
Diapsids are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The earliest traditionally identified diapsids, the araeoscelidians, appeared about three hundred million years ago during the late Carboniferous period. All diapsids other than the most primitive ones in the clade Araeoscelidia are often placed into the clade Neodiapsida. The diapsids are extremely diverse, and include birds and all modern reptile groups, including turtles, which were historically thought to lie outside the group. All modern reptiles and birds are placed within the neodiapsid subclade Sauria. Although some diapsids have lost either one hole (lizards), or both holes, or have a heavily restructured skull, they are still classified as diapsids based on their ancestry. At least 17,084 species of diapsid animals are extant: 9,159 birds, and 7,925 snakes, lizards, tuatara, turtles, and crocodiles.

Godinotia is an extinct genus of strepsirrhine primate belonging to the Adapidae family. It lived during the Eocene epoch, and its fossils have been found in the Messel Pit, Germany.

Walking with Dinosaurs is a 1999 six-part nature documentary television miniseries created by Tim Haines and produced by the BBC Science Unit, the Discovery Channel and BBC Worldwide, in association with TV Asahi, ProSieben and France 3. Envisioned as the first "Natural History of Dinosaurs", Walking with Dinosaurs depicts dinosaurs and other Mesozoic animals as living animals in the style of a traditional nature documentary. The series first aired on the BBC in the United Kingdom in 1999 with narration by Kenneth Branagh. The series was subsequently aired in North America on the Discovery Channel in 2000, with Avery Brooks replacing Branagh.

Walking with Beasts, marketed as Walking with Prehistoric Beasts in North America, is a 2001 six-part nature documentary television miniseries created by Impossible Pictures and produced by the BBC Science Unit, the Discovery Channel, ProSieben and TV Asahi. The sequel to the 1999 miniseries Walking with Dinosaurs, Walking with Beasts explores the life in the Cenozoic era, after the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs, particularly focusing on the rise of the mammals to dominance. The UK version of the series is narrated by Kenneth Branagh, who also narrated Walking with Dinosaurs, and the US version is narrated by Stockard Channing.

Xiphactinus, colloquially referred to as the X-fish, is an extinct genus of large predatory marine bony fish that lived during the late Albian to the late Maastrichtian. The genus grew up to 5–6 metres (16–20 ft) in length, and superficially resembled a gargantuan, fanged tarpon.

Nothosaurus is an extinct genus of sauropterygian reptile from the Triassic period, approximately 240–210 million years ago, with fossils being distributed throughout the former Tethys Ocean, from North Africa and Europe to China. It is the best known member of the nothosaur order.

Iberomesornis is a monotypic genus of enantiornithine bird of the Cretaceous of Spain.

Cynodictis is an extinct amphicyonid carnivoran which inhabited Eurasia from the Late Eocene subepoch to the Early Oligocene subepoch living from 37.2 to 28.4 million years ago, existing for approximately 8.8 million years.

Sea Monsters, marketed as Chased by Sea Monsters in the United States, is a 2003 three-part nature documentary television miniseries created by Impossible Pictures and produced by the BBC Studios Science Unit, the Discovery Channel and ProSieben. Following in the footsteps of The Giant Claw (2002) and Land of Giants (2003), special episodes of the nature documentary series Walking with Dinosaurs, Sea Monsters stars British wildlife presenter Nigel Marven as a "time-travelling zoologist" who travels to seven different periods of time in prehistory, diving in the "seven deadliest seas of all time" and encountering and interacting with the prehistoric creatures who inhabit them. The series is narrated by Karen Hayley in the BBC version and by Christopher Cook in the American version.

Walking with Monsters – Life Before Dinosaurs, marketed as Before the Dinosaurs – Walking with Monsters in North America, is a 2005 three-part nature documentary television miniseries created by Impossible Pictures and produced by the BBC Studios Science Unit, the Discovery Channel, ProSieben and France 3. Walking with Monsters explores life in the Paleozoic era, showcasing the early development of groups such as arthropods, fish, amphibians, reptiles and synapsids. Like its predecessors Walking with Dinosaurs (1999) and Walking with Beasts (2001), Walking with Monsters is narrated by Kenneth Branagh.

Eustreptospondylus is a genus of megalosaurid theropod dinosaur, from the Oxfordian stage of the Late Jurassic period in southern England, at a time when Europe was a series of scattered islands.

