Related Research Articles
In the United States, a 401(k) plan is an employer-sponsored, defined-contribution, personal pension (savings) account, as defined in subsection 401(k) of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code. Periodic employee contributions come directly out of their paychecks, and may be matched by the employer. This pre-tax option is what makes 401(k) plans attractive to employees, and many employers offer this option to their (full-time) workers. 401(k) payable is a general ledger account that contains the amount of 401(k) plan pension payments that an employer has an obligation to remit to a pension plan administrator. This account is classified as a payroll liability, since the amount owed should be paid within one year.

Payroll taxes are taxes imposed on employers or employees, and are usually calculated as a percentage of the salaries that employers pay their employees. By law, some payroll taxes are the responsibility of the employee and others fall on the employer, but almost all economists agree that the true economic incidence of a payroll tax is unaffected by this distinction, and falls largely or entirely on workers in the form of lower wages. Because payroll taxes fall exclusively on wages and not on returns to financial or physical investments, payroll taxes may contribute to underinvestment in human capital, such as higher education.

The Federal Insurance Contributions Act is a United States federal payroll tax payable by both employees and employers to fund Social Security and Medicare—federal programs that provide benefits for retirees, people with disabilities, and children of deceased workers.
Superannuation in Australia, or "super", is a savings system for workplace pensions in retirement. It involves money earned by an employee being placed into an investment fund to be made legally available to members upon retirement. Employers make compulsory payments to these funds at a proportion of their employee's wages. From July 2024, the mandatory minimum "guarantee" contribution is 11.5%, rising to 12% from 2025. The superannuation guarantee was introduced by the Hawke government to promote self-funded retirement savings, reducing reliance on a publicly funded pension system. Legislation to support the introduction of the superannuation guarantee was passed by the Keating Government in 1992.
A severance package is pay and benefits that employees may be entitled to receive when they leave employment at a company unwilfully. In addition to their remaining regular pay, it may include some of the following:
Tax deduction at source (TDS) is an Indian withholding tax that is a means of collecting tax on income, dividends, or asset sales by requiring the payer to deduct tax due before paying the balance to the payee.
Truck Acts is the name given to legislation that outlaws truck systems, which are also known as "company store" systems, commonly leading to debt bondage. In England and Wales such laws date back to the 15th century.
India has a robust social security legislative framework governing social security, encompassing multiple labour laws and regulations. These laws govern various aspects of social security, particularly focusing on the welfare of the workforce. The primary objective of these measures is to foster sound industrial relations, cultivate a high-quality work environment, ensure legislative compliance, and mitigate risks such as accidents and health concerns. Moreover, social security initiatives aim to safeguard against social risks such as retirement, maternity, healthcare and unemployment while tax-funded social assistance aims to reduce inequalities and poverty. The Directive Principles of State Policy, enshrined in Part IV of the Indian Constitution reflects that India is a welfare state. Food security to all Indians are guaranteed under the National Food Security Act, 2013 where the government provides highly subsidised food grains or a food security allowance to economically vulnerable people. The system has since been universalised with the passing of The Code on Social Security, 2020. These cover most of the Indian population with social protection in various situations in their lives.
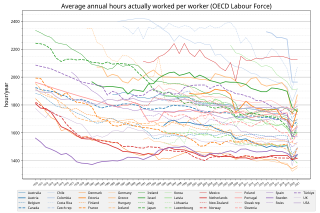
Labour in India refers to employment in the economy of India. In 2020, there were around 476.67 million workers in India, the second largest after China. Out of which, agriculture industry consist of 41.19%, industry sector consist of 26.18% and service sector consist 32.33% of total labour force. Of these over 94 percent work in unincorporated, unorganised enterprises ranging from pushcart vendors to home-based diamond and gem polishing operations. The organised sector includes workers employed by the government, state-owned enterprises and private sector enterprises. In 2008, the organised sector employed 27.5 million workers, of which 17.3 million worked for government or government owned entities.

The California Labor Code, more formally known as "the Labor Code", is a collection of civil law statutes for the State of California. The code is made up of statutes which govern the general obligations and rights of persons within the jurisdiction of the State of California. The stated goal of the Department of Industrial Relations is to promote and develop the welfare of the wage earners of California, to improve their working conditions and to advance their opportunities for profitable employment."

