Related Research Articles

William Kennedy Laurie Dickson was a British-American inventor who devised an early motion picture camera under the employment of Thomas Edison.
The following is an overview of the events of 1895 in film, including a list of films released and notable births.
The following is an overview of the events of 1894 in film, including a list of films released and notable births.

The Kinetoscope is an early motion picture exhibition device, designed for films to be viewed by one person at a time through a peephole viewer window. The Kinetoscope was not a movie projector, but it introduced the basic approach that would become the standard for all cinematic projection before the advent of video: it created the illusion of movement by conveying a strip of perforated film bearing sequential images over a light source with a high-speed shutter. First described in conceptual terms by U.S. inventor Thomas Edison in 1888, it was largely developed by his employee William Kennedy Laurie Dickson between 1889 and 1892. Dickson and his team at the Edison lab in New Jersey also devised the Kinetograph, an innovative motion picture camera with rapid intermittent, or stop-and-go, film movement, to photograph movies for in-house experiments and, eventually, commercial Kinetoscope presentations.
The following is an overview of the events of 1891 in film, including a list of films released and notable births.
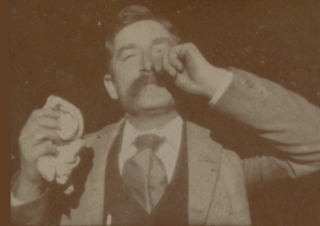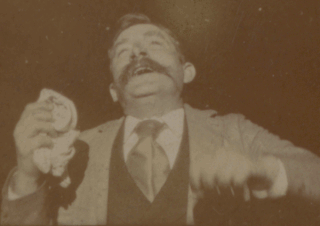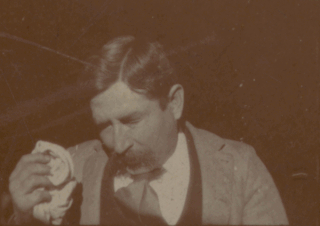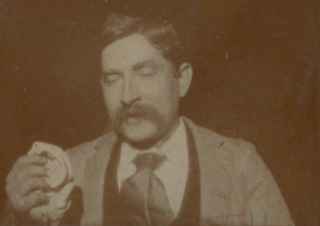
Fred Ott's Sneeze is an 1894 short, black-and-white silent film shot by William K.L. Dickson and featuring Fred Ott. According to the Library of Congress, it is the second oldest surviving U.S. motion picture to be copyrighted, although it is now in the public domain.

The Black Maria was Thomas Edison's film production studio in West Orange, New Jersey. It was the world's first film studio.

Edison Studios was an American film production organization, owned by companies controlled by inventor and entrepreneur, Thomas Edison. The studio made close to 1,200 films, as part of the Edison Manufacturing Company (1894–1911) and then Thomas A. Edison, Inc. (1911–1918), until the studio's closing in 1918. Of that number, 54 were feature length, and the remainder were shorts. All of the company's films have fallen into the public domain because they were released before 1928.

Actuality film is a non-fiction film genre that uses footage of real events, places, and things, a predecessor to documentary film. Unlike documentaries, actuality films are not structured into a larger narrative or coherent whole. During the era of early cinema, actualities—usually lasting no more than a minute or two and usually assembled together into a program by an exhibitor—were just as popular and prominent as their fictional counterparts. The line between "fact" and "fiction" was not as prominent in early cinema as it would become once documentaries became the predominant non-fiction filmmaking form. Actuality as a film genre is related to still photography.

William Heise was a German-born American film cinematographer and director, active in the 1890s and credited for more than 175 short silent films. Heise filmed a "We All Smoke" skit promoting Admiral Cigarettes in 1897.

Carmencita is an 1894 American short black-and-white silent documentary film directed and produced by William K.L. Dickson, the Scottish inventor credited with the invention of the motion picture camera under the employ of Thomas Edison. The film is titled after the dancer who features in it.

Bucking Broncho is an 1894 American black-and-white silent film from Edison Studios, produced by William K. L. Dickson with William Heise as cinematographer. Filmed on a single reel, using standard 35 mm gauge, it has a 32-second runtime. One of the earliest known films in the Western genre, it is preserved by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences and available in the DVD collection More Treasures from American Film Archives (2004).

