
Algae is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotes, which include species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular microalgae such as Chlorella, Prototheca and the diatoms, to multicellular macroalgae such as the giant kelp, a large brown algae

In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called omega−3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or n−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their chemical structure. They are widely distributed in nature, being important constituents of animal lipid metabolism, and they play an important role in the human diet and in human physiology. The three types of omega−3 fatty acids involved in human physiology are α-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA can be found in plants, while DHA and EPA are found in algae and fish. Marine algae and phytoplankton are primary sources of omega−3 fatty acids. DHA and EPA accumulate in fish that eat these algae. Common sources of plant oils containing ALA include walnuts, edible seeds, and flaxseeds as well as hempseed oil, while sources of EPA and DHA include fish and fish oils, and algae oil.
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that are required by humans and other animals for normal physiological function that cannot be synthesized in the body. As they are not synthesized in the body, the essential fatty acids – alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) and linoleic acid – must be obtained from food or from a dietary supplement. Essential fatty acids are needed for various cellular metabolic processes and for the maintenance and function of tissues and organs. These fatty acids also are precursors to vitamins, cofactors, and derivatives, including prostaglandins, leukotrienes, thromboxanes, lipoxins, and others.
Linoleic acid (LA) is an organic compound with the formula HOOC(CH2)7CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)4CH3. Both alkene groups are cis. It is a fatty acid sometimes denoted 18:2 (n−6) or 18:2 cis-9,12. A linoleate is a salt or ester of this acid.
Fish oil is oil derived from the tissues of oily fish. Fish oils contain the omega−3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), precursors of certain eicosanoids that are known to reduce inflammation in the body and improve hypertriglyceridemia. There has been a great deal of controversy in the 21st century about the role of fish oil in cardiovascular disease, with recent meta-analyses reaching different conclusions about its potential impact.

Astaxanthin is a keto-carotenoid within a group of chemical compounds known as carotenones or terpenes. Astaxanthin is a metabolite of zeaxanthin and canthaxanthin, containing both hydroxyl and ketone functional groups.
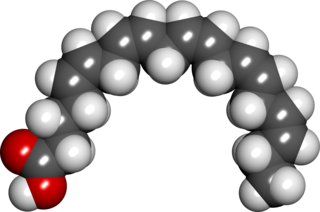
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; also icosapentaenoic acid) is an omega−3 fatty acid. In physiological literature, it is given the name 20:5(n−3). It also has the trivial name timnodonic acid. In chemical structure, EPA is a carboxylic acid with a 20-carbon chain and five cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the third carbon from the omega end.

Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega−3 fatty acid that is an important component of the human brain, cerebral cortex, skin, and retina. It is given the fatty acid notation 22:6(n−3). It can be synthesized from alpha-linolenic acid or obtained directly from maternal milk (breast milk), fatty fish, fish oil, or algae oil. The consumption of DHA (e.g., from fatty fish such as salmon, herring, mackerel and sardines) contributes to numerous physiological benefits, including cognition. As a component of neuronal membranes, the function of DHA is to support neuronal conduction and to allow the optimal functioning of neuronal membrane proteins (such as receptors and enzymes).

Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid and is a component of the cell membrane. It plays a key role in cell cycle signaling, specifically in relation to apoptosis. It is a key pathway for viruses to enter cells via apoptotic mimicry. Its exposure on the outer surface of a membrane marks the cell for destruction via apoptosis.

Tetraselmis suecica is a marine green alga. It grows as single, motile cells visible under light microscope up to concentrations over one million cells per milliliter. It can be grown as a foodstock in aquaculture, being amenable to species such as rotifers of the genus Brachionus. It is a motile chlorophyte and contains a high lipid content. T. suecica proved to have cytotoxic effects on HL-60, MCF-7 and NCI-H460 tumor cells and antioxidant activity. Therefore, they could offer greater benefits as possible natural nutraceuticals for the pharmaceutical industry. More studies are necessary to identify the specific bioactive fractions of each EPS

Isochrysis galbana is a species of Haptophyta. It is the type species of the genus Isochrysis. It is an outstanding food for various bivalve larvae and is now widely cultured for use in the bivalve aquaculture industry. This unicellular is investigated for its high amount of fucoxanthin. The Isochrysis galbana extract is said to have certain cosmetic and hair-growth properties when using hexane, ethyl acetate, ethanol, water, methanol, or isopropanol as extractants. I. galbana has a chloroplast, whose genome sequence has been published in 2020.