Indian labour law refers to law regulating labour in India. Traditionally, the Indian government at the federal and state levels has sought to ensure a high degree of protection for workers, but in practice, this differs due to the form of government and because labour is a subject in the concurrent list of the Indian Constitution. The Minimum Wages Act 1948 requires companies to pay the minimum wage set by the government alongside limiting working weeks to 40 hours. Overtime is strongly discouraged with the premium on overtime being 100% of the total wage. The Payment of Wages Act 1936 mandates the payment of wages on time on the last working day of every month via bank transfer or postal service. The Factories Act 1948 and the Shops and Establishment Act 1960 mandate 18 working days of fully paid vacation or earned leaves and 7 casual leaves each year to each employee, with an additional 7 fully paid sick days. The Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017 gives female employees of every company the right to take 6 months' worth of fully paid maternity leave. It also provides for 6 weeks worth of paid leaves in case of miscarriage or medical termination of pregnancy. The Employees' Provident Fund Organisation and the Employees' State Insurance, governed by statutory acts provide workers with necessary social security for retirement benefits and medical and unemployment benefits respectively. Workers entitled to be covered under the Employees' State Insurance are also entitled to 90 days worth of paid medical leaves. A contract of employment can always provide for more rights than the statutory minimum set rights. The Indian parliament passed four labour codes in the 2019 and 2020 sessions. These four codes will consolidate 44 existing labour laws. They are: The Industrial Relations Code 2020, The Code on Social Security 2020, The Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020 and The Code on Wages 2019. Despite having one of the longest working hours, India has one of the lowest workforce productivity levels in the world.
Wages and salaries are the remuneration paid or payable to employees for work performed on behalf of an employer or services provided. Normally, an employer is not permitted to withhold the wages or any part thereof, except as permitted or required by law. Employers are required by law to deduct from wages, commonly termed "withhold", income taxes, social contributions and for other purposes, which are then paid directly to tax authorities, social security authority, etc., on behalf of the employee. Garnishment is a court ordered withholding from wages to pay a debt.

Revenue and Customs Commissioners v Annabel's Ltd [2009] EWCA Civ 361 is a UK labour law case regarding the treatment of tips under the National Minimum Wage Act 1998. It led to the abolition of tips being considered part of wages for the purpose of assessing compliance with the national minimum wage.
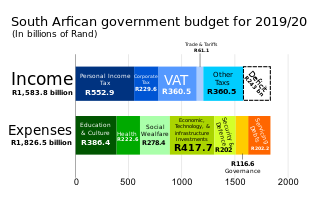
Taxation may involve payments to a minimum of two different levels of government: central government through SARS or to local government. Prior to 2001 the South African tax system was "source-based", where in income is taxed in the country where it originates. Since January 2001, the tax system was changed to "residence-based" wherein taxpayers residing in South Africa are taxed on their income irrespective of its source. Non residents are only subject to domestic taxes.
Mandatory tipping is a tip which is added automatically to the customer's bill, without the customer determining the amount or being asked. It may be implemented in several ways, such as applying a fixed percentage to all customer's bills, or to large groups, or on a customer-by-customer basis. Economists have varied opinions on the issue of mandatory tipping. Arguments against mandatory tipping include higher food price at the restaurant to make up for wages and loss of control of dining experience.
The Wage Earner Protection Program Act, is an act of the Parliament of Canada. It was part of a package of reforms to the insolvency law of Canada that were brought into force in 2008 and 2009 to compensate employees of companies made bankrupt or placed into receivership under the Bankruptcy and Insolvency Act. It was subsequently expanded in 2011 to cover employees who lose their jobs when their employer's attempt at restructuring subsequently ends in bankruptcy or receivership.
The Minimum Wages Act 1948 is an act of parliament concerning Indian labour law that sets the minimum wages that must be paid to skilled and unskilled workers.
The Inter-State Migrant Workmen Act, 1979 was an Act of the Parliament of India enacted to regulate the condition of service of inter-state labourers in Indian labour law. The Act's purpose was to protect workers whose services are requisitioned outside their native states in India. Whenever an employer faces shortage of skills among the locally available workers, the act created provisions to employ better skilled workers available outside the state. The act was replaced by the Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020
Profession tax is the tax levied and collected by the state governments in India. It is a direct tax. A person earning an income from salary or anyone practicing a profession such as chartered accountant, company secretary, cost accountant, Software Engineer, lawyer, doctor etc. are required to pay this professional tax. Different states have different rates and methods of collection. In India, profession tax is imposed every month. However, not all states impose this tax. The states which impose professional tax are Karnataka, Bihar, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Assam, Kerala, Meghalaya, Odisha, Tripura, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand and Sikkim, Mizoram. Business owners, working individuals, merchants and people carrying out various occupations come under the purview of this tax.
In Argentina, termination of employment occurs when an employer ends an employee's contract, either with or without a specific reason. As the requirements to proceed with a termination of employment and the consequences of the decision are regulated by each piece of legislation, there are differences depending on the country whose legislation is to be applied. This article refers exclusively to termination of employees who, having worked in Argentina, are governed by the laws of that country.
References
- ↑ "Payment of Gratuity in India" (PDF). Chief Labour Commissioner (Central).
- ↑ "Indian Hume Pipe Co. Ltd vs Their Workmen on 8 February, 1968". indiankanoon.org. Retrieved 22 January 2020.
- 1 2 3 "The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972" (PDF). Retrieved 22 January 2020.
- ↑ "Centre clears bill to double tax-free gratuity to Rs 20 lakh". The Economic Times. 12 September 2017. Retrieved 22 January 2020.