Petrolacosaurus is an extinct genus of diapsid reptile from the late Carboniferous period. It was a small, 40-centimetre (16 in) long reptile, and one of the earliest known reptile with two temporal fenestrae. This means that it was at the base of Diapsida, the largest and most successful radiation of reptiles that would eventually include all modern reptile groups, as well as dinosaurs and other famous extinct reptiles such as plesiosaurs, ichthyosaurs, and pterosaurs. However, Petrolacosaurus itself was part of Araeoscelida, a short-lived early branch of the diapsid family tree which went extinct in the mid-Permian.

Cephalaspis is a possibly monotypic genus of extinct osteostracan agnathan vertebrate. It was a trout-sized detritivorous fish that lived in the early Devonian.
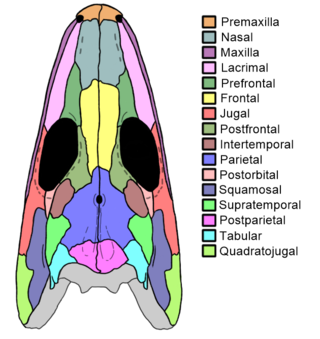
Proterogyrinus is an extinct genus of early tetrapods from the order Embolomeri. Fossil remains of Proterogyrinus have been found in Scotland, UK, and West Virginia, United States, and date back to the Serpukhovian, which is from about 331 to 323 million years ago. The genus was originally named by renowned vertebrate paleontologist Alfred Sherwood Romer in 1970. A comprehensive redescription was later published by Canadian paleontologist Robert Holmes in 1984. The generic name "Proterogyrinus" is Greek for "earlier wanderer" or "earlier tadpole". This name was chosen by Romer in keeping with a trend of naming long-bodied early tetrapods with the suffix "-gyrinus".

Peteinosaurus was a prehistoric genus of pterosaur. It lived in the late Triassic period in the late Norian age, and at a wingspan of around 60 cm (24 in), was one of the smallest and earliest pterosaurs, although other estimates suggest a wingspan of up to 1 m (3.3 ft).
Tim Haines is a screenwriter, producer and director who is best known for his work on the BBC popular science shows Walking with Dinosaurs, Walking with Beasts, and Walking with Monsters. He is co-creator and executive producer of the ITV sci-fi drama Primeval, and founder of the production company Impossible Pictures.

Land of Giants and The Giant Claw, marketed together as Chased by Dinosaurs in the United States, are two special episodes of the nature documentary television series Walking with Dinosaurs. Created by Impossible Pictures and produced by the BBC Studios Science Unit, the Discovery Channel and ProSieben, The Giant Claw was first broadcast on 30 December 2002, followed by Land of Giants on 1 January 2003. The two episodes stars British wildlife presenter Nigel Marven as a "time-travelling zoologist", interacting with dinosaurs and other prehistoric creatures, a drastic change in presentation from preceding entries in the Walking with... franchise.

Walking with... is a palaeontology media franchise produced and broadcast by the BBC Studios Science Unit. The franchise began with the series Walking with Dinosaurs (1999), created by Tim Haines. By far the most watched science programme in British television during the 20th century, Walking with Dinosaurs spawned companion material and four sequel series: Walking with Beasts (2001), Walking with Cavemen (2003), Sea Monsters (2003) and Walking with Monsters (2005). Each series uses a combination of computer-generated imagery and animatronics, incorporated with live action footage shot at various locations, to portray prehistoric animals in the style of a traditional nature documentary.

Eunotosaurus is an extinct genus of amniote, possibly a close relative of turtles. Eunotosaurus lived in the late Middle Permian and fossils can be found in the Karoo Supergroup of South Africa and Malawi. Eunotosaurus resided in the swamps of what is now southern Africa. Its ribs were wide and flat, forming broad plates similar to a primitive turtle shell, and the vertebrae were nearly identical to those of some turtles. Accordingly, it is often considered as a possible transitional fossil between turtles and their prehistoric ancestors. However, it is possible that these turtle-like features evolved independently of the same features in turtles, since other anatomical studies and phylogenetic analyses suggest that Eunotosaurus may instead have been a parareptile, an early-diverging neodiapsid unrelated to turtles, or a synapsid.
Susan Elizabeth Evans is a British palaeontologist and herpetologist. She is the author or co-author of over 100 peer-reviewed papers and book chapters.


















