
Owens Lake is a mostly dry lake in the Owens Valley on the eastern side of the Sierra Nevada in Inyo County, California. It is about 5 miles (8.0 km) south of Lone Pine. Unlike most dry lakes in the Basin and Range Province that have been dry for thousands of years, Owens held significant water until 1913, when much of the Owens River was diverted into the Los Angeles Aqueduct, causing Owens Lake to desiccate by 1926. A 2004 court order required the LADWP to reestablish a small flow from the river into the lake. As of 2013, it is the largest single source of dust pollution in the United States.

The St. Francis Dam was a concrete gravity dam located in San Francisquito Canyon in northern Los Angeles County, California that was built between 1924 and 1926 to serve the city of Los Angeles's growing water needs. It failed catastrophically in 1928 due to a defective soil foundation and design flaws, unleashing a flood that claimed the lives of at least 431 people. The collapse of the dam is considered to have been one of the worst American civil engineering disasters of the 20th century, and remains the 3rd-greatest loss of life in California's history, exceeded only by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake and fire and the Great Flood of 1862.

William Mulholland was an Irish American self-taught civil engineer who was responsible for building the infrastructure to provide a water supply that allowed Los Angeles to grow into the largest city in California. As the head of a predecessor to the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power, Mulholland designed and supervised the building of the Los Angeles Aqueduct, a 233-mile-long (375 km) system to move water from Owens Valley to the San Fernando Valley. The creation and operation of the aqueduct led to the disputes known as the California Water Wars. In March 1928, Mulholland's career came to an end when the St. Francis Dam failed just over 12 hours after he and his assistant gave it a safety inspection.

The Los Angeles Aqueduct system, comprising the Los Angeles Aqueduct and the Second Los Angeles Aqueduct, is a water conveyance system, built and operated by the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power. The Owens Valley aqueduct was designed and built by the city's water department, at the time named The Bureau of Los Angeles Aqueduct, under the supervision of the department's Chief Engineer William Mulholland. The system delivers water from the Owens River in the eastern Sierra Nevada mountains to Los Angeles.

The Governor Edmund G. Brown California Aqueduct is a system of canals, tunnels, and pipelines that conveys water collected from the Sierra Nevada Mountains and valleys of Northern and Central California to Southern California. Named after California Governor Edmund Gerald "Pat" Brown Sr., the over 400-mile (640 km) aqueduct is the principal feature of the California State Water Project.

Frederick Eaton, known as Fred Eaton, was a major individual in the transformation and expansion of Los Angeles in the latter 19th century through early 20th century, in California. Eaton was the political mastermind behind the early 20th century Los Angeles Aqueduct project, designed by William Mulholland.

The Colorado River Aqueduct, or CRA, is a 242 mi (389 km) water conveyance in Southern California in the United States, operated by the Metropolitan Water District of Southern California (MWD). The aqueduct impounds water from the Colorado River at Lake Havasu on the California-Arizona border, west across the Mojave and Colorado deserts to the east side of the Santa Ana Mountains. It is one of the primary sources of drinking water for Southern California.

The Owens River is a river in eastern California in the United States, approximately 183 miles (295 km) long. It drains into and through the Owens Valley, an arid basin between the eastern slope of the Sierra Nevada and the western faces of the Inyo and White Mountains. The river terminates at the endorheic Owens Lake south of Lone Pine, at the bottom of a 2,600 sq mi (6,700 km2) watershed.

Pyramid Lake is a reservoir formed by Pyramid Dam on Piru Creek in the eastern San Emigdio Mountains, near Castaic, Southern California. It is a part of the West Branch California Aqueduct, which is a part of the California State Water Project. Its water is fed by the system after being pumped up from the San Joaquin Valley and through the Tehachapi Mountains.

Parker Dam is a concrete arch-gravity dam that crosses the Colorado River 155 miles (249 km) downstream of Hoover Dam. Built between 1934 and 1938 by the Bureau of Reclamation, it is 320 feet (98 m) high, 235 feet (72 m) of which are below the riverbed (the deep excavation was necessary in order to reach the bedrock on which the foundation of the dam was built), making it the deepest dam in the world. The portion of the dam above the foundation stands 85 feet (25.9 m) tall, making it the only dam in the world that stands more underground than above ground. The dam's primary functions are to create a reservoir, and to generate hydroelectric power. The reservoir behind the dam is called Lake Havasu and can store 647,000 acre⋅ft (798,000,000 m3; 2.11×1011 US gal; 1.76×1011 imp gal). The dam straddles the Arizona-California state border at the narrows the river passes through between the Whipple Mountains in San Bernardino County, California and the Buckskin Mountains in La Paz County, Arizona.

