Related Research Articles

The Old Babylonian Empire, or First Babylonian Empire, is dated to c. 1894–1595 BC, and comes after the end of Sumerian power with the destruction of the Third Dynasty of Ur, and the subsequent Isin-Larsa period. The chronology of the first dynasty of Babylonia is debated; there is a Babylonian King List A and also a Babylonian King List B, with generally longer regnal lengths. In this chronology, the regnal years of List A are used due to their wide usage.

Yamhad (Yamḫad) was an ancient Semitic-speaking kingdom centered on Ḥalab (Aleppo) in Syria. The kingdom emerged at the end of the 19th century BC and was ruled by the Yamhad dynasty, who counted on both military and diplomacy to expand their realm. From the beginning of its establishment, the kingdom withstood the aggressions of its neighbors Mari, Qatna and the Old Assyrian Empire, and was turned into the most powerful Syrian kingdom of its era through the actions of its king Yarim-Lim I. By the middle of the 18th century BC, most of Syria minus the south came under the authority of Yamhad, either as a direct possession or through vassalage, and for nearly a century and a half, Yamhad dominated northern, northwestern and eastern Syria, and had influence over small kingdoms in Mesopotamia at the borders of Elam. The kingdom was eventually destroyed by the Hittites, then annexed by Mitanni in the 16th century BC.
Ishme-Dagan I was a monarch of Ekallatum and Assur during the Old Assyrian period. The much later Assyrian King List (AKL) credits Ishme-Dagan I with a reign of forty years; however, it is now known from a limmu-list of eponyms unearthed at Kanesh in 2003 that his reign in Assur lasted eleven years. According to the AKL, Ishme-Dagan I was the son and successor of Shamshi-Adad I. Also according to the AKL, Ishme-Dagan I was succeeded by his son Mut-Ashkur.
Eshnunna was an ancient Sumerian city and city-state in central Mesopotamia 12.6 miles northwest of Tell Agrab and 15 miles northwest of Tell Ishchali. Although situated in the Diyala Valley northwest of Sumer proper, the city nonetheless belonged securely within the Sumerian cultural milieu. It is sometimes, in archaeological papers, called Ashnunnak or Tuplias.
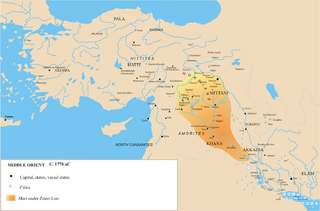
Zimri-Lim was in the Middle Bronze Age the king of Mari.
Tell al-Rimah is an archaeological settlement mound, in Nineveh Province (Iraq) roughly 80 kilometres (50 mi) west of Mosul and ancient Nineveh in the Sinjar region. It lies 15 kilometers south of the site of Tal Afar.

The Battle of the Vale of Siddim, also often called the War of Nine Kings or the Slaughter of Chedorlaomer, is an event in the Hebrew Bible book of Genesis 14:1–17 that occurs in the days of Abram and Lot. The Vale of Siddim was the battleground for the cities of the Jordan River plain revolting against Mesopotamian rule.
Diniktum, inscribed Di-ni-ik-tumKI, was a still unlocated middle bronze-age town often thought to be located somewhere in the Diyala Governorate of Iraq.
Yarim-Lim I, also given as Yarimlim, was the second king of the ancient Amorite kingdom of Yamhad in modern-day Aleppo, Syria.
Hammurabi I is the third attested king of Yamhad (Halab).
Rapiqum, ra-bi-qa-wiKI, was a city of the ancient Near East. The city was located in the north of Mesopotamia, probably on the eastern bank of the Euphrates River, in modern Iraq. It is firmly attested from early in the 2nd Millennium BC until early in the 1st Millennium BC.

Ibal pi’el II was a king of the city kingdom of Eshnunna in ancient Mesopotamia. He reigned c. 1779–1765 BC).
Amut-piʾel II was a king of Qatna in the 18th century BC, during the Middle Bronze IIA.

The Shimashki dynasty was an early dynasty of the ancient region of Elam, to the southeast of Babylonia,. A list of twelve kings of Shimashki is found in the Elamite king-list of Susa, which also contains a list of kings of Awan dynasty. It is uncertain how historically accurate the list is, although some of its kings can be corroborated by their appearance in the records of neighboring peoples. The dynasty corresponds to the second Paleo-Elamite period. It was followed by the Sukkalmah dynasty. Shimashki was likely near today's Masjed Soleyman.

The Sukkalmah or Epartid dynasty, was an early dynasty of West Asia in the ancient region of Elam, to the southeast of Babylonia. It corresponds to the third Paleo-Elamite period. The Sukkalmah dynasty followed the Shimashki dynasty. The title of Sukkalmah means "Grand Regent" and was used by some Elamite rulers. Numerous cuneiform documents and inscriptions remain from this period, particularly from the area of Susa, making the Sukkalmah period one of the best documented in Elamite history.
Kunnam also often called Kunnam of Elam was a military expedition leader of the kingdom of Elam in the 18th century BC. He was part of a military campaign into Mesopotamia and is mainly known from cuneiform letters found at Mari, a Syrian city state where there are the royal archives preserved. He was a contemporary of Zimri-Lim of Mari and Hammurabi of Babylon.
Andarig or Andariq was a Middle Bronze Age kingdom in the Sinjar Plain region of northern Mesopotamia, located between the Habur and Tigris river. It is mentioned several times in the documents found in Mari. Andarig was one of the largest and most powerful kingdoms in the region. It was the most important holding of the Amorite Yamutbal tribe.

The Shutrukid dynasty was a dynasty of the Elamite empire, in modern Iran. Under the Shutrukids, Elam reached a height in power.
Shirukduh was an Elamite king who ruled over the Kingdom of Anshan and Susa. This ruler was one of the so-called Sukkalmahs, or Grand Regents, and ruled at a time roughly contemporary with that of Shamshi-Addu of Assyria
Shimut-wartash I was an Elamite king, and a member of the Sukkalmah dynasty, the ruling house of Elam during the middle Bronze Age.
References
- 1 2 Edwards, I.E.S.; Gadd, C.J.; Hammond, N.G.L.; Sollberger, E. (1973). The Cambridge Ancient History (3rd ed.). Cambridge: University of Cambridge. pp. 263–265. ISBN 0521082307.
- 1 2 Van de Mieroop, Marc (2005). King Hammurabi of Babylon. Malden, Ma: Blackwell Publishing. pp. 16–30. ISBN 1-4051-2660-4.