Related Research Articles

Raymond Kurzweil is an American computer scientist, author, entrepreneur, futurist, and inventor. He is involved in fields such as optical character recognition (OCR), text-to-speech synthesis, speech recognition technology and electronic keyboard instruments. He has written books on health technology, artificial intelligence (AI), transhumanism, the technological singularity, and futurism. Kurzweil is a public advocate for the futurist and transhumanist movements and gives public talks to share his optimistic outlook on life extension technologies and the future of nanotechnology, robotics, and biotechnology.

Technology is the application of conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word technology can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible tools such as utensils or machines, and intangible ones such as software. Technology plays a critical role in science, engineering, and everyday life.
The technological singularity—or simply the singularity—is a hypothetical future point in time at which technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, resulting in unforeseeable consequences for human civilization. According to the most popular version of the singularity hypothesis, I. J. Good's intelligence explosion model of 1965, an upgradable intelligent agent could eventually enter a positive feedback loop of self-improvement cycles, each successive; and more intelligent generation appearing more and more rapidly, causing a rapid increase ("explosion") in intelligence which would ultimately result in a powerful superintelligence, qualitatively far surpassing all human intelligence.

Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity, realizing or redistributing value". Others have different definitions; a common element in the definitions is a focus on newness, improvement, and spread of ideas or technologies.

Science and technology in China have developed rapidly since the 1980s to the 2020s, with major scientific and technological progress over the last four decades. From the 1980s to the 1990s, the Chinese government successively launched the 863 Program and the "Strategy for Rejuvenating the Country through Science and Education", which greatly promoted the development of China's science and technological institutions. Governmental focus on prioritizing the advancement of science and technology in China is evident in its allocation of funds, investment in research, reform measures, and enhanced societal recognition of these fields. These actions undertaken by the Chinese government are seen as crucial foundations for bolstering the nation's socioeconomic competitiveness and development, projecting its geopolitical influence, and elevating its national prestige and international reputation.
The Small Business Innovation Research program is a U.S. government funding program, coordinated by the Small Business Administration, intended to help certain small businesses conduct research and development (R&D). Funding takes the form of contracts or grants. The recipient projects must have the potential for commercialization and must meet specific U.S. government R&D needs.
Microsoft Research (MSR) is the research subsidiary of Microsoft. It was created in 1991 by Richard Rashid, Bill Gates and Nathan Myhrvold with the intent to advance state-of-the-art computing and solve difficult world problems through technological innovation in collaboration with academic, government, and industry researchers. The Microsoft Research team has more than 1,000 computer scientists, physicists, engineers, and mathematicians, including Turing Award winners, Fields Medal winners, MacArthur Fellows, and Dijkstra Prize winners.
Technology forecasting attempts to predict the future characteristics of useful technological machines, procedures or techniques. Researchers create technology forecasts based on past experience and current technological developments. Like other forecasts, technology forecasting can be helpful for both public and private organizations to make smart decisions. By analyzing future opportunities and threats, the forecaster can improve decisions in order to achieve maximum benefits. Today, most countries are experiencing huge social and economic changes, which heavily rely on technology development. By analyzing these changes, government and economic institutions could make plans for future developments. However, not all of historical data can be used for technology forecasting, forecasters also need to adopt advanced technology and quantitative modeling from experts’ researches and conclusions.

Clean technology, also called cleantech or climatetech, is any process, product, or service that reduces negative environmental impacts through significant energy efficiency improvements, the sustainable use of resources, or environmental protection activities. Clean technology includes a broad range of technology related to recycling, renewable energy, information technology, green transportation, electric motors, green chemistry, lighting, grey water, and more. Environmental finance is a method by which new clean technology projects can obtain financing through the generation of carbon credits. A project that is developed with concern for climate change mitigation is also known as a carbon project.
There are several approaches to defining the substance and scope of technology policy.
Technology Intelligence (TI) is an activity that enables companies to identify the technological opportunities and threats that could affect the future growth and survival of their business. It aims to capture and disseminate the technological information needed for strategic planning and decision making. As technology life cycles shorten and business become more globalized having effective TI capabilities is becoming increasingly important.
The Utah Science Technology and Research Initiative (USTAR) is a technology-based economic development agency funded by the state of Utah. The organization works to develop ideas and research into marketable products and successful companies through its competitive grant and entrepreneur support programs. USTAR facilitates the diversification of the state’s tech economy, increases private follow-on investment, and supports the creation of technology-based start-up firms, higher-paying jobs and additional business activity leading to a statewide expansion of Utah’s tax base.
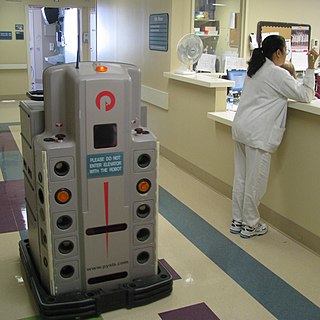
Technological unemployment is the loss of jobs caused by technological change. It is a key type of structural unemployment. Technological change typically includes the introduction of labour-saving "mechanical-muscle" machines or more efficient "mechanical-mind" processes (automation), and humans' role in these processes are minimized. Just as horses were gradually made obsolete as transport by the automobile and as labourer by the tractor, humans' jobs have also been affected throughout modern history. Historical examples include artisan weavers reduced to poverty after the introduction of mechanized looms. Thousands of man-years of work was performed in a matter of hours by the bombe codebreaking machine during World War II. A contemporary example of technological unemployment is the displacement of retail cashiers by self-service tills and cashierless stores.