Castaic Dam is an embankment dam in northwestern Los Angeles County, California, in the unincorporated area of Castaic. Although located on Castaic Creek, a major tributary of the Santa Clara River, Castaic Creek provides little of its water. The lake is the terminus of the West Branch of the California Aqueduct, part of the State Water Project. The dam was built by the California Department of Water Resources and construction was completed in 1973. The lake has a capacity of 325,000 acre-feet (401,000,000 m3) and stores drinking water for the western portion of the Greater Los Angeles Area.

The San Luis Reservoir is an artificial lake on San Luis Creek in the eastern slopes of the Diablo Range of Merced County, California, approximately 12 mi (19 km) west of Los Banos on State Route 152, which crosses Pacheco Pass and runs along its north shore. It is the fifth largest reservoir in California. The reservoir stores water taken from the San Joaquin-Sacramento River Delta. Water is pumped uphill into the reservoir from the O'Neill Forebay which is fed by the California Aqueduct and is released back into the forebay to continue downstream along the aqueduct as needed for farm irrigation and other uses. Depending on water levels, the reservoir is approximately nine miles (14 km) long from north to south at its longest point, and five miles (8 km) wide. At the eastern end of the reservoir is the San Luis Dam, the fourth largest embankment dam in the United States, which allows for a total capacity of 2,041,000 acre-feet (2,518,000 dam3). Pacheco State Park lies along its western shores.
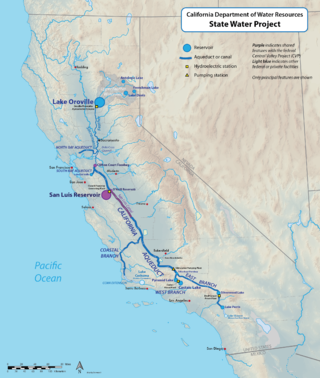
The California State Water Project, commonly known as the SWP, is a state water management project in the U.S. state of California under the supervision of the California Department of Water Resources. The SWP is one of the largest public water and power utilities in the world, providing drinking water for more than 27 million people and generating an average of 6,500 GWh of hydroelectricity annually. However, as it is the largest single consumer of power in the state itself, it has a net usage of 5,100 GWh.

Castaic Lake is a reservoir formed by Castaic Dam on Castaic Creek, in the Sierra Pelona Mountains of northwestern Los Angeles County, California, United States, near the town of Castaic.

Bouquet Reservoir is an artificial lake in the Angeles National Forest of Los Angeles County, California about 15 miles (24 km) west from Palmdale.

California's interconnected water system serves over 30 million people and irrigates over 5,680,000 acres (2,300,000 ha) of farmland. As the world's largest, most productive, and potentially most controversial water system, it manages over 40 million acre-feet (49 km3) of water per year.
Fish Springs is a set of springs in Inyo County, California.
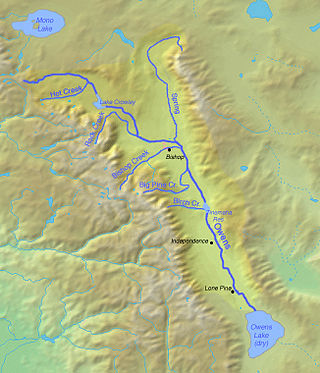
The Owens River course includes headwaters points near the Upper San Joaquin Watershed, reservoirs and diversion points, and the river's mouth at Owens Lake. The river drains the Crowley Lake Watershed of 1,900 sq mi (4,900 km2) and the north portion of the Owens Lake Watershed of 1,340 sq mi (3,500 km2).

The Chatsworth Nature Preserve (CNP) is a 1,325-acre (536 ha) open-space preserve located in the northwest corner of the San Fernando Valley in Los Angeles, California, United States. The preserve contains oak woodlands, savanna, riparian areas, grassland, vernal pools, and an Ecology Pond, all of which support more than 200 bird species and numerous mammals, amphibians and reptiles.




















