
Transhumanism is a philosophical and intellectual movement which advocates for the enhancement of the human condition by developing and making widely available sophisticated technologies that can greatly enhance longevity and cognition. It also predicts the inevitability of such technologies in the future.
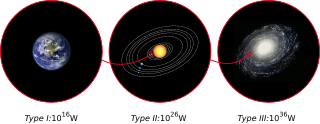
The Kardashev scale is a method of measuring a civilization's level of technological advancement based on the amount of energy it is able to use. The measure was proposed by Soviet astronomer Nikolai Kardashev in 1964.

Deepak Chopra is an Indian-American author and alternative medicine advocate. A prominent figure in the New Age movement, his books and videos have made him one of the best-known and wealthiest figures in alternative medicine. His discussions of quantum healing have been characterised as technobabble – "incoherent babbling strewn with scientific terms" which drives those who actually understand physics "crazy" and as "redefining Wrong".
Doubleday is an American publishing company. It was founded as the Doubleday & McClure Company in 1897 and was the largest in the United States by 1947. It published the work of mostly U.S. authors under a number of imprints and distributed them through its own stores. In 2009 Doubleday merged with Knopf Publishing Group to form the Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group, which is now part of Penguin Random House. In 2019, the official website presents Doubleday as an imprint, not a publisher.

Michio Kaku is an American theoretical physicist, futurist, and popularizer of science. He is a professor of theoretical physics in the City College of New York and CUNY Graduate Center. Kaku is the author of several books about physics and related topics and has made frequent appearances on radio, television, and film. He is also a regular contributor to his own blog, as well as other popular media outlets. For his efforts to bridge science and science fiction, he is a 2021 Sir Arthur Clarke Lifetime Achievement Awardee.

The Elegant Universe: Superstrings, Hidden Dimensions, and the Quest for the Ultimate Theory is a book by Brian Greene published in 1999, which introduces string and superstring theory, and provides a comprehensive though non-technical assessment of the theory and some of its shortcomings. In 2000, it won the Royal Society Prize for Science Books and was a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize for General Non-Fiction. A new edition was released in 2003, with an updated preface.

Masaru Emoto was a Japanese businessman, author and pseudo-scientist who claimed that human consciousness could affect the molecular structure of water. His 2004 book The Hidden Messages in Water was a New York Times best seller. His conjecture evolved over the years, and his early work revolved around pseudo-scientific hypotheses that water could react to positive thoughts and words and that polluted water could be cleaned through prayer and positive visualization.

Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th Dimension is a book by Michio Kaku, a theoretical physicist from the City College of New York. It focuses on Kaku's studies of higher dimensions referred to as hyperspace. The recurring theme of the book is that all four forces of the universe become more coherent and their description simpler in higher dimensions.

John Horgan is an American science journalist best known for his 1996 book The End of Science. He has written for many publications, including National Geographic, Scientific American, The New York Times, Time, Newsweek, and IEEE Spectrum. His awards include two Science Journalism Awards from the American Association for the Advancement of Science and the National Association of Science Writers Science-in-Society Award. His articles have been included in the 2005, 2006 and 2007 editions of The Best American Science and Nature Writing. Since 2010 he has written the "Cross-check" blog for ScientificAmerican.com.

Beyond Einstein: The Cosmic Quest for the Theory of the Universe is a book by Michio Kaku, a theoretical physicist from the City College of New York, and Jennifer Trainer Thompson. It focuses on the development of superstring theory, which might become the unified field theory of the strong force, the weak force, electromagnetism and gravity. The book was initially published on February 1, 1987, by Bantam Books.

Parallel Worlds: A Journey Through Creation, Higher Dimensions, and the Future of the Cosmos is a popular science book by Michio Kaku first published in 2004.

Physics of the Impossible: A Scientific Exploration Into the World of Phasers, Force Fields, Teleportation, and Time Travel is a book by theoretical physicist Michio Kaku. Kaku uses discussion of speculative technologies to introduce topics of fundamental physics to the reader. The topic of invisibility becomes a discussion on why the speed of light is slower in water than in vacuum, that electromagnetism is similar to ripples in a pond, and Kaku discusses newly developed composite materials. The topic of Star Trek "phasers" becomes a lesson on how lasers work and how laser-based research is conducted. The cover of his book depicts a TARDIS, a device used in the British science fiction television show Doctor Who to travel in space and time, in its disguise as a police box, continuously passing through a time loop. With each discussion of science fiction technology topics he also "explains the hurdles to realizing these science fiction concepts as reality".

Physics of the Future: How Science Will Shape Human Destiny and Our Daily Lives by the Year 2100 is a 2011 book by theoretical physicist Michio Kaku, author of Hyperspace and Physics of the Impossible. In it Kaku speculates about possible future technological development over the next 100 years. He interviews notable scientists about their fields of research and lays out his vision of coming developments in medicine, computing, artificial intelligence, nanotechnology, and energy production. The book was on the New York Times Bestseller List for five weeks.

The left-brain interpreter is a neuropsychological concept developed by the psychologist Michael S. Gazzaniga and the neuroscientist Joseph E. LeDoux. It refers to the construction of explanations by the left brain hemisphere in order to make sense of the world by reconciling new information with what was known before. The left-brain interpreter attempts to rationalize, reason and generalize new information it receives in order to relate the past to the present.
Memoirs of the Twentieth Century is an early work of speculative fiction by Irish writer Samuel Madden. This 1733 epistolary novel takes the form of a series of diplomatic letters written in 1997 and 1998. The work is a satire perhaps modeled after Jonathan Swift's Gulliver's Travels published seven years before. Madden was an Anglican clergyman, and the book is focused on the dangers of Catholicism and Jesuits, depicting a future where they dominate.

Susan Schneider is an American academic and public philosopher. She is the founding director of the Center for the Future Mind at Florida Atlantic University where she also holds the William F. Dietrich Distinguished Professorship. Schneider has also held the Baruch S. Blumberg NASA/Library of Congress Chair in Astrobiology, Exploration, and Scientific Innovation at NASA and the Distinguished Scholar Chair at the Library of Congress.

A planetary civilization or global civilization is a civilization of Type I on the Kardashev scale. This type of civilization is likely to be reliant on renewable energy sources such as stellar power, as well as powerful non-renewable sources such as nuclear fusion. A Type I civilization's energy consumption level is roughly equivalent to the solar insolation on Earth (between 1016 and 1017 watts) ─ around 3 orders of magnitude higher than that of contemporary humanity (around 2×1013 as of 2020).

The Future of Humanity: Terraforming Mars, Interstellar Travel, Immortality, and Our Destiny Beyond Earth is a popular science book by the futurist and physicist Michio Kaku. The book was initially published on February 20, 2018 by Doubleday. The book was on The New York Times Best Seller list for four weeks.

The God Equation: The Quest for a Theory of Everything is a popular science book by the futurist and physicist Michio Kaku. The book was initially published on April 6, 2021 by Doubleday.

