TIAX LLC is a laboratory-based technology development company that takes early stage inventions, and in its labs, transforms them into technology-enabled products ready for spin-out and commercialization. TIAX is headquartered in Lexington, MA.

Race Against the Machine is a non-fiction book from 2011 by Erik Brynjolfsson and Andrew McAfee about the interaction of digital technology, employment and organization. The full title of the book is: Race Against the Machine: How the Digital Revolution Is Accelerating Innovation, Driving Productivity, and Irreversibly Transforming Employment and the Economy.

"Fourth Industrial Revolution", "4IR", or "Industry 4.0" is a neologism describing rapid technological advancement in the 21st century. It follows the Third Industrial Revolution. The term was popularised in 2016 by Klaus Schwab, the World Economic Forum founder and executive chairman, who asserts that these developments represent a significant shift in industrial capitalism.
Daniel Peter Huttenlocher is an American computer scientist, academic administrator and corporate director. He is the inaugural dean of the Schwarzman College of Computing at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Prior to this, he notably served as the inaugural dean of Cornell Tech at Cornell University, and as a member of Amazon's board of directors.
Christopher L. Magee is an American mechanical engineer, academic and researcher. He is Professor of the practice Emeritus in Mechanical Engineering Department and Institute for Data, Systems and Society at Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He co-directs the International Design Center of Singapore University of Technology and Design.
Karen Hao is an American journalist and data scientist. Currently a contributing writer for The Atlantic and previously a foreign correspondent based in Hong Kong for The Wall Street Journal and senior artificial intelligence editor at the MIT Technology Review, she is best known for her coverage on AI research, technology ethics and the social impact of AI. Hao also co-produces the podcast In Machines We Trust and writes the newsletter The Algorithm.

Louis Barry Rosenberg is an American engineer, researcher, inventor, and entrepreneur. He researches augmented reality, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence. He was the Cotchett Endowed Professor of Educational Technology at the California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo. He founded the Immersion Corporation and Unanimous A.I., and he wrote the screenplay for the 2009 romantic comedy film, Lab Rats.
References
- 1 2 "A comprehensive study of technological change". MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 2021-08-02. Retrieved 2024-11-03.
- 1 2 "New AI tool by MIT predicts how fast any technology is improving". ETCIO.com. Retrieved 2024-11-03.
- ↑ "New AI tool by MIT predicts how fast any technology is improving". The Week. Retrieved 2024-11-03.
- ↑ "MIT built a Google search to spot the most important tech innovations of the future". Fast Company.
- ↑ Singh, Anuraag; Triulzi, Giorgio; Magee, Christopher L. (2021-11-01). "Technological improvement rate predictions for all technologies: Use of patent data and an extended domain description". Research Policy. 50 (9): 104294. arXiv: 2004.13919 . doi:10.1016/j.respol.2021.104294. ISSN 0048-7333.
- ↑ "10 startups harnessing the power of AI". mitsloan.mit.edu. 2024-10-29. Retrieved 2024-11-03.
- 1 2 Macaulay, Thomas (2021-08-04). "MIT researchers use AI to predict the next big things in tech". Deep-Tech. Retrieved 2024-11-06.
- ↑ "TechNext Patent US12099572". Patents Gazette.
- ↑ Robinson, Teresa (2022-02-23). "Now, there Is a New AI Tool to Assess Improvement of Technologies". GRC Viewpoint. Retrieved 2024-11-17.
- ↑ Niggli, Matthias; Rutzer, Christian (2023-01-13). "Digital technologies, technological improvement rates, and innovations "Made in Switzerland"". Swiss Journal of Economics and Statistics. 159 (1): 1. doi: 10.1186/s41937-023-00104-z . ISSN 2235-6282.
- ↑ Dischinger, Sarah M.; Miller, Daniel J.; Vermaas, David A.; Kingsbury, Ryan S. (2024-02-09). "Unifying the Conversation: Membrane Separation Performance in Energy, Water, and Industrial Applications". ACS ES&T Engineering. 4 (2): 277–289. doi:10.1021/acsestengg.3c00475. ISSN 2690-0645. PMC 10862477 . PMID 38357245.
- ↑ Jiang, Shuo; Luo, Jianxi (2022-10-03). "Technology fitness landscape for design innovation: a deep neural embedding approach based on patent data". Journal of Engineering Design. 33 (10): 716–727. arXiv: 2110.13624 . doi:10.1080/09544828.2022.2143155. ISSN 0954-4828.
- ↑ "Technext Inc". legacy.www.sbir.gov. Retrieved 2024-11-17.
- ↑ Thornhill, John (23 September 2021). "Innovation stillrequiressmart, even barmy, innovators". Financial Times. Retrieved 2024-11-03.
- ↑ Mims, Christopher (2021-09-18). "New Research Busts Popular Myths About Innovation". The Wall Street Journal .
- ↑ "Anuraag Singh | Falling Walls". apply.falling-walls.com. Retrieved 2024-11-06.