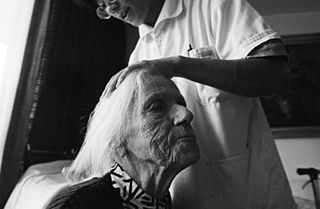
Home care is supportive care provided in the home. Care may be provided by licensed healthcare professionals who provide medical treatment needs or by professional caregivers who provide daily assistance to ensure the activities of daily living (ADLs) are met. In-home medical care is often and more accurately referred to as home health care or formal care. Often, the term home health care is used to distinguish it from non-medical care, custodial care, or private-duty care which refers to assistance and services provided by persons who are not nurses, doctors, or other licensed medical personnel. For terminally ill patients, home care may include hospice care. For patients recovering from surgery or illness, home care may include rehabilitative therapies.
Nursing assessment is the gathering of information about a patient's physiological, psychological, sociological, and spiritual status by a licensed Registered Nurse. Nursing assessment is the first step in the nursing process. A section of the nursing assessment may be delegated to certified nurses aides. Vitals and EKG's may be delegated to certified nurses aides or nursing techs. It differs from a medical diagnosis. In some instances, the nursing assessment is very broad in scope and in other cases it may focus on one body system or mental health. Nursing assessment is used to identify current and future patient care needs. It incorporates the recognition of normal versus abnormal body physiology. Prompt recognition of pertinent changes along with the skill of critical thinking allows the nurse to identify and prioritize appropriate interventions. An assessment format may already be in place to be used at specific facilities and in specific circumstances.
Home health nursing is a nursing specialty in which nurses provide multidimensional home care to patients of all ages. Home health care is a cost efficient way to deliver quality care in the convenience of the client's home. Home health nurses create care plans to achieve goals based on the client's diagnosis. These plans can include preventive, therapeutic, and rehabilitative actions. Home health nurses also supervise certified nursing assistants. The professional nursing organization for home health nurses is the Home Healthcare Nurses Association (HHNA). Home health care is intended for clients that are well enough to be discharged home, but still require skilled nursing personnel to assess, initiate and oversee nursing interventions.
Case management is a managed care technique within the health care coverage system of the United States. It involves an integrated system that manages the delivery of comprehensive healthcare services for enrolled patients. Case managers are employed in almost every aspect of health care and these employ different approaches in the control of clinical actions.
Originated in 1969 by staff nurses at the University of Minnesota, Primary Nursing is a system of nursing care delivery which emphasizes continuity of care and responsibility acceptance by having one registered nurse (RN), often teamed with a licensed practical nurse (LPN) and/or nursing assistant (NA), who together provide complete care for a group of patients throughout their stay in a hospital unit or department. While the patient is on the nurses' unit, the primary nurse accepts responsibility for administering some and coordinating all aspects of the patient's nursing care, with the support of other members of the nursing staff. This results in the nurse having greater insight into the patient's condition, both medical and emotional.
The University of Virginia School of Nursing, established in 1901, is a school of nursing education. For nearly 120 years, it has been at the forefront of nursing education, service, and research. It has an enrollment of approximately 800 students, and is consistently rated in the top 4% of U.S. nursing schools. After the retirement of Dorrie K. Fontaine as the fifth dean of the School, two-term American Nurses Association President Pam Cipriano, a research faculty member at UVA for years, stepped in as interim dean in August 2019.

Emergency nursing is a specialty within the field of professional nursing focusing on the care of patients who require prompt medical attention to avoid long-term disability or death. In addition to addressing "true emergencies," emergency nurses increasingly care for people who are unwilling or unable to get primary medical care elsewhere and come to emergency departments for help. In fact, only a small percentage of emergency department (ED) patients have emergency conditions such as a stroke, heart attack or major trauma. Emergency nurses also tend to patients with acute alcohol and/or drug intoxication, psychiatric and behavioral problems and those who have been raped.
A surgical nurse, also referred to as a theatre nurse or scrub nurse, specializes in perioperative care, providing care to patients before, during and after surgery. To become a theatre nurse, Registered Nurses or Enrolled Nurses must complete extra training. There are different speciality areas that theatre nurses can focus in depending on which areas they are interested in.

Neonatal nursing is a sub-specialty of nursing care for newborn infants up to 28 days after birth. The term neonatal comes from neo, "new", and natal, "pertaining to birth or origin". Neonatal nursing requires a high degree of skill, dedication and emotional strength as the nurses care for newborn infants with a range of problems, varying between prematurity, birth defects, infection, cardiac malformations and surgical problems. Neonatal nurses are a vital part of the neonatal care team and are required to know basic newborn resuscitation, be able to control the newborn's temperature and know how to initiate cardiopulmonary and pulse oximetry monitoring. Most neonatal nurses care for infants from the time of birth until they are discharged from the hospital.

