Related Research Articles

Chroma key compositing, or chroma keying, is a visual-effects and post-production technique for compositing (layering) two or more images or video streams together based on colour hues. The technique has been used in many fields to remove a background from the subject of a photo or video – particularly the newscasting, motion picture, and video game industries. A colour range in the foreground footage is made transparent, allowing separately filmed background footage or a static image to be inserted into the scene. The chroma keying technique is commonly used in video production and post-production. This technique is also referred to as colour keying, colour-separation overlay, or by various terms for specific colour-related variants such as green screen or blue screen; chroma keying can be done with backgrounds of any colour that are uniform and distinct, but green and blue backgrounds are more commonly used because they differ most distinctly in hue from any human skin colour. No part of the subject being filmed or photographed may duplicate the colour used as the backing, or the part may be erroneously identified as part of the backing.

William Friese-Greene was a prolific English inventor and professional photographer. He was known as a pioneer in the field of motion pictures, having devised a series of cameras between 1888–1891 and shot moving pictures with them in London. He went on to patent an early two-colour filming process in 1905. Wealth came with inventions in printing, including phototypesetting and a method of printing without ink, and from a chain of photographic studios. However, Friese-Greene spent all his money on inventing, went bankrupt three times, was jailed once, and died in poverty.
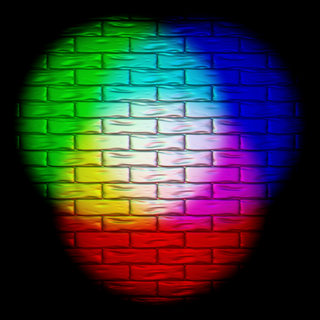
Additive color or additive mixing is a property of a color model that predicts the appearance of colors made by coincident component lights, i.e. the perceived color can be predicted by summing the numeric representations of the component colors. Modern formulations of Grassmann's laws describe the additivity in the color perception of light mixtures in terms of algebraic equations. Additive color predicts perception and not any sort of change in the photons of light themselves. These predictions are only applicable in the limited scope of color matching experiments where viewers match small patches of uniform color isolated against a gray or black background.

The Autochrome Lumière was an early color photography process patented in 1903 by the Lumière brothers in France and first marketed in 1907. Autochrome was an additive color "mosaic screen plate" process. It was the principal color photography process in use before the advent of subtractive color film in the mid-1930s.

Photographic paper is a paper coated with a light-sensitive chemical formula, like photographic film, used for making photographic prints. When photographic paper is exposed to light, it captures a latent image that is then developed to form a visible image; with most papers the image density from exposure can be sufficient to not require further development, aside from fixing and clearing, though latent exposure is also usually present. The light-sensitive layer of the paper is called the emulsion. The most common chemistry was based on silver halide but other alternatives have also been used.

Color photography is photography that uses media capable of capturing and reproducing colors. By contrast, black-and-white or gray-monochrome photography records only a single channel of luminance (brightness) and uses media capable only of showing shades of gray.

Spirit of Eden is the fourth studio album by English band Talk Talk, released in 1988 on Parlophone Records. The songs were written by singer Mark Hollis and producer Tim Friese-Greene and the album was compiled from a lengthy recording process at London's Wessex Studios between 1987 and 1988. Often working in darkness, the band recorded many hours of improvised performances that drew on elements of jazz, ambient, blues, classical music, and dub. These long-form recordings were then heavily edited and re-arranged into an album in mostly digital format.

Kinemacolor was the first successful colour motion picture process. Used commercially from 1909 to 1915, it was invented by George Albert Smith in 1906. It was a two-colour additive colour process, photographing a black-and-white film behind alternating red/orange and blue/green filters and projecting them through red and green filters. It was demonstrated several times in 1908 and first shown to the public in 1909. From 1909 on, the process was known and trademarked as Kinemacolor and was marketed by Charles Urban’s Natural Color Kinematograph Company, which sold Kinemacolor licences around the world.

The Magic Box is a 1951 British Technicolor biographical drama film directed by John Boulting. The film stars Robert Donat as William Friese-Greene, with numerous cameo appearances by performers such as Peter Ustinov and Laurence Olivier. It was produced by Ronald Neame and distributed by British Lion Film Corporation.
Claude Friese-Greene was a British-born cinema technician, filmmaker and cinematographer, most famous for his 1926 collection of films entitled The Open Road.

