Related Research Articles

Babylonia was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia. It emerged as an Akkadian populated but Amorite-ruled state c. 1894 BC. During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was retrospectively called "the country of Akkad", a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older ethno-linguistically related state of Assyria in the north of Mesopotamia and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the region after Hammurabi created a short-lived empire, succeeding the earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apart after the death of Hammurabi and reverted to a small kingdom centered around the city of Babylon.

Elam was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of modern-day Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of southern Iraq. The modern name Elam stems from the Sumerian transliteration elam(a), along with the later Akkadian elamtu, and the Elamite haltamti. Elamite states were among the leading political forces of the Ancient Near East. In classical literature, Elam was also known as Susiana, a name derived from its capital Susa.

Manishtushu (Man-ištušu) c. 2270-2255 BC was the third king of the Akkadian Empire, reigning 15 years from c. 2270 BC until his death in c. 2255 BC. His name means "Who is with him?". He was the son of Sargon the Great, the founder of the Akkadian Empire, and he was succeeded by his son, Naram-Sin who also deified him posthumously. A cylinder seal, of unknown provenance, clearly from the reign of Naram-Sin or later, refers to the deified Manishtushu i.e. "(For) the divine Man-istusu: Taribu, the wife of Lugal-ezen, had fashioned". Texts from the later Ur III period show offerings to the deified Manishtushu. The same texts mention a town of ᵈMa-an-iš-ti₂-su where there was a temple of Manishtushu. This temple was known in the Sargonic period as Ma-an-iš-t[i-s]uki.
Ruhurater or Lahuratil was an Elamite deity.
Humban was an Elamite god. He is already attested in the earliest sources preserving information about Elamite religion, but seemingly only grew in importance in the neo-Elamite period, in which many kings had theophoric names invoking him. He was connected with the concept of kitin, or divine protection.

Inshushinak was the tutelary god of the city of Susa in Elam. His name has a Sumerian etymology, and can be translated as "lord of Susa". He was associated with kingship, and as a result appears in the names and epithets of multiple Elamite rulers. In Susa he was the main god of the local pantheon, though his status in other parts of Elam might have been different. He was also connected with justice and the underworld. His iconography is uncertain, though it is possible snakes were his symbolic animals. Two Mesopotamian deities incorporated into Elamite tradition, Lagamal and Ishmekarab, were regarded as his assistants. He was chiefly worshiped in Susa, where multiple temples dedicated to him existed. Attestations from other Elamite cities are less common. He is also attested in Mesopotamian sources, where he could be recognized as an underworld deity or as an equivalent of Ninurta. He plays a role in the so-called Susa Funerary Texts, which despite being found in Susa were written in Akkadian and might contain instructions for the dead arriving in the underworld.

The Proto-Elamite period, also known as Susa III, is a chronological era in the ancient history of the area of Elam, dating from c. 3100 BC to 2700 BC. In archaeological terms this corresponds to the late Banesh period. Proto-Elamite sites are recognized as the oldest civilization in Iran. The Proto-Elamite script is an Early Bronze Age writing system briefly in use before the introduction of Elamite cuneiform.

Nebuchadnezzar I, reigned c. 1121–1100 BC, was the fourth king of the Second Dynasty of Isin and Fourth Dynasty of Babylon. He ruled for 22 years according to the Babylonian King List C, and was the most prominent monarch of this dynasty. He is best known for his victory over Elam and the recovery of the cultic idol of Marduk.
Haft Tepe is an archaeological site situated in the Khuzestan Province in south-western Iran, about 15 kilometers southwest of the ancient city of Susa. At this site the possible remains of the Elamite city of Kabnak were discovered in 1908, and excavations are still carried out.

Meli-Šipak II, or alternatively Melišiḫu in contemporary inscriptions, was the 33rd king of the Kassite or 3rd Dynasty of Babylon c. 1186–1172 BC and ruled for 15 years. Tablets with two of his year names, 4 and 10, were found at Ur. His reign marks the critical synchronization point in the chronology of the Ancient Near East.

The Awan Dynasty was the first dynasty of Elam of which very little of anything is known today, appearing at the dawn of historical record. The Dynasty corresponds to the early part of the Old Elamite period, it was succeeded by the Shimashki Dynasty and later the Sukkalmah Dynasty. The Elamites were likely major rivals of neighboring Sumer from remotest antiquity; they were said to have been defeated by Enmebaragesi of Kish, who is the earliest archaeologically attested Sumerian king, as well as by a later monarch, Eannatum I of Lagash.

Kurigalzu I, usually inscribed ku-ri-gal-zu but also sometimes with the m or d determinative, the 17th king of the Kassite or 3rd dynasty that ruled over Babylon, was responsible for one of the most extensive and widespread building programs for which evidence has survived in Babylonia. The autobiography of Kurigalzu is one of the inscriptions which record that he was the son of Kadašman-Ḫarbe. Galzu, whose possible native pronunciation was gal-du or gal-šu, was the name by which the Kassites called themselves and Kurigalzu may mean Shepherd of the Kassites.
Kadašman-Ḫarbe I, inscribed in cuneiform contemporarily as Ka-da-áš-ma-an-Ḫar-be and meaning “he believes in Ḫarbe ,” was the 16th King of the Kassite or 3rd dynasty of Babylon, and the kingdom contemporarily known as Kar-Duniaš, during the late 15th to early 14th century BC. It is now considered possible that he was the contemporary of Tepti Ahar, King of Elam, as preserved in a tablet found at Haft Tepe in Iran. This is dated to the “year when the king expelled Kadašman-KUR.GAL,” thought by some historians to represent him although this identification has been contested. If this name is correctly assigned to him, it would imply previous occupation of, or suzerainty over, Elam.
Kadašman-Ḫarbe II, inscribed dKa-dáš-man-Ḫar-be, Kad-aš-man-Ḫar-be or variants and meaning I believe in Ḫarbe, the lord of the Kassite pantheon corresponding to Enlil, succeeded Enlil-nādin-šumi, as the 30th Kassite or 3rd dynasty king of Babylon. His reign was recorded as lasting only one year, six months, c. 1223 BC, as "MU 1 ITI 6" according to the Kinglist A, a formula which is open to interpretation.

Enlil-nādin-aḫe, “Enlil gives a brother,” or Enlil-šuma-uṣur, “Enlil protect the son,” depending on the reading of –MU-ŠEŠ, ca. 1157—1155 BC, was the 36th and final king of the Kassite or 3rd dynasty that had ruled over Babylon and the land known as Karduniash since perhaps around 1500 BC.
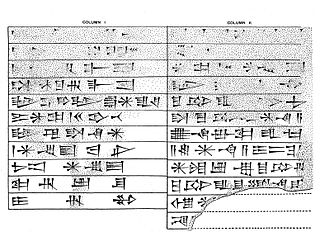
The Enlil-bānī land grant kudurru is an ancient Mesopotamian narû ša ḫaṣbi, or clay stele, recording the confirmation of a beneficial grant of land by Kassite king Kadašman-Enlil I or Kadašman-Enlil II to one of his officials. It is actually a terra-cotta cone, extant with a duplicate, the orientation of whose inscription, perpendicular to the direction of the cone, in two columns and with the top facing the point, indicates it was to be erected upright,, like other entitlement documents of the period.

Kindattu was the 6th king of the Shimashki Dynasty, in Elam, at the time of the third dynasty of Ur in ancient Lower Mesopotamia.