Tav or TAV may refer to:
Tav or TAV may refer to:
Alta or ALTA may refer to:

Susa is a town and comune in the Metropolitan City of Turin, Piedmont, Italy. In the middle of Susa Valley, it is situated on at the confluence of the Cenischia with the Dora Riparia, a tributary of the Po River, at the foot of the Cottian Alps, 51 km (32 mi) west of Turin.

The Italian railway system is one of the most important parts of the infrastructure of Italy, with a total length of 24,227 km (15,054 mi) of which active lines are 16,723 km. The network has recently grown with the construction of the new high-speed rail network. Italy is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC Country Code for Italy is 83.
Hitachi Rail Italy S.p.A. is a multinational rolling stock manufacturer company based in Pistoia, Italy. Formerly AnsaldoBreda S.p.A., a subsidiary of state-owned Finmeccanica, the company was sold in 2015 to Hitachi Rail of Japan. After the deal was finalized, the current name was adapted in November 2015 to reflect the new ownership.

Eurostar Italia was the name given to high-speed trains operated by Trenitalia in Italy. The brand was discontinued and replaced with Le Frecce in December 2012.
Treno Alta Velocità SpA (TAV) is special-purpose entity owned by Rete Ferroviaria Italiana for the planning and construction of a high-speed rail network in Italy.

ETR 450 was the first series Italian tilting train.

Roma Tiburtina is the second largest railway station in Rome, after Roma Termini. Located in the north-eastern part of the city, it was originally constructed during the 1860s as a terminal station. In recent years, the station has been redeveloped to better serve as a hub for the Italian high-speed rail services. The station is connected to Rome's Metro line B at Tiburtina metro station, as well as to local bus services via an adjacent bus depot while private vehicle users are provided with more than 100,000 spaces across multiple on-site car parks.

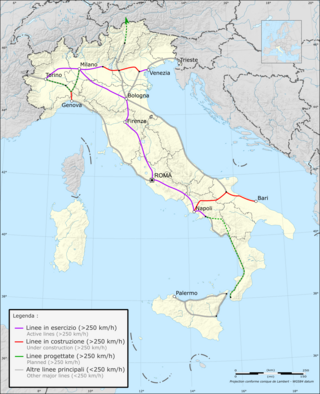
High-speed rail in Italy consists of two lines connecting most of the country's major cities. The first line connects Turin to Salerno via Milan, Bologna, Florence, Rome and Naples, the second runs from Turin to Venice via Milan and Verona, and is under construction in parts. Trains are operated with a top speed of 300 km/h (190 mph).

The ETR 200 is an Italian electric multiple unit (EMU) introduced in 1936.

The Bologna–Florence high-speed railway is a link in the Italian high-speed rail network. It is part of Corridor 1 of the European Union's Trans-European high-speed rail network, which connects Berlin and Palermo. Full commercial operations commenced on 5 December 2009. High-speed passenger trains take 37 minutes over the route compared to about 59 minutes previously.

Rome has an extensive internal transport system and is one of the most important road, rail and air hubs in Italy.
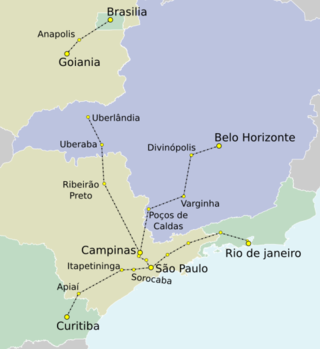
The TAV is Brazil's first planned high-speed rail service. The first line is proposed to run between Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. It will travel 403 kilometres (250 mi) between Barão de Mauá station and Campo de Marte Airport. The journey will take 85 minutes, reaching a maximum speed of 350 kilometres per hour (220 mph).

Novara railway station is the main station serving the city and comune of Novara, in the Piedmont region, northwestern Italy. Opened in 1854, it forms part of the Turin–Milan and is origin of the lines to Arona, to Alessandria, to Biella, Varallo, Domodossola and Luino, respectively.

ETR 500 is a family of Italian high-speed trains built by AnsaldoBreda and introduced in 1993.
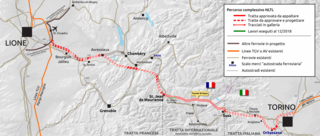
The Turin–Lyon high-speed railway is an international rail line under construction between the cities of Turin and Lyon. It is intended to link the Italian and French high-speed rail networks and will be 270 km (170 mi) long. The core of the project is its international section, which will cross the Alps through the Mont d'Ambin Base Tunnel between the Susa Valley in Piedmont and Maurienne in Savoie. At 57.5 kilometres (35.7 mi), that tunnel will be the longest rail tunnel in the world, ahead of the 57.1 km (35.5 mi) Gotthard Base Tunnel. The estimated total cost of the line is €25 billion, of which €8 billion is for the international section. The latter is the only part of the line where work has started.

The Frecciarossa 1000, is a high-speed train operated by Italian state railway operator Trenitalia and the private Spanish high-speed rail operator Iryo. It was co-developed as a joint venture between Italian rail manufacturer Hitachi Rail Italy and multinational conglomerate Alstom. Both design and production work were divided between the two partner companies.
Velocita may refer to:

The Livraga derailment is the only railway accident to date on the Italian high speed rail network. It took place on 6 February 2020 when a high-speed train derailed at Livraga, Lombardy, Italy. Two people died and 31 were injured.

María Soledad Rosas was an Argentine activist who was falsely charged with eco-terrorism in Italy. Soon after arriving in Turin in 1997, she became involved in the squatting movement, staying at a self-managed social centre named Asilo. She attended protests and lived as a squatter. In March 1998, she was arrested by Italian law enforcement, along with her boyfriend, Edoardo Massari, and Silvano Pelissero. They were accused of being affiliated with an organisation called Lupi Grigi that authorities said had been sabotaging construction sites for the Treno Alta Velocità. The activists maintained their innocence but were branded eco-terrorists in the media. Massari hanged himself in his cell later that month. Rosas was released to house arrest and hanged herself on 11 July.