The hull is the watertight body of a ship or boat. Atop the hull may be a deckhouse or some other form of superstructure, like a mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline.

Maritime archaeology is a discipline within archaeology as a whole that specifically studies human interaction with the sea, lakes and rivers through the study of associated physical remains, be they vessels, shore-side facilities, port-related structures, cargoes, human remains and submerged landscapes. A specialty within maritime archaeology is nautical archaeology, which studies ship construction and use.

A shipwreck is the remains of a ship that has wrecked, which are found either beached on land or sunken to the bottom of a body of water. Shipwrecking may be deliberate or accidental. In January 1999, Angela Croome estimated that there have been about three million shipwrecks worldwide.

Boat building is the design and construction of boats and their systems. This includes at a minimum a hull, with propulsion, mechanical, navigation, safety and other systems as a craft requires.

The Uluburun Shipwreck is a Late Bronze Age shipwreck dated to the late 14th century BC, discovered close to the east shore of Uluburun, and about 6 miles (9.7 km) miles southeast of Kaş, in south-western Turkey. The shipwreck was discovered in the summer of 1982 by Mehmed Çakir, a local sponge diver from Yalıkavak, a village near Bodrum.
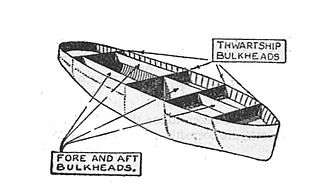
A bulkhead is an upright wall within the hull of a ship or within the fuselage of an aeroplane. Other kinds of partition elements within a ship are decks and deckheads.

The Hjortspring boat is a vessel designed as a large canoe, from the Scandinavian Pre-Roman Iron Age. It was built circa 400–300 BCE. The hull and remains were rediscovered and excavated in 1921–1922 from the bog of Hjortspring Mose on the island of Als in Sønderjylland, southern Denmark. The vessel is a clinker-built wooden boat of more than 19 metres length overall, 13.6 metres long inside, and 2 metres wide. Ten thwarts fit to be seats span the boat with room for two persons each; this suggests space for a crew of at least 20 who propelled the boat with paddles. The boat would have weighed an estimated 530 kilograms, making it easily portable by its crew. When found, it contained a great quantity of weapons and armour, including 131 shields of the Celtic type, 33 well-crafted shield bosses, 138 spearheads of iron, 31 spearheads of bone or antler, 11 single-edged iron swords, and the remains of several mailcoats. Two of the swords were deliberately bent, a practice associated with Iron Age rituals. The largest of the spearheads is a massive 43.5 centimetres long. The find also contained bowls, boxes, blacksmith's tools, and other everyday goods. The sinking of the vessel in the bog has been interpreted as a deliberate votive offering. This is reinforced by the presence of a dismembered horse placed beneath the boat at the time of burial along with a lamb, a calf, and two dogs. Numerous graves have been discovered in Denmark from this time period containing similar grave goods and sacrificed horses, dogs, lambs, cows, other animals, and human beings.

Floodability is the susceptibility of a ship's construction to flooding. It also refers to the ability to intentionally flood certain areas of the hull for damage control purposes, or to increase stability, which is particularly important in combat vessels, which often face the possibility of serious hull breach due to enemy action, and which rely on well-trained Damage Controlmen to equalize and then stop flooding of the hull.

The Antikythera wreck is a Roman-era shipwreck dating from the second quarter of the first century BC.
The Black Assarca shipwreck was first discovered by tourists in 1995, at Black Assarca Island, Eritrea. The wreck was surveyed in 1995 and partially excavated in 1997 by the Institute of Nautical Archaeology, under the auspices of the Ministry of Marine Resources of Eritrea.

SS Admella was an Australian passenger steamship that was shipwrecked on a submerged reef off the coast of Carpenter Rocks, south west of Mount Gambier South Australia, in the early hours of Saturday 6 August 1859. Survivors clung to the wreck for over a week and many people took days to die as they glimpsed the land from the sea and watched as one rescue attempt after another failed.

Lone Star is a wooden hull, steam-powered stern-wheeled towboat in LeClaire, Iowa, United States. She is dry docked and on display at the Buffalo Bill Museum in LeClaire. Built in 1868, she is the oldest of three surviving steam-powered towboats, and the only one with a wooden hull. She was declared a National Historic Landmark on 20 December 1989.
Shell plating is the outer-most structure on the hull of a steel or aluminum ship or boat.

A dolium is a large earthenware vase or vessel used in ancient Roman times for storage or transportation of goods. It's similar to Kvevri which is widely used for wine farming in Georgia to this day.

The Narval class were a group of submarines built for the Imperial Russian Navy. They were designed by the Electric Boat Company and ordered in the 1911 programme as the "Holland 31A" design. The Narval class had advanced features including watertight bulkheads, a crash diving tank and gravitationally filled ballast tanks which did not feature in contemporary Russian-designed boats. The boats were well regarded by the Russian Navy and served in the Black Sea Fleet during World War I, during which they sank 8 merchant ships and 74 coastal vessels.
Ship construction techniques can be categorized as one of hide, log, sewn, lashed-plank, clinker, shell-first, and frame-first. While the frame-first technique dominates the modern ship construction industry, the ancients relied primarily on the other techniques to build their watercraft. In many cases, these techniques were very labor-intensive and/or inefficient in their use of raw materials. Regardless of differences in ship construction techniques, the vessels of the ancient world, particularly those that plied the waters of the Mediterranean Sea and the islands of Southeast Asia were seaworthy craft, capable of allowing people to engage in large-scale maritime trade.
The Blackfriars shipwrecks were a series of wrecks discovered by archaeologist Peter Marsden in the Blackfriars area of the banks of the River Thames in London, England. The wrecks were discovered while building a riverside embankment wall along the River Thames. Marsden discovered the first on 6 September 1962 and the next two were discovered in 1970. A later discovery added to the previous three wrecks, constituting now what is known as the four Blackfriars wrecks.
Ancient Black Sea shipwrecks found in the Black Sea date to Antiquity. In 1976, Willard Bascom suggested that the deep, anoxic waters of the Black Sea might have preserved ships from antiquity because typical wood-devouring organisms could not survive there. At a depth of 150m, the Black Sea contains insufficient oxygen to support most familiar biological life forms.
Sinop D is an ancient Black Sea shipwreck located to the east of Sinop, Turkey. The ship was discovered by a team led by Robert Ballard in 2000. The team discovered the well-preserved wreck at a 320m depth, in the Black Sea's deep anoxic waters. The vessel's entire hull and cargo are intact, buried in sediments. Its deck structures are also intact, including a mast rising some 11 m into the water column. Radiocarbon dating of wood from the wreck provides a date of 410-520 AD.

The Belitung shipwreck is the wreck of an Arabian dhow which sailed en route from Africa to China around 830 CE. The ship completed the outward journey, but sank on the return journey, approximately 1 mile (1.6 km) off the coast of Belitung Island, Indonesia. It is unclear why the ship was so far from its expected route back from China. Belitung is to the south-east of the Singapore Strait by 380 miles (610 km), and this secondary route is more normal for ships travelling from the Java Sea, which is south of Belitung Island.