Related Research Articles

Dyslexia, previously known as word blindness, is a learning disability that affects either reading or writing. Different people are affected to different degrees. Problems may include difficulties in spelling words, reading quickly, writing words, "sounding out" words in the head, pronouncing words when reading aloud and understanding what one reads. Often these difficulties are first noticed at school. The difficulties are involuntary, and people with this disorder have a normal desire to learn. People with dyslexia have higher rates of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), developmental language disorders, and difficulties with numbers.
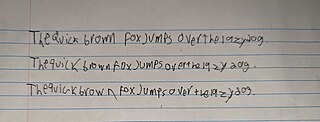
Dysgraphia is a neurological disorder and learning disability that concerns impairments in written expression, which affects the ability to write, primarily handwriting, but also coherence. It is a specific learning disability (SLD) as well as a transcription disability, meaning that it is a writing disorder associated with impaired handwriting, orthographic coding and finger sequencing. It often overlaps with other learning disabilities and neurodevelopmental disorders such as speech impairment, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or developmental coordination disorder (DCD).
A reading disability is a condition in which a person displays difficulty reading. Examples of reading disabilities include developmental dyslexia and alexia.

Dame Uta Frith is a German-British developmental psychologist and emeritus professor in cognitive development at the Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience at University College London (UCL). She pioneered much of the current research into autism and dyslexia. Her book Autism: Explaining the Enigma introduced the cognitive neuroscience of autism. She is credited with creating the Sally–Anne test along with fellow scientists Alan Leslie and Simon Baron-Cohen. Among students she has mentored are Tony Attwood, Maggie Snowling, Simon Baron-Cohen and Francesca Happé.

Management of dyslexia depends on a multitude of variables; there is no one specific strategy or set of strategies that will work for all who have dyslexia.
Zdeněk Matějček was a Czech child psychologist, researcher, and childcare reformer, who pioneered the study of the institutional conditions of raising children in an environment of psychological deprivation. He was a significant reformer of child care, emphasising the irreplaceable role of the family. He was known for studies of the effects on children of being held in prison camps during World War II, was a co-founder and the first chairman of an association that involved animals, such as dogs and horses, in child therapy, and was the principal organizer of a meeting of the International Association for Research in Learning Disabilities, held in Prague on October 2–5, 1989. He placed 93rd on Největší Čech.
Deep dyslexia is a form of dyslexia that disrupts reading processes. Deep dyslexia may occur as a result of a head injury, stroke, disease, or operation. This injury results in the occurrence of semantic errors during reading and the impairment of nonword reading.
Brian Lewis Butterworth FBA is emeritus professor of cognitive neuropsychology in the Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience at University College London, England. His research has ranged from speech errors and pauses, short-term memory deficits, reading and the dyslexias both in alphabetic scripts and Chinese, and mathematics and dyscalculia. He has also pioneered educational neuroscience, notably in the study of learners with special educational needs.
The history of dyslexia research spans from the late 1800s to the present.
Dyslexia is a reading disorder wherein an individual experiences trouble with reading. Individuals with dyslexia have normal levels of intelligence but can exhibit difficulties with spelling, reading fluency, pronunciation, "sounding out" words, writing out words, and reading comprehension. The neurological nature and underlying causes of dyslexia are an active area of research. However, some experts believe that the distinction of dyslexia as a separate reading disorder and therefore recognized disability is a topic of some controversy.
Dyslexia is a complex, lifelong disorder involving difficulty in learning to read or interpret words, letters and other symbols. Dyslexia does not affect general intelligence, but is often co-diagnosed with ADHD. There are at least three sub-types of dyslexia that have been recognized by researchers: orthographic, or surface dyslexia, phonological dyslexia and mixed dyslexia where individuals exhibit symptoms of both orthographic and phonological dyslexia. Studies have shown that dyslexia is genetic and can be passed down through families, but it is important to note that, although a genetic disorder, there is no specific locus in the brain for reading and writing. The human brain does have language centers, but written language is a cultural artifact, and a very complex one requiring brain regions designed to recognize and interpret written symbols as representations of language in rapid synchronization. The complexity of the system and the lack of genetic predisposition for it is one possible explanation for the difficulty in acquiring and understanding written language.