Corbett and Courtney Before the Kinetograph is an 1894 American short black-and-white silent film produced by William K.L. Dickson and starring James J. Corbett. It was only the second boxing match to be filmed, following The Leonard-Cushing Fight which had been filmed by Dickson on June 14, 1894.

Buffalo Dance is an 1894 black-and-white silent film from Edison Studios, produced by William K. L. Dickson with William Heise as cinematographer. Filmed on a single reel, using standard 35 mm gauge, it has a 16-second runtime. The film, with English intertitles, was shot in Edison's Black Maria studio at the same time as Sioux Ghost Dance. These are two of the earliest films made which feature Native Americans. According to the Edison catalog, the performers in both films were Sioux people wearing traditional costumes and war paint. All were veterans of Buffalo Bill's Wild West show. Buffalo Dance has three dancers and two drummers. Hair Coat, Last Horse and Parts His Hair dance in a circle while drummers Pine and Strong Talker provide their rhythm.

Luis Martinetti, Contortionist is an 1894 American short film produced by the Edison Manufacturing Company. The film, which runs 12.5 seconds, consists of a contortionist act performed by Luis Martinetti of the Martinetti Brothers trapeze act. Martinetti wears tiger-striped tights and performs contortionist poses on a pair of trapeze rings.

Men Boxing is an 1891 American short silent film, produced and directed by William K. L. Dickson and William Heise for the Edison Manufacturing Company, featuring two Edison employees with boxing gloves, pretending to spar in a boxing ring. The 12 feet of film was shot between May and June 1891 at the Edison Laboratory Photographic Building in West Orange, New Jersey, on the Edison-Dickson-Heise experimental horizontal-feed kinetograph camera and viewer, through a round aperture on 3/4 inch (19mm) wide film with a single edge row of sprocket perforations, as an experimental demonstration and was never publicly shown. A print has been preserved in the US Library of Congress film archive as part of the Gordon Hendricks collection.
Annabelle Serpentine Dance is a short silent American film produced and distributed by Edison Manufacturing Company in 1895. It is one of several released by the studio in the late 19th century. Each short film depicts the popular serpentine dance performed by Annabelle Moore. Many of the prints were distributed in color, which was hand-tinted.

Annie Oakley is an 1894 American black-and-white silent film from Edison Studios, produced by William K. L. Dickson with William Heise as cinematographer.

The Barbershop is an 1894 American short narrative silent film directed by William K.L. Dickson and William Heise. It was produced by the Edison Manufacturing Company at the Black Maria Studio, in West Orange, New Jersey. The film was one of the first created for the Kinetoscope.

The Leonard–Cushing Fight is an 1894 American short black-and-white silent film produced by William K.L. Dickson, starring Mike Leonard and Jack Cushing. Leonard and Cushing participate in a six-round boxing match under special conditions that allow for it to be filmed and displayed on a Kinetograph. The film was shot on an uncertain date between May 24 and June 14, 1894, in a specially configurated ring in Edison's Black Maria film studio in West Orange, New Jersey. Premiered on August 4, 1894 in Manhattan, the movie is the first sports film ever released. As of 2023, no full print of the film is known to have survived, making it a partially lost film. A 23-second fragment is available at the Library of Congress.
References
- 1 2 3 "The boxing cats (Prof. Welton's)". LoC.gov . Library of Congress . Retrieved September 16, 2021.
- 1 2 Waters, Michael (June 19, 2017). "This Feline Boxing Match From 1894 Is a Precursor to the Cat Video". Atlas Obscura . Retrieved September 16, 2021.
- ↑ Florin, Bo; de Klerk, Nico; Vonderau, Patrick, eds. (2017). Films that Sell: Moving Pictures and Advertising. British Film Institute. ISBN 978-1844578924.
- ↑ Gray, Frank (2019). The Brighton School and the Birth of British Film. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-3030175047.
- 1 2 Gutoskey, Ellen (August 17, 2019). "This Caturday, Watch Two Kitties Duke It Out in the World's Oldest Cat 'Video'". Mental Floss . Retrieved September 16, 2021.