
In computer network communications, the HTTP 404, 404 not found, 404, 404 error, page not found, or file not found error message is a hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) standard response code, to indicate that the browser was able to communicate with a given server, but the server could not find what was requested. The error may also be used when a server does not wish to disclose whether it has the requested information.
Spamdexing is the deliberate manipulation of search engine indexes. It involves a number of methods, such as link building and repeating unrelated phrases, to manipulate the relevance or prominence of resources indexed in a manner inconsistent with the purpose of the indexing system.

In computing, a hyperlink, or simply a link, is a digital reference to data that the user can follow or be guided to by clicking or tapping. A hyperlink points to a whole document or to a specific element within a document. Hypertext is text with hyperlinks. The text that is linked from is known as anchor text. A software system that is used for viewing and creating hypertext is a hypertext system, and to create a hyperlink is to hyperlink. A user following hyperlinks is said to navigate or browse the hypertext.
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of improving the quality and quantity of website traffic to a website or a web page from search engines. SEO targets unpaid traffic rather than direct traffic or paid traffic. Unpaid traffic may originate from different kinds of searches, including image search, video search, academic search, news search, and industry-specific vertical search engines.

Googlebot is the web crawler software used by Google that collects documents from the web to build a searchable index for the Google Search engine. Googlebot was created to function concurrently on thousands of machines in order to enhance its performance and adapt to the expanding size of the internet. This name is actually used to refer to two different types of web crawlers: a desktop crawler and a mobile crawler.
Inline linking is the use of a linked object, often an image, on one site by a web page belonging to a second site. One site is said to have an inline link to the other site where the object is located.
Pop-up ads or pop-ups are forms of online advertising on the World Wide Web. A pop-up is a graphical user interface (GUI) display area, usually a small window, that suddenly appears in the foreground of the visual interface. The pop-up window containing an advertisement is usually generated by JavaScript that uses cross-site scripting (XSS), sometimes with a secondary payload that uses Adobe Flash. They can also be generated by other vulnerabilities/security holes in browser security.
Doorway pages are web pages that are created for the deliberate manipulation of search engine indexes (spamdexing). A doorway page will affect the index of a search engine by inserting results for particular phrases while sending visitors to a different page. Doorway pages that redirect visitors without their knowledge use some form of cloaking. This usually falls under Black Hat SEO.
URL redirection, also called URL forwarding, is a World Wide Web technique for making a web page available under more than one URL address. When a web browser attempts to open a URL that has been redirected, a page with a different URL is opened. Similarly, domain redirection or domain forwarding is when all pages in a URL domain are redirected to a different domain, as when wikipedia.com and wikipedia.net are automatically redirected to wikipedia.org.
Affiliate marketing is a marketing arrangement in which affiliates receive a commission for each visit, signup or sale they generate for a merchant. This arrangement allows businesses to outsource part of the sales process. It is a form of performance-based marketing where the commission acts as an incentive for the affiliate; this commission is usually a percentage of the price of the product being sold, but can also be a flat rate per referral.
Google AdSense is a program run by Google through which website publishers in the Google Network of content sites serve text, images, video, or interactive media advertisements that are targeted to the site content and audience. These advertisements are administered, sorted, and maintained by Google. They can generate revenue on either a per-click or per-impression basis. Google beta-tested a cost-per-action service, but discontinued it in October 2008 in favor of a DoubleClick offering. In Q1 2014, Google earned US$3.4 billion, or 22% of total revenue, through Google AdSense. AdSense is a participant in the AdChoices program, so AdSense ads typically include the triangle-shaped AdChoices icon. This program also operates on HTTP cookies. In 2021, over 38.3 million websites use AdSense.

AVG AntiVirus is a line of antivirus software developed by AVG Technologies, a subsidiary of Avast, a part of Gen Digital. It is available for Windows, macOS and Android.
A paysite or pay site, in the adult entertainment industry, is a website that charges money to become a member and view its content, and often produces original adult content. They can be contrasted with "free-sites", which do not charge a membership fee. Most paysites offer "free tours" which allow non-members to view a limited number of short trailers. The vast majority of paysite memberships are bought by men. Some of the earliest paysites began by scanning images from pornographic magazines. The number of sites then grew until the market was saturated, and now many thousands of sites cater to every legal pornographic niche.
Christopher Boyd, also known by his online pseudonym Paperghost, is a computer security researcher.
A free hosted gallery (FHG) is a web page of sample content which is provided at no charge to affiliates of subscription websites (paysites). Affiliates promote these galleries to web surfers in order to drive web traffic to the paysite; every subscription sold generates a commission for the affiliate. The FHGs are usually hosted by the paysite and employ a simple URL-based system to distinguish between affiliates, so that commissions will be paid to the right party.

In HTTP, "Referer" is an optional HTTP header field that identifies the address of the web page, from which the resource has been requested. By checking the referrer, the server providing the new web page can see where the request originated.
Rogue security software is a form of malicious software and internet fraud that misleads users into believing there is a virus on their computer and aims to convince them to pay for a fake malware removal tool that actually installs malware on their computer. It is a form of scareware that manipulates users through fear, and a form of ransomware. Rogue security software has been a serious security threat in desktop computing since 2008. An early example that gained infamy was SpySheriff and its clones, such as Nava Shield.
A web widget is a web page or web application that is embedded as an element of a host web page but which is substantially independent of the host page, having limited or no interaction with the host. A web widget commonly provides users of the host page access to resources from another web site, content that the host page may be prevented from accessing itself by the browser's same-origin policy or the content provider's CORS policy. That content includes advertising, sponsored external links (Taboola), user comments (Disqus), social media buttons, news, and weather (AccuWeather). Some web widgets though serve as user-selectable customizations of the host page itself.

HTTP 301 is the HTTP response status code for 301 Moved Permanently. It is used for permanent redirecting, meaning that links or records returning this response should be updated. The new URL should be provided in the Location field, included with the response. The 301 redirect is considered a best practice for upgrading users from HTTP to HTTPS.
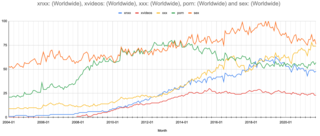
Internet pornography is any pornography that is accessible over the internet; primarily via websites, FTP connections, peer-to-peer file sharing, or Usenet newsgroups. The greater accessibility of the World Wide Web from the late 1990s led to an incremental growth of internet pornography, the use of which among adolescents and adults has since become increasingly popular.




