Related Research Articles

Taumarunui is a small town in the King Country of the central North Island of New Zealand. It is on an alluvial plain set within rugged terrain on the upper reaches of the Whanganui River, 65 km south of Te Kuiti and 55 km west of Turangi. It is under the jurisdiction of Ruapehu District and Manawatū-Whanganui region.

The Raurimu Spiral is a single-track railway spiral, starting with a horseshoe curve, overcoming a 139-metre (456 ft) height difference, in the central North Island of New Zealand, on the North Island Main Trunk railway (NIMT) between Wellington and Auckland. It is a notable feat of civil engineering, having been called an "engineering masterpiece." The Institute of Professional Engineers of New Zealand has designated the spiral as a significant engineering heritage site.

The North Island Main Trunk (NIMT) is the main railway line in the North Island of New Zealand, connecting the capital city Wellington with the country's largest city, Auckland. The line is 682 kilometres (424 mi) long, built to the New Zealand rail gauge of 1,067 mm and serves the large cities of Palmerston North and Hamilton.

The New Zealand EF class locomotive is a class of 25 kV 50 Hz AC electric locomotives that operate on the North Island Main Trunk (NIMT) between Palmerston North and Te Rapa in New Zealand. Built by Brush Traction in Loughborough, England between 1986 and 1988 to run on the new electrified central section of the NIMT, at 3,000 kilowatts (4,000 hp), they are the most powerful locomotives to operate in New Zealand.

The Okaihau Branch, sometimes known as the Kaikohe Branch and rarely the Rangiahua Branch, was a branch line railway that joined the North Auckland Line of the national rail network of New Zealand at Otiria. It was the most northerly line in New Zealand and was intended to run all the way to Kaitaia. It opened to Ōkaihau in 1923 and closed in 1987.

The New Zealand X class was a pioneering class of eighteen 4-8-2 steam locomotives built for New Zealand Railways Department (NZR) and designed by A. L. Beattie that operated on the national rail network of New Zealand. In 1908, a heavy and powerful locomotive was required to haul traffic on the newly completed mountainous central section of the North Island Main Trunk Railway, and as a logical progression of the 4-6-2 Q class design, the 4-8-2 wheel arrangement was created for the X class.
The New Zealand Railways Department, NZR or NZGR and often known as the "Railways", was a government department charged with owning and maintaining New Zealand's railway infrastructure and operating the railway system. The Department was created in 1880 and was corporatised on 1 April 1982 into the New Zealand Railways Corporation. Originally, railway construction and operation took place under the auspices of the former provincial governments and some private railways, before all of the provincial operations came under the central Public Works Department. The role of operating the rail network was subsequently separated from that of the network's construction. From 1895 to 1993 there was a responsible Minister, the Minister of Railways. He was often also the Minister of Public Works.
The New Plymouth Night Express was a passenger express train operated by the New Zealand Railways Department (NZR) that ran between Auckland and New Plymouth. It ran in various forms from 1933 until 1983, though the Express designation was lost in 1956 and later incarnations did not operate at night and terminated in Taumarunui rather than Auckland. The New Plymouth Night Express should not be confused with the New Plymouth Express that operated between New Plymouth and Wellington.

The Stratford–Okahukura Line (SOL) is a secondary railway line in the North Island of New Zealand, between the Marton - New Plymouth Line (MNPL) and the North Island Main Trunk (NIMT) Railway, with 15 intermediate stations. It is 144 km (89 mi) long through difficult country, with 24 tunnels, 91 bridges and a number of sections of 1 in 50 grade. Near Okahukura there is an unusual combined road-rail bridge over the Ongarue River, with the one-lane road carriageway below the single rail track. The line is not currently in service for rail traffic and is under a 30-year lease for a tourist venture. In July 2019 KiwiRail's CEO stated that reopening the line was a priority. Minister of Transport Michael Wood announced the government's 10-year plan for rail investment on 6 May 2021, which specifically stated that plans could include re-opening the Stratford to Okahukura line.

Manunui is a small Whanganui River settlement, about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) east of Taumarunui on State Highway 4, in New Zealand's King Country. It was once known as Waimarino, but John Burnand of the Ellis and Burnand sawmilling firm renamed it Manunui around 1905.
Tyer's Electric Train Tablet system is a form of railway signalling for single line railways used in several countries; it was first devised in Great Britain by engineer Edward Tyer after the Thorpe rail accident of 1874, which left 21 people dead. It was used in New Zealand for close to 100 years until June 1994. The system used a hard disk called a tablet, a form of token.
Peter Irwin Cape was a New Zealand singer, songwriter, writer and radio producer. He is best remembered for his simple folk songs, including "Taumarunui On The Main Trunk Line", "She'll Be Right" and "Coffee Bar Blues".
The Waitara Branch is a 7.245 km long branch line railway in the Taranaki region of New Zealand's North Island. It was built as part of the region's first railway, linking New Plymouth with the closest suitable port, then the river port of Waitara. In 1884 the Breakwater port was opened in New Plymouth, but the line was saved when a (meat) freezing works was opened at Waitara in 1885.

