Related Research Articles
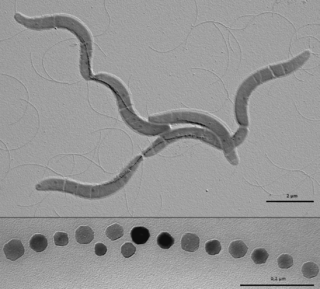
The Rhodospirillales are an order of Pseudomonadota.
The Phyllobacteriaceae are a family of bacteria. The most common genus is Mesorhizobium which contains some of the rhizobia species.
The Aurantimonadaceae are a small family of marine bacteria.

The Hyphomicrobiaceae are a family of bacteria. Among others, they include Rhodomicrobium, a genus of purple bacteria.
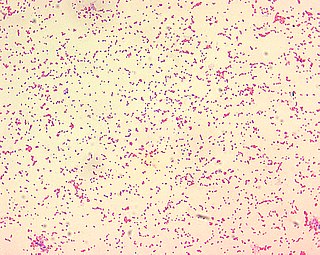
The Brucellaceae are a family of the Gram-negative Hyphomicrobiales. They are named after Sir David Bruce, a Scottish microbiologist. They are aerobic chemoorganotrophes. The family comprises pathogen and soil bacteria
The Coriobacteriales are an order of Actinomycetota.
The Nitrobacteraceae are a family of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria. They include plant-associated bacteria such as Bradyrhizobium, a genus of rhizobia associated with some legumes. It also contains animal-associated bacteria such as Afipia felis, formerly thought to cause cat-scratch disease. Others are free-living, such as Rhodopseudomonas, a purple bacterium found in marine water and soils. The strain Rhodopseudomonas palustris DX-1 can generate an electric current with no hydrogen production, a trait being explored in the development of the microbial fuel cell. The genus Afipia has also been found in the atmosphere, where it uses methylsulfonylmethane as a carbon source.
The Sphingomonadales are an order of the Alphaproteobacteria.
Devosiaceae is a family of Alphaproteobacteria.
Kaistiaceae is a family of Alphaproteobacteria.
Stappiaceae is a family of Alphaproteobacteria.
Pleomorphomonadaceae is a family of Alphaproteobacteria.
Amorphaceae is a family of Alphaproteobacteria.
Ahrensiaceae is a family of Alphaproteobacteria.
Parvibaculaceae is a family of Alphaproteobacteria.
Methylorubrum is a genus of bacteria from the family Methylobacteriaceae.
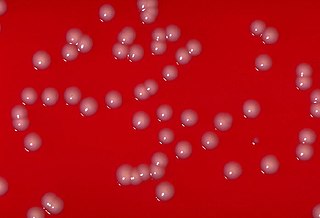
The Mycobacteriales are an order of bacteria.
The Streptosporangiales are an order of bacteria.
The Propionibacteriales are an order of bacteria.
Balneolales is an order of bacteria.
References
- 1 2 Hördt A, García López M, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Schleuning M, Weinhold LM, Tindall BJ, Gronow A, Kyrpides NC, Woyke T, Göker M (2020). "Analysis of 1,000+ Type-Strain Genomes Substantially Improves Taxonomic Classification of Alphaproteobacteria". Front. Microbiol. 11: 468. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00468 . PMC 7179689 . PMID 32373076.
- 1 2 Euzéby JP, Parte AC. "Tepidamorphaceae". List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). Retrieved May 15, 2021.
- ↑ Yarza P, Yilmaz P, Pruesse E, Glöckner FO, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH, Whitman WB, Euzéby J, Amann R, Rosselló-Móra R (2014). "Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences". Nat Rev Microbiol. 12 (9): 635–45. doi:10.1038/nrmicro3330. hdl:10261/123763. PMID 25118885. S2CID 21895693.