Related Research Articles

In telecommunications, RS-232 or Recommended Standard 232 is a standard originally introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a DTE such as a computer terminal or PC, and a DCE, such as a modem. The standard defines the electrical characteristics and timing of signals, the meaning of signals, and the physical size and pinout of connectors. The current version of the standard is TIA-232-F Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange, issued in 1997.

A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes. Wireless networking allows homes, telecommunications networks and business installations to avoid the costly process of introducing cables into a building, or as a connection between various equipment locations. Admin telecommunications networks are generally implemented and administered using radio communication. This implementation takes place at the physical level (layer) of the OSI model network structure.
In a telecommunications network, a link is a communication channel that connects two or more devices for the purpose of data transmission. The link may be a dedicated physical link or a virtual circuit that uses one or more physical links or shares a physical link with other telecommunications links.
A virtual circuit (VC) is a means of transporting data over a data network, based on packet switching and in which a connection is first established across the network between two endpoints. The network, rather than having a fixed data rate reservation per connection as in circuit switching, takes advantage of the statistical multiplexing on its transmission links, an intrinsic feature of packet switching.
Data communication, including data transmission and data reception, is the transfer of data, transmitted and received over a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication channel. Examples of such channels are copper wires, optical fibers, wireless communication using radio spectrum, storage media and computer buses. The data are represented as an electromagnetic signal, such as an electrical voltage, radiowave, microwave, or infrared signal.

Data terminal equipment (DTE) is an end instrument that converts user information into signals or reconverts received signals. It is also called data processing terminal equipment or tail circuit. A DTE device communicates with the data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE), such as a modem. The DTE/DCE classification was introduced by IBM.

In telecommunications, frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) is a technique by which the total bandwidth available in a communication medium is divided into a series of non-overlapping frequency bands, each of which is used to carry a separate signal. This allows a single transmission medium such as a microwave radio link, cable or optical fiber to be shared by multiple independent signals. Another use is to carry separate serial bits or segments of a higher rate signal in parallel.

The Joint Tactical Information Distribution System (JTIDS) is an L band Distributed Time Division Multiple Access (DTDMA) network radio system used by the United States Department of Defense and their allies to support data communications needs, principally in the air and missile defense community. It produces a spread spectrum signal using Frequency-shift keying (FSK) and Phase-shift keying (PSK) to spread the radiated power over a wider spectrum (range of frequencies) than normal radio transmissions. This reduces susceptibility to noise, jamming, and interception. In JTIDS Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) (similar to cell phone technology), each time interval (e.g., 1 second) is divided into time slots (e.g. 128 per second). Together, all 1536 time slots in a 12-second interval are called a "frame". Each time slot is "bursted" (transmitted) at several different carrier frequencies sequentially. Within each slot, the phase angle of the transmission burst is varied to provide PSK. Each type of data to be transmitted is assigned a slot or block of slots (channel) to manage information exchanges among user participation groups. In traditional TDMA, the slot frequencies remain fixed from second to second (frame to frame). In JTIDS TDMA, the slot frequencies and/or slot assignments for each channel do not remain fixed from frame to frame but are varied in a pseudo-random manner. The slot assignments, frequencies, and information are all encrypted to provide computer-to-computer connectivity in support of every type of military platform to include Air Force fighters and Navy submarines.

A communication channel refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel in telecommunications and computer networking. A channel is used for information transfer of, for example, a digital bit stream, from one or several senders to one or several receivers. A channel has a certain capacity for transmitting information, often measured by its bandwidth in Hz or its data rate in bits per second.
A satellite modem or satmodem is a modem used to establish data transfers using a communications satellite as a relay. A satellite modem's main function is to transform an input bitstream to a radio signal and vice versa.

A pager, also known as a beeper or bleeper, is a wireless telecommunications device that receives and displays alphanumeric or voice messages. One-way pagers can only receive messages, while response pagers and two-way pagers can also acknowledge, reply to, and originate messages using an internal transmitter. In Japanese, it was commonly called a pocket bell or pokeberu (ポケベル), which is an example of wasei-eigo.

The U.S. Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is a network of American communications satellites and ground stations used by NASA for space communications. The system was designed to replace an existing network of ground stations that had supported all of NASA's crewed flight missions. The prime design goal was to increase the time spacecraft were in communication with the ground and improve the amount of data that could be transferred. Many Tracking and Data Relay Satellites were launched in the 1980s and 1990s with the Space Shuttle and made use of the Inertial Upper Stage, a two-stage solid rocket booster developed for the shuttle. Other TDRS were launched by Atlas IIa and Atlas V rockets.

Satellite Internet access is Internet access provided through communication satellites; if it can sustain high speeds, it is termed satellite broadband. Modern consumer grade satellite Internet service is typically provided to individual users through geostationary satellites that can offer relatively high data speeds, with newer satellites using the Ku band to achieve downstream data speeds up to 506 Mbit/s. In addition, new satellite internet constellations are being developed in low-earth orbit to enable low-latency internet access from space.
An access network is a type of telecommunications network which connects subscribers to their immediate service provider. It is contrasted with the core network, which connects local providers to one another. The access network may be further divided between feeder plant or distribution network, and drop plant or edge network.
Digital Signal 1 is a T-carrier signaling scheme devised by Bell Labs. DS1 is the primary digital telephone standard used in the United States, Canada and Japan and is able to transmit up to 24 multiplexed voice and data calls over telephone lines. E-carrier is used in place of T-carrier outside the United States, Canada, Japan, and South Korea. DS1 is the logical bit pattern used over a physical T1 line; in practice, the terms DS1 and T1 are often used interchangeably.
Power-system automation is the act of automatically controlling the power system via instrumentation and control devices. Substation automation refers to using data from Intelligent electronic devices (IED), control and automation capabilities within the substation, and control commands from remote users to control power-system devices.
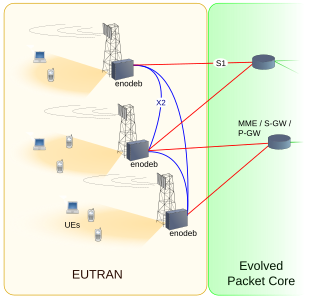
E-UTRA is the air interface of 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Long Term Evolution (LTE) upgrade path for mobile networks. It is an acronym for Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access, also known as the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access in early drafts of the 3GPP LTE specification. E-UTRAN is the combination of E-UTRA, user equipment (UE), and a Node B.
Multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO) is a set of multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) technologies for multipath wireless communication, in which multiple users or terminals, each radioing over one or more antennas, communicate with one another. In contrast, single-user MIMO (SU-MIMO) involves a single multi-antenna-equipped user or terminal communicating with precisely one other similarly equipped node. Analogous to how OFDMA adds multiple-access capability to OFDM in the cellular-communications realm, MU-MIMO adds multiple-user capability to MIMO in the wireless realm.
The British Armed Forces operates a wide range of communications and information systems (CIS). Some of these are specialised military systems, while others are procured off-the-shelf. They fall into three main categories: satellite ground terminals, terrestrial trunk communications systems, and combat net radio systems. Every part of the British Army uses combat net radio, but only the Royal Corps of Signals and the Royal Air Force operates trunk systems and multi-channel satellite communications.
Space Network (SN) is a NASA program that combines space and ground elements to support spacecraft communications in Earth vicinity. The SN Project Office at Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) manages the SN, which consists of:
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.