Dyslexia is a disorder characterized by problems with the visual notation of speech, which in most languages of European origin are problems with alphabet writing systems which have a phonetic construction. Examples of these issues can be problems speaking in full sentences, problems correctly articulating Rs and Ls as well as Ms and Ns, mixing up sounds in multi-syllabic words, problems of immature speech such as "wed and gween" instead of "red and green".
Dislecksia: The Movie is a documentary film. It was released in 2012 by Captured Time Productions, LLC, a production company based in Litchfield, Connecticut. Dislecksia is the company's seventh film. It is directed by Emmy Award-winning director Harvey Hubbell V, who is a dyslexic himself.
Gerald Samuel Lesser was an American psychologist who served on the faculty of Harvard University from 1963 until his retirement in 1998. Lesser was one of the chief advisers to the Children's Television Workshop in the development and content of the educational programming included in the children's television program Sesame Street. At Harvard, he was chair of the university's Human Development Program for 20 years, which focused on cross-cultural studies of child rearing, and studied the effects of media on young children. In 1974, he wrote Children and Television: Lessons From Sesame Street, which chronicled how Sesame Street was developed and put on the air. Lesser developed many of the research methods the CTW used throughout its history and for other TV shows. In 1968, before the debut of Sesame Street, he led a series of content seminars, an important part of the "CTW Model", which incorporated educational pedagogy and research into TV scripts and was used to develop other educational programs and organizations all over the world. He died in 2010, at the age of eighty-four.
Dr Hollis Scarborough is an American psychologist and literacy expert who is a senior scientist at Haskins Laboratories in New Haven, Connecticut. She has been a leading researcher in the area of reading acquisition since 1981, and has been involved with efforts to improve US national policy on the teaching of reading.
Julian George Charles "Joe" Elliott, FAcSS is a British academic and educational psychologist. He has been Principal of Collingwood College, Durham since 2011, and a Professor of Education at Durham University since 2004. He has caused controversy by describing dyslexia as a 'useless term' and a 'meaningless label'.

Dorothy Vera Margaret Bishop is a British psychologist specialising in developmental disorders specifically, developmental language impairments. She is Professor of Developmental Neuropsychology and Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellow in the Department of Experimental Psychology at the University of Oxford, where she has been since 1998. Bishop is Principal Investigator for the Oxford Study of Children's Communication Impairments (OSCCI). She is a supernumerary fellow of St John's College, Oxford.
Jagannath Prasad Das is an Indo-Canadian educational psychologist who specialized in educational psychology, intelligence and childhood development. Among his contributions to psychology are the PASS theory of intelligence and the Das-Naglieri Cognitive Assessment System. Das was the Director of the JP Das Developmental Disabilities Centre at the University of Alberta. He formally retired in 1996 and is currently Emeritus Director of the Centre on Developmental and Learning Disabilities and Emeritus Professor of Educational Psychology at the University of Alberta. He is a member of the Royal Society of Canada, was inducted into the Order of Canada and has an Honorary Doctorate degree from the University of Vigo in Spain.
Usha Claire Goswami is a researcher and professor of Cognitive Developmental Neuroscience at the University of Cambridge, a Fellow of St. John's College, Cambridge, and the director of the Centre for Neuroscience in Education, Downing Site. She obtained her Ph.D. in developmental psychology from the University of Oxford before becoming a professor of cognitive developmental psychology at the University College London. Goswami's work is primarily in educational neuroscience with major focuses on reading development and developmental dyslexia.
Margaret Byrd Rawson was an American educator, researcher and writer. She was an early leader in the field of dyslexia, conducting one of the longest-running studies of language disorders ever undertaken and publishing nine books on dyslexia.