Related Research Articles

William Ronald Reid Jr. (Haida) was a Canadian artist whose works include jewelry, sculpture, screen-printing, and paintings. Producing over one thousand original works during his fifty-year career, Reid is regarded as one of the most significant Northwest Coast artists of the late twentieth century.

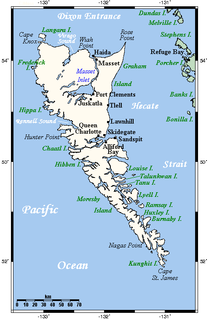
Haida are an indigenous group who have traditionally occupied Haida Gwaii, an archipelago just off the coast of British Columbia, Canada, for at least 12,500 years.
The Haida are one of the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast of North America. Their national territories lie along the west coast of Canada and include parts of south east Alaska. Haida mythology is an indigenous religion that can be described as a nature religion, drawing on the natural world, seasonal patterns, events and objects for questions that the Haida pantheon provides explanations for. Haida mythology is also considered animistic for the breadth of the Haida pantheon in imbuing daily events with Sǥā'na qeda's.
Ta'xet is the Haida god of violent death. He is considered to be one half of a duality; his counterpart is Tia, the goddess of peaceful death.

Haida Gwaii is an archipelago located between 55–125 km (34–78 mi) off the northern Pacific coast of Canada. The islands are separated from the mainland to the east by the shallow Hecate Strait. Queen Charlotte Sound lies to the south, with Vancouver Island beyond. To the north, the disputed Dixon Entrance separates Haida Gwaii from the Alexander Archipelago in the U.S. state of Alaska.

Kiidk'yaas, also known as the Golden Spruce, was a Sitka spruce tree that grew on the banks of the Yakoun River on the Haida Gwaii archipelago in British Columbia, Canada. It had a rare genetic mutation that caused its needles to be golden in colour. Kiidk'yaas was considered sacred by the Haida people.
Singa may refer to:

HMCS Haida is a Tribal-class destroyer that served in the Royal Canadian Navy (RCN) from 1943 to 1963, participating in World War II and the Korean War. She was named for the Haida people.
Haida manga is a contemporary style of Haida comics and print cartoons that explores the elements of both traditional North Pacific indigenous arts and narrative, while also adapting contemporary techniques of artistic design from the western portion of the North Pacific, namely the Japanese manga from which its name derives. Haida manga have so far been published in several countries including Japan, South Korea, China, Taiwan, Macao, France, and Canada.
Gwaii Haanas National Park Reserve, National Marine Conservation Area, and Haida Heritage Site, usually referred to simply as Gwaii Haanas, is located in southernmost Haida Gwaii, 130 kilometres off the mainland of British Columbia, Canada. Gwaii Haanas protects an archipelago of 138 islands, the largest being Moresby Island and the southernmost being Kunghit Island. "Gwaii Haanas" means "Islands of Beauty" in X̱aayda kíl, the language of the Haida people.

The Spirit of Haida Gwaii is a sculpture by British Columbia Haida artist Bill Reid (1920–1998). There are two versions of it: the black canoe and the jade canoe. The black canoe features on Canadian $20 bills issued between 2004 and 2012.

Haida is the language of the Haida people, spoken in the Haida Gwaii archipelago off the coast of Canada and on Prince of Wales Island in Alaska. An endangered language, Haida currently has 24 native speakers, though revitalization efforts are underway. At the time of the European arrival at Haida Gwaii in 1774, it is estimated that Haida speakers numbered about 15,000. Epidemics soon led to a drastic reduction in the Haida population, which became limited to three villages: Masset, Skidegate, and Hydaburg. Positive attitudes towards assimilation combined with the ban on speaking Haida in residential schools led to a sharp decline in the use of the Haida language among the Haida people, and today almost all ethnic Haida use English to communicate.
Sealand of the Pacific was a public aquarium in South Oak Bay at The Oak Bay Marina, near the city of Victoria, in British Columbia, Canada. It housed a number of orcas: Haida, Nootka, and Tilikum. In 1991, all three were involved in an incident in which a trainer, Keltie Byrne, was killed. The aquarium subsequently closed and sold its orcas to SeaWorld.

Many references to ravens exist in world lore and literature. Most depictions allude to the appearance and behavior of the wide-ranging common raven. Because of its black plumage, croaking call, and diet of carrion, the raven is often associated with loss and ill omen. Yet, its symbolism is complex. As a talking bird, the raven also represents prophecy and insight. Ravens in stories often act as psychopomps, connecting the material world with the world of spirits.
Skaay was a blind, crippled storyteller of the Haida village of Ttanuu born c. 1827 at Qquuna. Skaay could neither read nor write, but his stories of Haida mythology have survived in the form of written transcriptions taken down by John Swanton with the aide of Henry Moody over the winter of 1900. These transcriptions of myths are unique in the literature, both for their fidelity to the precise wordings of the mythteller, and for the survival of the pre-translation originals.

SG̱ang Gwaay Llanagaay, commonly known by its English name Ninstints, is a village site of the Haida people and part of the Gwaii Haanas National Park Reserve and Haida Heritage Site on Haida Gwaii on the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada.
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to Indigenous peoples in Canada, comprising the First Nations, Inuit and Métis peoples.
The 1862 Pacific Northwest smallpox epidemic was a smallpox outbreak that started in Victoria on Vancouver Island and spread among the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast and into the indigenous peoples of the Northwest Plateau, killing a large portion of natives from the Puget Sound region to Southeast Alaska. Two-thirds of British Columbia natives died—around 20,000 people. The death rate was highest in southeast Alaska and Haida Gwaii—over 70% among the Haida and 60% among the Tlingit. Almost all native nations along the coast, and many in the interior, were devastated, with a death rate of over 50% for the entire coast from Puget Sound to Sitka, Alaska, part of Russian America at the time. In some areas the native population fell by as much as 90%. The disease was controlled among colonists in 1862 but it continued to spread among natives through 1863.
References
- ↑ Gods, Goddesses, and Mythology: Vol. 4. Tarrytown, New York: Marshall Cavendish. 2005. p. 447. ISBN 978-0761475637.