
Sikkim is a state in northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Koshi Province of Nepal in the west, and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Siliguri Corridor, which borders Bangladesh. Sikkim is the least populous and second-smallest among the Indian states. Situated in the Eastern Himalaya, Sikkim is notable for its biodiversity, including alpine and subtropical climates, as well as being a host to Kangchenjunga, the highest peak in India and third-highest on Earth. Sikkim's capital and largest city is Gangtok. Almost 35% of the state is covered by Khangchendzonga National Park – a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Gangtok is the capital and the most populous city of the Indian state of Sikkim. The seat of eponymous district, Gangtok is in the eastern Himalayan range, at an elevation of 1,650 m (5,410 ft). The city's population of 100,000 consists of the three Sikkimese ethnicities the Bhutias, Lepchas, Gorkhalis and also plainsmen from other states of India have settled here. Within the higher peaks of the Himalayas and with a year-round mild temperate climate, Gangtok is at the centre of Sikkim's tourism industry.

Teesta River is a 414 km (257 mi) long river that rises in the Pauhunri Mountain of eastern Himalayas, flows through the Indian states of Sikkim and West Bengal and subsequently enters Bangladesh through Rangpur division. In Bangladesh, it merges with Brahmaputra River which after meeting some other major rivers of the Bengal delta finally falls into the Bay of Bengal. It drains an area of 12,540 km2 (4,840 sq mi). In India, the Teesta flows through Mangan District, Gangtok District, Pakyong District, Kalimpong district, Darjeeling District, Jalpaiguri District, Cooch Behar districts and the cities of Rangpo, Jalpaiguri and Mekhliganj. In Bangladesh, it flows through Lalmonirhat District, Rangpur District, Kurigram District and Gaibandha District. It joins the Brahmaputra River at Phulchhari Upazila in Bangladesh. 305 km (190 mi) of the river lies in India and 109 km (68 mi) in Bangladesh. The Teesta is the largest river of Sikkim and second largest river of West Bengal after the Ganges.

Gangtok District is an administrative district of the Indian state of Sikkim. It was renamed in 2021 as a result of administrative reorganisation of the state, which also saw three subdivisions of the East Sikkim district spawned off as a separate Pakyong district.

North Sikkim is a district of the Indian state of Sikkim. Its district headquarters is Mangan. It is the seventh least populous district in the country.

The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) is a statutory body under the ownership of the Ministry of Defence of the Government of India. BRO develops and maintains road networks in India's border areas and friendly neighboring countries. This includes infrastructure operations in 19 states and three union territories and neighboring countries such as Afghanistan, Bhutan, Myanmar, Tajikistan and Sri Lanka. By 2022, BRO had constructed over 55,000 kilometres (34,000 mi) of roads, over 450 permanent bridges with a total length of over 44,000 metres (27 mi) length and 19 airfields in strategic locations. BRO is also tasked with maintaining this infrastructure including operations such as snow clearance.

Rangpo is a Municipal town in Pakyong district in the Indian state of Sikkim. The town borders West Bengal's Kalimpong district and is situated along the Teesta river and Rangpo River. It is the first town of Sikkim lying on National Highway 10 that links Siliguri to Gangtok. It is about 300 m above sea level with a sub-tropical climate. It is the 'Gateway to Sikkim' and all vehicles entering Sikkim have to stop at the Rangpo Police check-post. Foreign tourists require documents to enter Sikkim state and have to show them at the police check post.

Chungthang is a town in Mangan district in the Indian state of Sikkim. It is located just 28 km from Mangan town, the district headquarters. It is situated at the confluence of the Lachen and Lachung rivers, which combine to form the Teesta River. Located at a distance of 95 kilometres (59 mi) from the state capital Gangtok, the Indian Army has a major forward base with a medical centre in Chungthang.

Gurudongmar Lake is one of the highest lakes in the world and in India, at an elevation of 5,430 m (17,800 ft) according to the Government of Sikkim. It is located in the Great Himalayas in the Mangan District in Indian state of Sikkim, and considered sacred by Buddhists and Sikhs. The lake is named after Guru Padmasambhava—also known as Guru Rinpoche—founder of Tibetan Buddhism, who visited in the 8th century.

