieved via increased lip and air pressure or through the use of an octave key. It plays a diatonic scale of up to two octaves, although contemporary instruments frequently have added keywork permitting some degree of chromaticism. A bombard player is known as a talabarder after 'talabard', the older Breton name for the bombard.

The torupill is a traditional bagpipe from Estonia.
This article defines a number of terms that are exclusive, or whose meaning is exclusive, to piping and pipers.

Chirimía is a Spanish term for a type of woodwind instrument similar to an oboe. The chirimía is a member of the shawm family of double-reed instruments, introduced to North, Central and South America in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries by the Spanish clergy.
Traditional French musical instruments, known as instruments traditionnels in French, are musical instruments used in the traditional folk music of France. They comprise a range of string, wind, and percussion instruments.

















