Related Research Articles

The economy of Paraguay is a market economy that is highly dependent on agriculture products. In recent years, Paraguay's economy has grown as a result of increased agricultural exports, especially soybeans. Paraguay has the economic advantages of a young population and vast hydroelectric power. Its disadvantages include the few available mineral resources, and political instability. The government welcomes foreign investment.
Privatization can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when a heavily regulated private company or industry becomes less regulated. Government functions and services may also be privatised ; in this case, private entities are tasked with the implementation of government programs or performance of government services that had previously been the purview of state-run agencies. Some examples include revenue collection, law enforcement, water supply, and prison management.

The economic history of Argentina is one of the most studied, owing to the "Argentine paradox." As a country, it had achieved advanced development in the early 20th century but experienced a reversal, which inspired an enormous wealth of literature and diverse analysis on the causes of this decline. Since independence from Spain in 1816, the country has defaulted on its debt nine times; inflation has often risen to the double digits, even as high as 5000%, resulting in several large currency devaluations.

The economy of Bolivia is the 95th-largest economy in the world in nominal terms and the 87th-largest economy in terms of purchasing power parity. Bolivia is classified by the World Bank to be a lower middle income country. With a Human Development Index of 0.703, it is ranked 114th. In recent history, Bolivia has consistently led Latin America in measures of economic growth, fiscal stability and foreign reserves.
Economic interventionism, sometimes also called state interventionism, is an economic policy position favouring government intervention in the market process with the intention of correcting market failures and promoting the general welfare of the people. An economic intervention is an action taken by a government or international institution in a market economy in an effort to impact the economy beyond the basic regulation of fraud, enforcement of contracts, and provision of public goods and services. Economic intervention can be aimed at a variety of political or economic objectives, such as promoting economic growth, increasing employment, raising wages, raising or reducing prices, promoting income equality, managing the money supply and interest rates, increasing profits, or addressing market failures.

A foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment in the form of a controlling ownership in a business, in real estate or in productive assets such as factories in one country by an entity based in another country. It is thus distinguished from a foreign portfolio investment or foreign indirect investment by a notion of direct control.
Offshore investment is the keeping of money in a jurisdiction other than one's country of residence. Offshore jurisdictions are used to pay less tax in many countries by large and small-scale investors. Poorly regulated offshore domiciles have served historically as havens for tax evasion, money laundering, or to conceal or protect illegally acquired money from law enforcement in the investor's country. However, the modern, well-regulated offshore centres allow legitimate investors to take advantage of higher rates of return or lower rates of tax on that return offered by operating via such domiciles. The advantage to offshore investment is that such operations are both legal and less costly than those offered in the investor's country—or "onshore".

Since the colonial era, Mexico's economic history has been characterized by resource extraction, agriculture, and a relatively underdeveloped industrial sector. Economic elites in the colonial period were predominantly Spanish-born, active as transatlantic merchants and mine owners, and diversifying their investments with the landed estates. The largest population sector was indigenous subsistence farmers, which predominantly inhabited the center and south.
Under-capitalization refers to any situation where a business cannot acquire the funds they need. An under-capitalized business may be one that cannot afford current operational expenses due to a lack of capital, which can trigger bankruptcy, may be one that is over-exposed to risk, or may be one that is financially sound but does not have the funds required to expand to meet market demand.
Rate-of-return regulation is a system for setting the prices charged by government-regulated monopolies, such as public utilities. Its main premise is that monopolies must charge the same price that would ideally prevail in a perfectly competitive market, equal to the efficient costs of production, plus a market-determined rate of return on capital.

The Central Argentine Railway, referred to as CA below, was one of the Big Four broad gauge, 5 ft 6 in British companies that built and operated railway networks in Argentina. The company had been established in the 19th century, to serve the provinces of Santa Fe and Córdoba, in the east-central region of the country. It would later extend its operations to Buenos Aires, Tucumán, and Santiago del Estero. The railroad had a complicated relationship with its employees in the 1910s, and then it had a complicated relationship with the government of Argentina in the 1920s.

The nationalization of oil supplies refers to the process of confiscation of oil production operations and private property, generally for the purpose of obtaining more revenue from oil for oil-producing countries' governments. This process, which should not be confused with restrictions on crude oil exports, represents a significant turning point in the development of oil policy. Nationalization eliminates private business operations—in which private international companies control oil resources within oil-producing countries—and allows oil-producing countries to gain control of private property. Once these countries become the sole owners of these confiscated resources, they have to decide how to maximize the net present value of their known stock of oil in the ground. Several key implications can be observed as a result of oil nationalization. "On the home front, national oil companies are often torn between national expectations that they should 'carry the flag' and their own ambitions for commercial success, which might mean a degree of emancipation from the confines of a national agenda."

Railway privatisation in Argentina was a process which began in 1993 under the presidency of Carlos Menem, following a series of neoliberal economic reforms. This primarily consisted of breaking up the state-owned railway company Ferrocarriles Argentinos (FA) and allowing the former lines to be operated by private companies instead of the state. This policy was met with widespread criticism and proved catastrophic for the Argentine railways whose service worsened significantly in the years that followed, with entire lines closing and infrastructure deteriorating beyond repair. Privatisation was ultimately reversed in 2015 with the creation of Nuevos Ferrocarriles Argentinos.