Singtam is a town which lies mostly in Gangtok District and partly in Pakyong District in the Indian state of Sikkim about 30 kilometres (19 mi) from the state capital Gangtok. The town lies on the banking of the rivers Teesta and Ranikhola, which join together just below the town. NH10 and NH510 meet in Singtam. The Indreni Bridge and Sherwani Bridge over the river Teesta are in the town. Singtam District Hospital, the district hospital of Pakyong District, lies at Golitar, Singtam.
The Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region is a Government of India ministry, established in September 2001, which functions as the nodal Department of the Central Government to deal with matters related to the socio-economic development of the eight States of Northeast India: Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura and Sikkim. It acts as a facilitator between the Central Ministries/ Departments and the State Governments of the North Eastern Region in the economic development including removal of infrastructural bottlenecks, provision of basic minimum services, creating an environment for private investment and to remove impediments to lasting peace and security in the North Eastern Region.

Sevoke is a small town near Siliguri in the Darjeeling district of West Bengal state of India near the border with Sikkim state. Situated in Dooars, Sevoke lies on the bank of River Teesta and has two bridges − namely Coronation Bridge and Sevoke Railway Bridge over it. Indian Army and Border Security Force camps are located in the area. The Mahananda Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in this area. National Highway NH10 passes through the town and connects Sevoke town to Gangtok and Siliguri. National Highway 17 originates from Sevoke near Coronation Bridge and terminates in Guwahati.

Mangan is a town and the headquarter of the district of Mangan District in the Indian state of Sikkim. The town lying near River Teesta is connected to the capital Gangtok by a metalled road. Mangan District is the largest district of Sikkim in terms of area. The town lies in the geographic south of the district. After the opening up of the district, Mangan has witnessed a spurt in its economy, mostly due to organic farming. The town opens up the Tibetan Plateau. Mangan also serves the towns of Lachung, Chungthang and Lachen in the far north. Owing to its elevation, the town enjoys a temperate climate.
The 2011 Sikkim earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 6.9 and was centered within the Kanchenjunga Conservation Area, near the border of Nepal and the Indian state of Sikkim, at on Sunday, 18 September. The earthquake was felt across northeastern India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and southern Tibet.

Pakyong Airport is a seasonal domestic airport serving Gangtok, the capital of Sikkim, India.
National Highway 10 is a national highway in North East India that connects Indo/Bangladesh border via Siliguri to Gangtok. It passes through the Indian states of West Bengal and Sikkim.The highway is being maintained by the National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL) from Rangpo to Ranipool in the state of Sikkim.
Rangpo railway station is an under-construction railway station lying on Sevoke-Rangpo Railway Line in Pakyong District of Sikkim. Its code is RNGPO. It will serve Rangpo city, and three districts of Sikkim, which are Pakyong District, Gangtok District and Mangan District. It is 38 km (24 mi) from the state capital of Gangtok and 21 km (13 mi) from Pakyong Airport. The station will consist of three platforms and four lines after completion. It is expected to be completed by December 2023.
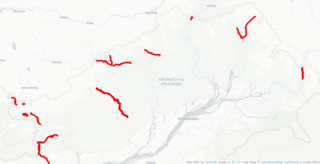
India–China Border Roads is a Government of India project for developing infrastructure along the Sino-Indian border by constructing strategic roads, including bridges and tunnels. The ICBR project is largely in response to Chinese infrastructure development along the borderlands with India.
Sivok-Rangpo Railway Line is a line currently under construction to connect the Indian states of West Bengal and Sikkim. It branches out from New Jalpaiguri–Alipurduar–Samuktala Road line at Sivok railway station, Sevoke Town near Siliguri in Darjeeling district and runs through villages and towns of Kalimpong district of West Bengal and terminates in Rangpo Railway Station in Rangpo, Pakyong District of Sikkim. In the second phase of construction, this line will be extended till Gangtok, the capital of Sikkim, and later to the Nathu La pass, along the border with Tibet. This railway line lies under Northeast Frontier Railway zone Alipurduar railway division. The total length of this railway line is 44.96 Kilometres.
On 4 October 2023, heavy rains caused the glacial South Lhonak lake in Sikkim, a state in northeastern India, to breach its banks, causing a glacial lake outburst flood. The flood reached the Teesta III Dam at Chungthang at midnight, before its gates could be opened, destroying the dam in minutes. Water levels downstream in the River Teesta rose by up to 20 feet (6.1 m), causing widespread damage.















