
A dolmen is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more vertical megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the early Neolithic and were sometimes covered with earth or smaller stones to form a tumulus. Small pad-stones may be wedged between the cap and supporting stones to achieve a level appearance. In many instances, the covering has eroded away, leaving only the stone "skeleton" of the mound intact.

Saqqara, also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English, is an Egyptian village in Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for the ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis. Saqqara contains numerous pyramids, including the Step pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Tomb, and a number of mastaba tombs. Located some 30 km (19 mi) south of modern-day Cairo, Saqqara covers an area of around 7 by 1.5 km.

The stone spheres of Costa Rica are an assortment of over 300 petrospheres in Costa Rica, on the Diquís Delta and on Isla del Caño. Locally, they are also known as bolas de piedra. The spheres are commonly attributed to the extinct Diquís culture, and they are sometimes referred to as the Diquís Spheres. They are the best-known stone sculptures of the Isthmo-Colombian area.

Kofun are megalithic tombs or tumuli in Northeast Asia. Kofun were mainly constructed in the Japanese archipelago between the middle of the 3rd century to the early 7th century CE.

Avroman or Hawraman, is a mountainous region located within the provinces of Kurdistan and Kermanshah in western Iran and in north-eastern Kurdistan Region in Iraq. The main part of the Hawraman region is located in Iran and encompasses two components of the Central-Eastern Valley ; and the Western Valley. The mode of human habitation in these two valleys has been adapted over millennia to the rough mountainous environment. Tiered steep-slope planning and architecture, gardening on dry-stone terraces, livestock breeding, and seasonal vertical migration are among the distinctive features of the local culture and life of the Hawrami Kurdish people who dwell in lowlands and highlands during different seasons of each year. On July 27, 2021, part of the Hawraman region along with Uramanat were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List as a cultural site under the name "Cultural Landscape of Hawraman/Uramanat".

Villefranche-de-Conflent is historically a town in the Conflent region of Catalonia, and now a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France.

The Gyeongju Historic Areas of South Korea were designated as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 2000. The protected areas encompass the ruins of temples and palaces, outdoor pagodas and statuary, and other cultural artifacts left by the Silla Kingdom. The historic areas are sometimes known as one of the largest outdoor museums in the world.

Kakopetria is a town in Cyprus located 55 kilometres (34 mi) southwest of the capital, Nicosia, on the north facing foothills of the Troodos Mountains. It stands at an altitude of 667 metres and it is the highest village in the Solea Valley. The community has about 1,200 permanent inhabitants and a couple hundred more who either have a summer house or are originally from Kakopetria but work in Nicosia. Near Kakopetria there is church from 11th century, Agios Nikolaos tis Stegis, UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Mount Longhu is located in Jiangxi, China. It is famous for being one of the birthplaces of Taoism, with many Taoist temples built upon the mountainside. It is particularly important to the Zhengyi Dao as the Shangqing Temple and the Mansion of the Taoist Master are located here. It is known as one of the Four Sacred Mountains of Taoism.

Tourism in Morocco is well developed, maintaining a strong tourist industry focused on the country's coast, culture, and history.The Moroccan government created a Ministry of Tourism in 1985. Tourism is considered one of the main foreign exchange sources in Morocco and since 2013 it had the highest number of arrivals out of the countries in Africa. In 2018, 12.3 million tourists were reported to have visited Morocco.

Ranigat is a collection of 2nd century CE Buddhist ruins spread over an area of 4 square kilometers which dates from the Gandhara civilization. Ranigat is located in valley Buner of Pakistan's Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province.
Ollei is a small fishing village in the Pacific island nation of Palau. It has a population of slightly over 100 people and is located in the State of Ngarchelong, near the northern tip of the Babeldaob island. The village is built along a single road which connects it the rest of the island. Facing west from the village is a large boating dock, which juts out about one fifth of a mile into the ocean. The nearest populated village is that of Mengellang, the capital of the state.
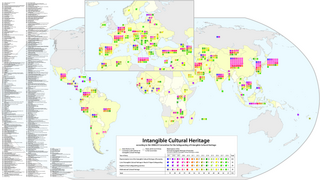
UNESCO established its Lists of Intangible Cultural Heritage with the aim of ensuring better protection of important intangible cultural heritages worldwide and the awareness of their significance. This list is published by the Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage, the members of which are elected by State Parties meeting in a General Assembly. Through a compendium of the different oral and intangible treasures of humankind worldwide, the programme aims to draw attention to the importance of safeguarding intangible heritage, which UNESCO has identified as an essential component and as a repository of cultural diversity and of creative expression.

The Roca dels Moros or Caves of El Cogul is a rock shelter containing paintings of prehistoric Levantine rock art and Iberian schematic art. The site is in El Cogul, in the autonomous community of Catalonia, Spain. Since 1998 the paintings have been protected as part of the Rock art of the Iberian Mediterranean Basin, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Inscriptions in Northeastern Iberian script and in Latin alphabet indicate that the place was used as a sanctuary into Iberian and Roman times.

The Caves of Nahal Me’arot / Wadi el-Mughara, named here by the Hebrew and Arabic name of the valley where they are located, are a UNESCO Site of Human Evolution in the Carmel mountain range near Haifa in northern Israel.
Xoan singing or hát xoan is a genre of Vietnamese folk music performed in spring during the first two months of the lunar new year (Tết) in Phú Thọ Province. The genre includes acting, ceremony, chant, dancing, drumming, and singing; with themes involve romance, riddles, and work. Traditionally occurring in temples, shrines, and communal homes, the songs are performed by a guild, led by a trùm, consisting of male instrumentalists, or kép, and female singers, or đào. A guild consists of ten to fifteen performers, but there are few remaining, increasingly aging, guilds and teachers of this primarily oral tradition.
Rijal Almaa or Rijal Almaʽa is a village located in the Rijal Almaa province, 'Asir Region, Saudi Arabia. It is about 50 km (31 mi) west of Abha, in the southwest of Saudi Arabia. The village is more than 900 years old. The village had an ideal location through which it linked the people coming from Yemen and the Levant through the Holy City of Makkah and Medina. As a result, it became a regional trade center.