
Corporatocracy is an economic, political and judicial system controlled by corporations or corporate interests.
A plutocracy or plutarchy is a society that is ruled or controlled by people of great wealth or income. The first known use of the term in English dates from 1631. Unlike most political systems, plutocracy is not rooted in any established political philosophy.

Joseph Eugene Stiglitz is an American New Keynesian economist, a public policy analyst, and a full professor at Columbia University. He is a recipient of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences (2001) and the John Bates Clark Medal (1979). He is a former senior vice president and chief economist of the World Bank. He is also a former member and chairman of the Council of Economic Advisers. He is known for his support of Georgist public finance theory and for his critical view of the management of globalization, of laissez-faire economists, and of international institutions such as the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank.
The invisible hand is a metaphor used by the Scottish moral philosopher Adam Smith that describes the unintended greater social impacts brought about by individuals acting in their own self-interests. Smith originally mentioned the term in his work Theory of Moral Sentiments in 1759, but it has actually become known from his main work The Wealth of Nations, where the phrase is mentioned only once, in connection with import restrictions.
Rent-seeking is the act of growing one's existing wealth by manipulating the social or political environment without creating new wealth. Rent-seeking activities have negative effects on the rest of society. They result in reduced economic efficiency through misallocation of resources, reduced wealth creation, lost government revenue, heightened income inequality, risk of growing political bribery, and potential national decline.

There are wide varieties of economic inequality, most notably income inequality measured using the distribution of income and wealth inequality measured using the distribution of wealth. Besides economic inequality between countries or states, there are important types of economic inequality between different groups of people.

An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations, generally referred to by its shortened title The Wealth of Nations, is the magnum opus of the Scottish economist and moral philosopher Adam Smith. First published in 1776, the book offers one of the world's first collected descriptions of what builds nations' wealth, and is today a fundamental work in classical economics. By reflecting upon the economics at the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, the book touches upon such broad topics as the division of labour, productivity, and free markets.

The Great Transformation is a book by Karl Polanyi, a Hungarian-American political economist. First published in 1944 by Farrar & Rinehart, it deals with the social and political upheavals that took place in England during the rise of the market economy. Polanyi contends that the modern market economy and the modern nation-state should be understood not as discrete elements but as the single human invention he calls the "Market Society".

Sir Anthony Barnes Atkinson was a British economist, Centennial Professor at the London School of Economics, and senior research fellow of Nuffield College, Oxford.
Thomas Byrne Edsall is an American journalist and academic. He is best known for his weekly opinion column for The New York Times, for his 25 years covering national politics for the Washington Post and for his eight years at the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism where he was the holder of the Joseph Pulitzer II and Edith Pulitzer Moore Chair.
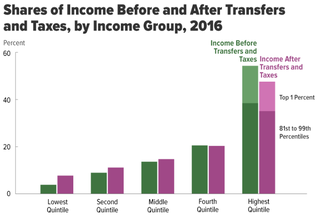
Income inequality in the United States is the extent to which income is distributed in differing amounts among the American population. It has fluctuated considerably since measurements began around 1915, moving in an arc between peaks in the 1920s and 2000s, with a 30-year period of relatively lower inequality between 1950 and 1980.

The Shock Doctrine: The Rise of Disaster Capitalism is a 2007 book by the Canadian author and social activist Naomi Klein. In the book, Klein argues that neoliberal free market policies have risen to prominence in some developed countries because of a deliberate strategy of "shock therapy". This centers on the exploitation of national crises to establish controversial and questionable policies, while citizens are too distracted to engage and develop an adequate response, and resist effectively. The book advances the idea that some man-made events, such as the Iraq War, were undertaken with the intention of pushing through such unpopular policies in their wake.

Wealth inequality in the United States is the unequal distribution of assets among residents of the United States. Wealth commonly includes the values of any homes, automobiles, personal valuables, businesses, savings, and investments, as well as any associated debts.
Socialism for the rich and capitalism for the poor is a classical political-economic argument asserting that, in advanced capitalist societies, state policies assure that more resources flow to the rich than to the poor, for example in the form of transfer payments.

Redistribution of income and wealth is the transfer of income and wealth from some individuals to others through a social mechanism such as taxation, welfare, public services, land reform, monetary policies, confiscation, divorce or tort law. The term typically refers to redistribution on an economy-wide basis rather than between selected individuals.

We are the 99% is a political slogan widely used and coined during the 2011 Occupy movement. The phrase directly refers to the income and wealth inequality in the United States, with a concentration of wealth among the top-earning 1%. It reflects an opinion that "the 99%" are paying the price for the mistakes of a tiny minority within the upper class.

Freefall: America, Free Markets, and the Sinking of the World Economy is a book on the causes and consequences of the Great Recession by economist and Nobel laureate Joseph E. Stiglitz, first published in 2010 by W. W. Norton & Company. While focusing on the roots of the financial crisis of 2007–2008 and the subsequent global economic slowdown, which he claims to find mainly in fiscal policy as conducted during the Bush presidency and decisions made by the Federal Reserve, Stiglitz also talks about the failure to cope with the recession during the months succeeding the Wall Street Crash of 2008. Finally, he sketches various schemes as to the possible future of the American economy, vigorously proposing a profound policy shift. In compliance with Stiglitz's general attitude towards economic policy, Freefall contains "proposals to tame the banking sector and to foster a more humanistic style of capitalism in the United States and abroad." According to an assessment written by Larry Elliott for The Guardian, the book "reeks of 'I told you so'." because during the years preceding the crisis, Stiglitz had "warned policy makers repeatedly that the United States was headed toward a deep, painful recession if pre-emptive interventions were not made."

Capital in the Twenty-First Century is a book written by French economist Thomas Piketty. It focuses on wealth and income inequality in Europe and the United States since the 18th century. It was initially published in French in August 2013; an English translation by Arthur Goldhammer followed in April 2014.

Winners Take All: The Elite Charade of Changing the World is a 2018 non-fiction book by American author Anand Giridharadas. It is his third book and was published by Alfred A. Knopf on August 28, 2018. The book appeared on The New York Times Best Seller list.
Progressive capitalism is an approach to capitalism that seeks to improve the current neoliberal American capitalism that emerged in 1980. Progressive capitalism aims to improve economic results through four defining beliefs, namely the vital role businesses play in the economy by creating jobs, fostering innovation, enabling voluntary exchange, and providing competitive goods and services; the recognition of the important role public goods, public institutions, public services and public infrastructure play in supporting businesses including: research, schools, health care, social insurance, taxation, labor law and regulation of markets; the need for the state to be involved in design and oversight of the playing field; and the integration of social justice, stewardship of natural resources and responsibility to all major stakeholders. It is being advocated by Ro Khanna and Joseph Stiglitz.














