
Bad Brains are an American rock band formed in Washington, D.C. in 1977. They are widely regarded as pioneers of hardcore punk, though the band's members have objected to the use of this term to describe their music. They are also an adept reggae band, while later recordings featured elements of other genres like funk, heavy metal, hip hop, and soul. Bad Brains are followers of the Rastafari movement.
A brain transplant or whole-body transplant is a procedure in which the brain of one organism is transplanted into the body of another organism. It is a procedure distinct from head transplantation, which involves transferring the entire head to a new body, as opposed to the brain only. Theoretically, a person with advanced organ failure could be given a new and functional body while keeping their own personality, memories, and consciousness through such a procedure. Neurosurgeon Robert J. White has grafted the head of a monkey onto the headless body of another monkey. EEG readings showed the brain was later functioning normally. Initially, it was thought to prove that the brain was an immunologically privileged organ, as the host's immune system did not attack it at first, but immunorejection caused the monkey to die after nine days. Brain transplants and similar concepts have also been explored in various forms of science fiction.
Foreign accent syndrome is a medical condition in which patients develop speech patterns that are perceived as a foreign accent that is different from their native accent, without having acquired it in the perceived accent's place of origin.

Vilayanur Subramanian Ramachandran is an Indian-American neuroscientist. Ramachandran is known for his wide-ranging experiments and theories in behavioral neurology, including the invention of the mirror box. He is a Distinguished Professor in UCSD's Department of Psychology, where he is the director of the Center for Brain and Cognition.
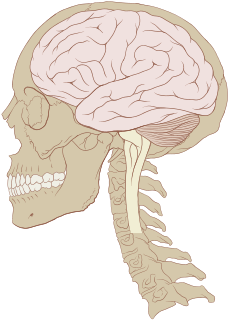
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the skull bones of the head.
Neuropsychiatry or Organic Psychiatry is a branch of medicine that deals with psychiatry as it relates to neurology, in an effort to understand and attribute behavior to the interaction of neurobiology and social psychology factors. Within neuropsychiatry, the mind is considered "as an emergent property of the brain", whereas other behavioral and neurological specialties might consider the two as separate entities. Neuropsychiatry preceded the current disciplines of psychiatry and neurology, which previously had common training, however, those disciplines have subsequently diverged and are typically practiced separately.
Caffeine-induced sleep disorder is a psychiatric disorder that results from overconsumption of the stimulant caffeine. Caffeine is one of the most widely consumed psychoactive drug, almost 90% of Americans in a survey consume some type of caffeine each day. "When caffeine is consumed immediately before bedtime or .... throughout the day, sleep onset may be delayed, total sleep time reduced, normal stages of sleep altered, and the quality of sleep decreased." Caffeine reduces slow-wave sleep in the early part of the sleep cycle and can reduce rapid eye movement sleep later in the cycle. Caffeine increases episodes of wakefulness, and high doses in the late evening can increase sleep onset latency. In elderly people, there is an association between use of medication containing caffeine and difficulty in falling asleep.

Daniel Gregory Amen is an American celebrity doctor who practices as a psychiatrist and brain disorder specialist as director of the Amen Clinics. He is a five-times New York Times best-selling author as of 2012.
Geriatric psychiatry, also known as geropsychiatry, psychogeriatrics or psychiatry of old age, is a branch of medicine and a subspecialty of psychiatry dealing with the study, prevention, and treatment of neurodegenerative, cognitive impairment, and mental disorders in people of old age. Geriatric psychiatry as a subspecialty has significant overlap with the specialties of geriatric medicine, behavioural neurology, neuropsychiatry, neurology, and general psychiatry. Geriatric psychiatry has become an official subspecialty of psychiatry with a defined curriculum of study and core competencies.

The Arrowsmith School is a private school in Toronto, Ontario, for children in Grades 1 to 12 with learning disabilities. The original Arrowsmith School was founded in Toronto in 1980 by Barbara Arrowsmith Young. A second location was opened in May 2005 in Peterborough, Ontario. The Eaton Arrowsmith School, which is modelled on the Toronto school and founded by Howard Eaton, was opened in 2005 in Vancouver, British Columbia with two further branches established in Canada and one in the United States between 2009 and 2014.

Is Google Making Us Stupid? What the Internet Is Doing to Our Brains! is a magazine article by technology writer Nicholas G. Carr, and is highly critical of the Internet's effect on cognition. It was published in the July/August 2008 edition of The Atlantic magazine as a six-page cover story. Carr's main argument is that the Internet might have detrimental effects on cognition that diminish the capacity for concentration and contemplation. Despite the title, the article is not specifically targeted at Google, but more at the cognitive impact of the Internet and World Wide Web. Carr expanded his argument in The Shallows: What the Internet Is Doing to Our Brains, a book published by W. W. Norton in June 2010.

The Black Dog Institute is a not-for-profit facility for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of mood disorders such as depression, anxiety and bipolar disorder. It was founded in 2002 by the UNSW School of Psychiatry Scientia Professor Gordon Parker and is based in Sydney, Australia.

The Master and His Emissary: The Divided Brain and the Making of the Western World is a 2009 book written by psychiatrist Iain McGilchrist that deals with the specialist hemispheric functioning of the brain. The differing world views of the right and left brain have, according to the author, shaped Western culture since the time of the ancient Greek philosopher Plato, and the growing conflict between these views has implications for the way the modern world is changing. In part, McGilchrist's book, which is the product of twenty years of research, reviews the evidence of previous related research and theories, and based on this and cultural evidence, the author arrives at his own conclusions.
Norman Doidge,, is a psychiatrist, psychoanalyst, and author of The Brain that Changes Itself and The Brain's Way of Healing.

The Tell-Tale Brain: A Neuroscientist's Quest for What Makes Us Human is a 2010 nonfiction book by V. S. Ramachandran that explores, from a neurological viewpoint, the uniqueness of human nature.

William W. Seeley is an American neurologist. He is an Associate Professor of Neurology at the UCSF Memory and Aging Center at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF). He leads the Selective Vulnerability Research Lab at UCSF. He is a 2011 MacArthur Fellow.
Perminder Sachdev is a neuropsychiatrist based in Australia. He is the Scientia Professor of Neuropsychiatry at the University of New South Wales (UNSW), Australia, the director of the Centre for Healthy Brain Ageing (CHeBA), UNSW, and the Clinical Director of the Neuropsychiatric Institute (NPI) at the Prince of Wales Hospital, Sydney, Australia.

Dick Ferdinand Swaab is a Dutch physician and neurobiologist. He is a professor of neurobiology at the University of Amsterdam and was until 2005 Director of the Netherlands Institute for Brain Research of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.
Charles L. Raison is an American psychiatrist and professor of psychiatry at the University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health as well as the Mary Sue and Mike Shannon Chair for Healthy Minds, Children & Families and Professor with the School of Human Ecology in Madison, Wisconsin.

Professor Richard Allan Bryant is an Australian medical scientist. He is Scientia Professor of Psychology at the University of New South Wales (UNSW) and Director of the UNSW Traumatic Stress Clinic, based at UNSW and Westmead Institute for Medical Research. His main areas of research are Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and Prolonged Grief Disorder. On 13 June 2016 he was appointed a Companion of the Order of Australia (AC), for eminent service to medical research in the field of psychotraumatology, as a psychologist and author, to the study of Indigenous mental health, as an advisor to a range of government and international organisations, and to professional societies.