In 1948, during President Juan Perón's first term of office, the seven British- and three French-owned railway companies then operating in Argentina, were purchased by the state. These companies, together with those that were already state-owned, where grouped, according to their track gauge and locality, into a total of six state-owned companies which later became divisions of the state-owned holding company Ferrocarriles Argentinos.

Foreign relations between the Argentine Republic and People's Republic of China has existed for decades. Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1945 as the Republic of China and again on March 19, 1972, with the PRC.

The forestry sector in Argentina has great potential. The geography of the country extends from north to south, encompassing 4,000 kilometres (2,500 mi). Its variety of climates, land quality, and reliable precipitation allow for the cultivation of different tree species at high growth rates. The climate varies and most areas are quite temperate. The country also enjoys short harvest periods for the most important species. This has allowed the industry to become more competitive and continue its high growth rates.

Green industrial policy (GIP) is strategic government policy that attempts to accelerate the development and growth of green industries to transition towards a low-carbon economy. Green industrial policy is necessary because green industries such as renewable energy and low-carbon public transportation infrastructure face high costs and many risks in terms of the market economy. Therefore, they need support from the public sector in the form of industrial policy until they become commercially viable. Natural scientists warn that immediate action must occur to lower greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change. Social scientists argue that the mitigation of climate change requires state intervention and governance reform. Thus, governments use GIP to address the economic, political, and environmental issues of climate change. GIP is conducive to sustainable economic, institutional, and technological transformation. It goes beyond the free market economic structure to address market failures and commitment problems that hinder sustainable investment. Effective GIP builds political support for carbon regulation, which is necessary to transition towards a low-carbon economy. Several governments use different types of GIP that lead to various outcomes.
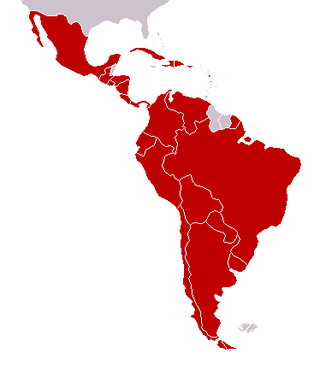
Latin America as a region has multiple nation-states, with varying levels of economic complexity. The Latin American economy is an export-based economy consisting of individual countries in the geographical regions of North America, Central America, South America, and the Caribbean. The socioeconomic patterns of what is now called Latin America were set in the colonial era when the region was controlled by the Spanish and Portuguese empires. Up until independence in the early nineteenth century, colonial Latin American regional economies thrived and worked things out. Many parts of the region had favorable factor endowments of deposits of precious metals, mainly silver, or tropical climatic conditions and locations near coasts that allowed for the development of cane sugar plantations. In the nineteenth century following independence, many economies of Latin America declined. In the late nineteenth century, much of Latin America was integrated into the world economy as an exporter of commodities. Foreign capital investment, construction of infrastructure, such as railroads, growth in the labor sector with immigration from abroad, strengthening of institutions, and expansion of education aided industrial growth and economic expansion. A number of regions have thriving economies, but "poverty and inequality have been deeply rooted in Latin American societies since the early colonial era."
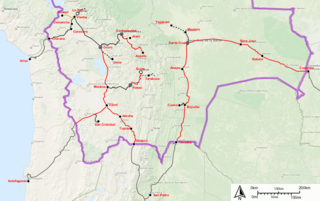
The history of rail transport in Bolivia began in the 1870s after almost three decades of failed efforts to build railroads to integrate the country, mining was the driving force for the construction of railways. The need to transport saltpeter to the coast triggered the first railway lines in Bolivia. It was the silver mining, however, that drove the construction of a railway from the Pacific coast to the high plateau during the nineteenth century. Later, at the beginning of the twentieth century, tin mining gave a new impetus to railway building, forming what is now known as the Andean or Western network. The eastern network, on the other hand, developed between the years 1940 and 1960 and is financed in exchange for oil through agreements with Argentina and Brazil. Bolivia being a landlocked country, the railways played a fundamental role and the history of its railroads is the history of the country's efforts to reach first ports on the Pacific coast and then the Atlantic.
Foreign direct investment by Great Britain into Argentina was attempted, initially with little success, from the early years after Argentina's independence in the 1820s. However, it grew to large proportions in the second half of the 19th century and remained so up to the Second World War, in association with greater political stability and favourable policies in Argentina. British ownership of large parts of Argentina's industry and railway system, and British control of the financial capital that backed Argentina's growing prosperity at that time, resulted in a strong relationship between the two countries, which is viewed by some as having contained elements of imperialism.
References
- ↑ Regalsky, Andres M. (October 1989). "Foreign Capital, Local Interests and Railway Development in Argentina: French Investments in Railways, 1900–1914*". Journal of Latin American Studies. 21 (3): 425–452. doi:10.1017/S0022216X00018502. ISSN 1469-767X. S2CID 145791632.
- ↑ Duncan, Julian S. (1937). "British Railways in Argentina". Political Science Quarterly. 52 (4): 559–582. doi:10.2307/2143973. JSTOR 2143973.
- 1 2 Lewis, Colin M. (2015-11-19). British Railways in Argentina 1857-1914: A Case Study of Foreign Investment. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 9781474241670.
- ↑ Bulmer-Thomas, Victor (2003-08-04). The Economic History of Latin America Since Independence. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521532747.