This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2025) |
Tertiary is a term used in organic chemistry to classify carbon atoms in organic molecules using the number of other carbon atoms attached to it. A carbon atom, that no bonds or one bond with other carbon atoms is called "primary", with two carbon atoms- secondary, and with three-tertiary. [1]
| Red highlighted central atoms in various groups of chemical compounds. Tertiary central atoms compared with primary, secondary and quaternary central atoms. | ||||
| primary | secondary | tertiary | quaternary | |
| Carbon atom in an alkane |  |  |  |  |
| Alcohol |  |  |  | does not exist |
| Amine |  |  |  |  |
| Amide | 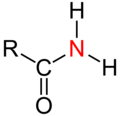 |  |  | does not exist |
| Phosphine |  |  |  |  |