The Lactobacillaceae are a family of lactic acid bacteria. It is the only family in the lactic acid bacteria which includes homofermentative and heterofermentative organisms; in the Lactobacillaceae, the pathway used for hexose fermentation is a genus-specific trait. Lactobacillaceae include the homofermentative lactobacilli Lactobacillus, Holzapfelia, Amylolactobacillus, Bombilactobacillus, Companilactobacillus, Lapidilactobacillus, Agrilactobacillus, Schleiferilactobacillus, Loigolactobacillus, Lacticaseibacillus, Latilactobacillus, Dellaglioa, Liquorilactobacillus, Ligilactobacillus, and Lactiplantibacillus; the heterofermentative lactobacilli Furfurilactobacillus, Paucilactobacillus, Limosilactobacillus, Fructilactobacillus, Acetilactobacillus, Apilactobacillus, Levilactobacillus, Secundilactobacillus, and Lentilactobacillus, which were previously classified in the genus Lactobacillus; and the heterofermentative genera Convivina, Fructobacillus, Leuconostoc, Oenococcus, and Weissella which were previously classified in the Leuconostocaceae.

Choricystis is a genus of green algae in the class Trebouxiophyceae, considered a characteristic picophytoplankton in freshwater ecosystems. Choricystis, especially the type species Choricystis minor, has been proposed as an effective source of fatty acids for biofuels. Choricystis algacultures have been shown to survive on wastewater. In particular, Choricystis has been proposed as a biological water treatment system for industrial waste produced by the processing of dairy goods.

Edible seaweed, or sea vegetables, are seaweeds that can be eaten and used for culinary purposes. They typically contain high amounts of fiber. They may belong to one of several groups of multicellular algae: the red algae, green algae, and brown algae. Seaweeds are also harvested or cultivated for the extraction of polysaccharides such as alginate, agar and carrageenan, gelatinous substances collectively known as hydrocolloids or phycocolloids. Hydrocolloids have attained commercial significance, especially in food production as food additives. The food industry exploits the gelling, water-retention, emulsifying and other physical properties of these hydrocolloids.

Nannochloropsis is a genus of algae comprising six known species. The genus in the current taxonomic classification was first termed by Hibberd (1981). The species have mostly been known from the marine environment but also occur in fresh and brackish water. All of the species are small, nonmotile spheres which do not express any distinct morphological features that can be distinguished by either light or electron microscopy. The characterisation is mostly done by rbcL gene and 18S rRNA sequence analysis.

Akkermansia muciniphila is a human intestinal symbiont, isolated from human feces. It is a mucin-degrading bacterium belonging to the genus Akkermansia, discovered in 2004 by Muriel Derrien and Willem de Vos at Wageningen University of the Netherlands. It belongs to the phylum Verrucomicrobiota and its type strain is MucT. It is under preliminary research for its potential association with metabolic disorders.

Asim K. Duttaroy is an Indian-born American medical scientist who, since 2001, has worked as a Professor at the Faculty of Medicine, University of Oslo, Norway. He was born in Gopinagar (Gangnapur), Nadia district, West Bengal, India.
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum PS128 is a specific strain of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, a bacterium of the genus Lactobacillus .

Thraustochytrids are single-celled saprotrophic eukaryotes (decomposers) that are widely distributed in marine ecosystems, and which secrete enzymes including, but not limited to amylases, proteases, phosphatases. They are most abundant in regions with high amounts of detritus and decaying plant material. They play an important ecological role in mangroves, where they aid in nutrient cycling by decomposing decaying matter. Additionally, they contribute significantly to the synthesis of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs): docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), which are essential fatty acids for the growth and reproduction of crustaceans. Thraustochytrids are members of the class Labyrinthulea, a group of protists that had previously been incorrectly categorized as fungi due to their similar appearance and lifestyle. With the advent of DNA sequencing technology, labyrinthulomycetes were appropriately placed with other stramenopiles and subsequently categorized as a group of Labyrinthulomycetes.