Color motion picture film refers both to unexposed color photographic film in a format suitable for use in a motion picture camera, and to finished motion picture film, ready for use in a projector, which bears images in color.
Timothy Alan Friese-Greene is an English musician and producer. He worked with the band Talk Talk from 1983 to their breakup in 1991. He currently releases solo albums under the name Heligoland. He is the grandson of filmmaker Claude Friese-Greene and great-grandson of photographer and inventor William Friese-Greene.

Dufaycolor is an early British additive colour photographic film process, introduced for motion picture use in 1932 and for still photography in 1935. It was derived from Louis Dufay's Dioptichrome plates, a glass-based product for colour still photography, introduced in France in 1909. Both Dioptichrome and Dufaycolor worked on the same principles as the Autochrome process, but achieved their results using a layer of tiny colour filter elements arrayed in a regular geometric pattern, unlike Autochrome's random array of coloured starch grains. The manufacture of Dufaycolor film ended in the late 1950s.
A field-sequential color system (FSC) is a color television system in which the primary color information is transmitted in successive images and which relies on the human vision system to fuse the successive images into a color picture. One field-sequential system was developed by Peter Goldmark for CBS, which was its sole user in commercial broadcasting. It was first demonstrated to the press on September 4, 1940, and first shown to the general public on January 12, 1950. The Federal Communications Commission adopted it on October 11, 1950, as the standard for color television in the United States, but it was later withdrawn.
The Lost World of Friese-Greene is a BBC documentary series produced in conjunction with the British Film Institute. Three one-hour episodes were broadcast on BBC Two in spring 2006.

The Friern Barnet Grammar School was a small private day school for boys located on Friern Barnet Road, North London.
Colour recovery is a process that restores lost colour to television programmes that were originally recorded on colour videotape but for which only black-and-white copies exist. This is not the same as colourisation, a process by which colour is artificially added to source material that was always black-and-white, or used to enhance poor-quality original sources. Colour recovery is a newer process and is fundamentally different from colourisation. Most of the work has been performed on PAL programmes, but the concept is not fundamentally restricted to that system.

Technicolor is a series of color motion picture processes, the first version dating back to 1916, and followed by improved versions over several decades.

Edward Raymond Turner was a pioneering British inventor and cinematographer. He produced the earliest known colour motion picture film footage.

The history of film technology traces the development of techniques for the recording, construction and presentation of motion pictures. When the film medium came about in the 19th century, there already was a centuries old tradition of screening moving images through shadow play and the magic lantern that were very popular with audiences in many parts of the world. Especially the magic lantern influenced much of the projection technology, exhibition practices and cultural implementation of film. Between 1825 and 1840, the relevant technologies of stroboscopic animation, photography and stereoscopy were introduced. For much of the rest of the century, many engineers and inventors tried to combine all these new technologies and the much older technique of projection to create a complete illusion or a complete documentation of reality. Colour photography was usually included in these ambitions and the introduction of the phonograph in 1877 seemed to promise the addition of synchronized sound recordings. Between 1887 and 1894, the first successful short cinematographic presentations were established. The biggest popular breakthrough of the technology came in 1895 with the first projected movies that lasted longer than 10 seconds. During the first years after this breakthrough, most motion pictures lasted about 50 seconds, lacked synchronized sound and natural colour, and were mainly exhibited as novelty attractions. In the first decades of the 20th century, movies grew much longer and the medium quickly developed into one of the most important tools of communication and entertainment. The breakthrough of synchronized sound occurred at the end of the 1920s and that of full color motion picture film in the 1930s. By the start of the 21st century, physical film stock was being replaced with digital film technologies at both ends of the production chain by digital image sensors and projectors.
References
- ↑ "The Open Road (1926)". British Film Institute . Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- ↑ "When Britain was a rose-tinted spectacle". The Guardian. 9 April 2006. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ↑ "Collections Search". British Film Institute . Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- 1 2 3 "Bathing beauties, Britain 1926 (in colour for the first time)" . The Independent. 1 April 2009. Archived from the original on 18 June 2022. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ↑ "Buy The Open Road". British Film Institute . Archived from the original on 21 October 2014. Retrieved 9 May 2020.