
The Bible is a collection of religious texts or scriptures, some, all of which, or a variant of which, are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, Islam, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthology, a compilation of texts of a variety of forms, originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, and other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text varies.

The Behistun Inscription is a multilingual Achaemenid royal inscription and large rock relief, produced during the reign of Darius I the Great. It is carved on a cliff at Mount Behistun in the Kermanshah Province of modern Iran. The inscription was important to the decipherment of cuneiform, because it is the longest known cuneiform text recorded in multiple languages, being written in Old Persian, Elamite, and Babylonian. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Persian, also known by its endonym Farsi, is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Iranian Persian, Dari Persian and Tajiki Persian. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate history in the cultural sphere of Greater Iran. It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in the Persian alphabet, a derivative of the Arabic script, and within Tajikistan in the Tajik alphabet, a derivative of the Cyrillic script.
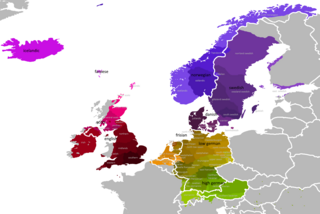
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English, is also the world's most widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia.
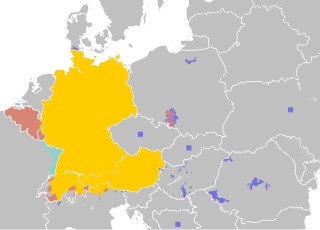
German is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Western Europe and Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also an official language of Luxembourg and Belgium, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France (Alsace), Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary (Sopron).
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Israelites. The second division of Christian Bibles is the New Testament, written in the Koine Greek language.

Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 8th to the 15th centuries.
Old English, or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase known now as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland.
S, or s, is the nineteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ess, plural esses.

Middle English is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English period. Scholarly opinion varies, but the Oxford English Dictionary specifies the period when Middle English was spoken as being from 1150 to 1500. This stage of the development of the English language roughly followed the High to the Late Middle Ages.

Old Trafford is a football stadium in Old Trafford, Greater Manchester, England, and the home of Manchester United. With a capacity of 74,310 it is the largest club football stadium in the United Kingdom, and the eleventh-largest in Europe. It is about 0.5 miles (800 m) from Old Trafford Cricket Ground and the adjacent tram stop.

Monkey is a common name that may refer to most mammals of the infraorder Simiiformes, also known as the simians. Traditionally, all animals in the group now known as simians are counted as monkeys except the apes, which constitutes an incomplete paraphyletic grouping; however, in the broader sense based on cladistics, apes (Hominoidea) are also included, making the terms monkeys and simians synonyms in regard to their scope.

No Country for Old Men is a 2007 American crime thriller film written and directed by Joel and Ethan Coen, based on Cormac McCarthy's 2005 novel of the same name. Starring Tommy Lee Jones, Javier Bardem, and Josh Brolin, the film is set in the desert landscape of 1980 West Texas. The film revisits the themes of fate, conscience, and circumstance that the Coen brothers had explored in the films Blood Simple (1984), Raising Arizona (1987), and Fargo (1996). The film follows three main characters: Llewelyn Moss (Brolin), a Vietnam War veteran and welder who stumbles upon a large sum of money in the desert; Anton Chigurh (Bardem), a hitman who is sent to recover the money; and Ed Tom Bell (Jones), a sheriff investigating the crime. The film also stars Kelly Macdonald as Moss's wife Carla Jean and Woody Harrelson as a bounty hunter seeking Moss and the return of the $2 million.
C, or c, is the third letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is cee, plural cees.

English is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family. It originated in early medieval England and, today, is the most spoken language in the world and the third most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish. English is the most widely learned second language and is either the official language or one of the official languages in 59 sovereign states. There are more people who have learned English as a second language than there are native speakers. As of 2005, it was estimated that there were over two billion speakers of English.

Odin is a widely revered god in Germanic paganism. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, victory, sorcery, poetry, frenzy, and the runic alphabet, and depicts him as the husband of the goddess Frigg. In wider Germanic mythology and paganism, the god was also known in Old English as Wōden, in Old Saxon as Uuôden, in Old Dutch as Wuodan, in Old Frisian as Wêda, and in Old High German as Wuotan, all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic theonym *Wōðanaz, meaning 'lord of frenzy', or 'leader of the possessed'.

The Amish, formally the Old Order Amish, are a group of traditionalist Anabaptist Christian church fellowships with Swiss German and Alsatian origins. They are closely related to Mennonite churches, a separate Anabaptist denomination. The Amish are known for simple living, plain dress, Christian pacifism, and slowness to adopt many conveniences of modern technology, with a view neither to interrupt family time, nor replace face-to-face conversations whenever possible, and a view to maintain self-sufficiency. The Amish value rural life, manual labor, humility and Gelassenheit.

Dutch, also known as Netherlandic or Netherlandish, is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. Afrikaans is a separate but somewhat mutually intelligible daughter language spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, evolving from the Cape Dutch dialects of Southern Africa. The dialects used in Belgium and in Suriname, meanwhile, are all guided by the Dutch Language Union.

In the United States, each state and territory sets the age of consent either by statute or the common law applies, and there are several federal statutes related to protecting minors from sexual predators. Depending on the jurisdiction, the legal age of consent is between 16 and 18. In some places, civil and criminal laws within the same state conflict with each other.

Montero Lamar Hill, known by his stage name Lil Nas X, is an American rapper, singer, and songwriter. He rose to prominence with the release of his country rap single "Old Town Road", which spent 19 weeks atop the U.S. Billboard Hot 100 chart, becoming the longest-running number-one song since the chart debuted in 1958. As the song was atop the Hot 100, Lil Nas X came out as gay, becoming the only artist to do so while having a number-one record.