Taumarunui railway station is the main railway station in Taumarunui, New Zealand. It was an important intermediate stop with a refreshment room on the North Island Main Trunk line; the subject of the ballad "Taumarunui on the Main Trunk Line" by Peter Cape.

A railway refreshment room is a catering facility attached to a railway station that was formerly common in Britain, Australia, New Zealand, and other countries that were formerly part of the British Empire. They were opened in the 19th century to serve passengers when trains did not convey catering facilities, and thus served passengers en route. Refreshment rooms were similar to tearooms, and generally served a variety of hot drinks, pastries, cakes, and light meals. With the introduction of buffet and restaurant cars, their importance began to decline.

The Ongarue railway disaster occurred on 6 July 1923 near the small settlement of Ongarue, near Taumarunui, North Island, New Zealand, when an overnight express ran into a landslip. Of the 200 passengers on board, 17 died and 28 were injured. The disaster marked the first major loss of life in New Zealand railway history; the Christchurch Press noted that each of the previous fatal railway accidents had resulted in no greater loss of life than that resulting from an overturned motor car.
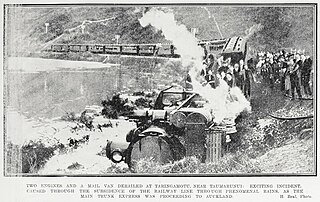
Taringamotu railway station was a station at Taringamotu on the North Island Main Trunk, in the Ruapehu District and Manawatū-Whanganui region.

Okahukura railway station was a station on the North Island Main Trunk in New Zealand.

Matapuna had several sidings on the North Island Main Trunk line, in the Ruapehu District of New Zealand, serving the east Taumarunui suburb on the north bank of the Whanganui River. It was 2.9 km (1.8 mi) north west of Manunui and 2.95 km (1.83 mi) east of Taumarunui. Work was largely complete by May 1903, and freight was handled from 22 June 1903. A fixed signal was placed at the station and a distant at the bridge in 1917 and the ballast pit siding was interlocked by tablet in 1918. A racecourse opened to the south of the bridge in 1916 and some trains served the course on race days, though no platform appears on aerial photos and only the ballast pit was mapped.

The first railway line in New Zealand was the line from Christchurch to Ferrymead opened in 1863. Under the “Grand Go-ahead Policy” of public works instituted by Sir Julius Vogel in 1870 the network was rapidly expanded. Initially lines went from the main town and port to the rural hinterland, but the line between the cities of Christchurch and Dunedin section of the South Island Main Trunk Railway opened in 1878. The New Zealand Railways Department was established in 1876, and the rail network was then run by the central government rather than by provincial governments. Signalling installation was handled by district engineers in the maintenance branch. The Rakaia rail accident in 1899 when four passengers were killed showed the deficiencies in railway signalling and braking; Rakaia did not have fixed signals, and rolling stock apart from locomotives did not have air brakes. But those lines with heavier traffic already had block working installed. The first signalling and interlocking engineer had already been appointed in 1899 at a salary of £400; Arthur H. Johnson, who had “considerable experience in England and America” and who was to design and develop a uniform system of interlocking points and signals. <!—NZ Herald 23 May 1898 --> But he resigned in 1899, and returned to England c1901. He was replaced by Henry John Wynne from 1900; with staff of a chief signal inspector in Wellington and several regional signal inspectors. Wynne retired in 1929. Wynne was replaced by Guy Wilfred Wyles (1887-1947) as Signalling and electrical engineer. Wyles had started with Sykes Interlocking Co in London. He married into Wynn’s family, and died of peritonitis three months before his retirement. The first three engineers all trained in England. Signalling in New Zealand was based on British practice for 60 years until about 1922, when it became “essentially indigenous” – partly British with two-aspect mechanical signalling and partly American with automatic three-aspect signalling using so-called ‘”speed’ indicators.
References
- 1 2 "Taumarunui on the Main Trunk Line," New Zealand Folk Song, 27 May 2005. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ↑ "New Zealand Ballads". Press. 17 November 1959. Retrieved 2 February 2022– via Paperspast.
- ↑ "Ceolskog - Taumarunui on the Main Trunk Line (New Zealand Folk Metal)". YouTube .