A flight nurse is a registered nurse who specialises in the field of providing comprehensive pre-hospital, emergency critical care, and hospital care to a vast scope of patients. The care of these patients is generally during aeromedical evacuation or rescue operations aboard helicopters, propeller aircraft or jet aircraft. On board a rescue aircraft you would find a flight nurse accompanied by flight medics and respiratory practitioners, as well as the option of a flight physician for comprehensive emergency and critical transport teams. The inclusion of a flight physician is more commonly seen in pediatric and neonatal transport teams. A critical care flight nurse must be able to deal with all age groups with broad critical emergencies. With no physicians on site the nurses scope of practice is expanded. The critical care experience is transferred over to a flight nurse with impacting factors such as altitude and changes in pressure, gravitational forces, and weather. Some patients may experience exacerbation's because of factors related to the cabin environment including hypoxia, limited mobility, gas expansion, and risk of injury related to turbulence and resources with definitive care are limited. Aeromedical evacuation crews coordinate coordinate with other organizations to plan for the safe and timely care and evacuation of patients. Crews must be prepared for patients suffering from trauma and mental health illnesses.
The California Nurses Association/National Nurses Organizing Committee (CNA/NNOC), is a labor union and professional association of registered nurses in the United States. CNA/NNOC has a four-member Council of Presidents, currently including Deborah Burger, RN; Zenei Cortez, RN; Cokie Giles, RN; and Malinda Markowitz, RN. The executive director of the CNA/NNOC is Bonnie Castillo, RN.

Nursing is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other health care providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialties with differing levels of prescription authority. Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurse practitioners are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings. Since the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Ambulatory care nursing is the nursing care of patients who receive treatment on an outpatient basis, ie they do not require admission to a hospital for an overnight stay. Ambulatory care includes those clinical, organizational and professional activities engaged in by registered nurses with and for individuals, groups, and populations who seek assistance with improving health and/or seek care for health-related problems. The American Academy of Ambulatory Care Nursing (AAACN) describes ambulatory care nursing as a comprehensive practice which is built on a broad knowledge base of nursing and health sciences, and applies clinical expertise rooted in the nursing process.
Unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) are paraprofessionals who assist individuals with physical disabilities, mental impairments, and other health care needs with their activities of daily living (ADLs). UAPs also provide bedside care—including basic nursing procedures—all under the supervision of a registered nurse, licensed practical nurse or other health care professional. UAPs must demonstrate their ability and competence before gaining any expanded responsibilities in a clinical setting. While providing this care, UAPs offer compassion and patience and are part of the patient's healthcare support system. Communication between UAPs and registered nurses (RNs) is key as they are working together in their patients' best interests. The scope of care UAPs are responsible for is delegated by RNs or other clinical licensed professionals.
As of 2017, approximately 1.4 million Americans live in a nursing home, two-thirds of whom rely on Medicaid to pay for their care. Residential nursing facilities receive Medicaid federal funding and approvals through a state health department. These facilities may be overseen by various types of state agency.
Marie Schuber Manthey is an American nurse, author, and entrepreneur. She is recognized as one of the originators of Primary Nursing, an innovative system of nursing care delivery.
An acute care nurse practitioner (ACNP) is a registered nurse who has completed an accredited graduate-level educational program that prepares them as a nurse practitioner. This program includes supervised clinical practice to acquire advanced knowledge, skills, and abilities. This education and training qualifies them to independently: (1) perform comprehensive health assessments; (2) order and interpret the full spectrum of diagnostic tests and procedures; (3) use a differential diagnosis to reach a medical diagnosis; and (4) order, provide, and evaluate the outcomes of interventions. The purpose of the ACNP is to provide advanced nursing care across the continuum of health care services to meet the specialized physiologic and psychological needs of patients with acute, critical, and/or complex chronic health conditions. This care is continuous and comprehensive and may be provided in any setting where the patient may be found. The ACNP is a licensed independent practitioner and may autonomously provide care. Whenever appropriate, the ACNP considers formal consultation and/or collaboration involving patients, caregivers, nurses, physicians, and other members of the interprofessional team.
This is an index of nursing articles on Wikipedia.
Margaret Ruth McCorkle FAAN, FAPOS is an international leader and award-winning pioneer in oncology nursing. She is currently the Florence Schorske Wald Professor of Nursing at the Yale School of Nursing.

Elizabeth June Werner was an American nursing executive and educator. She was chair of the department of nursing for 19 years at Evanston Hospital, Illinois, and retired in 1990 as chairperson emerita. During this period she launched the nation's first primary nursing model, transforming the relationship between patients and their caregivers. She also formalized mentoring and professionalized the nursing staff.





