Related Research Articles

Fruitarianism is a diet that consists primarily of consuming fruits and possibly nuts and seeds, but without any animal products. Fruitarian diets are subject to criticism and health concerns.

Sir Frederick Grant Banting was a Canadian medical scientist, physician, painter, and Nobel laureate noted as the co-discoverer of insulin and its therapeutic potential.

Breakfast cereal is a breakfast food made from processed cereal grains. It is traditionally eaten as part of breakfast, or a snack food, primarily in Western societies.

Maximilian Oskar Bircher-Benner, M.D. was a Swiss physician and a pioneer nutritionist credited for popularizing muesli and raw food vegetarianism.

The Hospital for Sick Children (HSC), corporately branded as SickKids, is a major pediatric teaching hospital located on University Avenue in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Affiliated with the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Toronto, the hospital was ranked the top pediatric hospital in the world by Newsweek in 2021.

Baby food is any soft easily consumed food other than breastmilk or infant formula that is made specifically for human babies between six months and two years old. The food comes in many varieties and flavors that are purchased ready-made from producers, or it may be table food eaten by the family that has been mashed or otherwise broken down.

The Temerty Faculty of Medicine is the medical school of the University of Toronto. Founded in 1843, the faculty is based in Downtown Toronto and is one of Canada's oldest institutions of medical studies, being known for the discovery of insulin, stem cells and the site of the first single and double lung transplants in the world.

Pablum is a processed cereal for infants originally marketed and co-created by the Mead Johnson & Company in 1931. The product was developed at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto to combat infant malnutrition.
William Thornton Mustard was a Canadian physician and cardiac surgeon. In 1949, he was one of the first to perform open-heart surgery using a mechanical heart pump and biological lung on a dog at the Banting Institute. He developed two operations named for him: the "Mustard operation" in orthopedics used to help hip use in people with polio and the "Mustard cardiovascular procedure" used to help correct heart problems in "blue babies," which has saved thousands of children worldwide. He was also the first to treat ALCAPA with a left carotid artery end to end anastamosis in 1953.

William Boyd, FRCPath, was a Scottish-Canadian physician, pathologist, academic, and author known for his medical textbooks.

John Ross Robertson was a Canadian newspaper publisher, politician, and philanthropist in Toronto, Ontario.
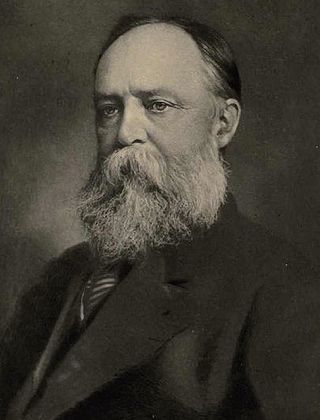
Sir Byron Edmund Walker, CVO was a Canadian banker. He was the president of the Canadian Bank of Commerce from 1907 to 1924, and a generous patron of the arts, helping to found and nurture many of Canada's cultural and educational institutions, including the University of Toronto, National Gallery of Canada, the Champlain Society, Appleby College, Art Gallery of Ontario and Royal Ontario Museum.
William Harding le Riche was a South African–born Canadian epidemiologist. He was Professor of Epidemiology (emeritus) at the University of Toronto.

Vesanto Melina is a Canadian Registered Dietitian and co-author of books that have become classics in the field of vegetarian, vegan, and raw foods nutrition, have sold almost a million copies in English and are in nine additional languages. She has presented talks and workshops on various aspects of vegetarian, vegan and raw foods and nutrition for dietitians, health professionals, and vegetarian associations in 17 American states and 9 Canadian provinces, and in 10 countries.

Stanley Howard Zlotkin, is a Canadian Professor of Paediatrics, Public Health Sciences and Nutritional Sciences at the University of Toronto.

Emmet Densmore was an American businessman, physician and natural hygiene advocate who promoted an early version of the Paleolithic diet.

Harry Campbell was a British physician, pathologist and writer.

Daniel Hartman Kress was a Canadian physician, anti-smoking activist, Seventh-day Adventist missionary and vegetarian.

Frank Wokes was an English biochemist, nutritionist and vegetarianism activist known for his research on the nutritional aspects of Vitamin B12 and Vitamin B12 deficiency. He was an early advocate of food fortification.
Alan Desmond is an Irish consultant gastroenterologist and writer known for his advocacy of plant-based nutrition.
References
- Toronto Globe and Mail, Feb 19, 1960