
Tocumwal is a town in the southern Riverina region of New South Wales, Australia, in the Berrigan Shire local government area. The town, 270 kilometres (170 mi) north of the city of Melbourne, lies on the northern bank of the Murray River, which forms the border with Victoria.

Wodonga railway station is located on the North East line in Victoria, Australia. It serves the city of Wodonga, and it opened on 25 June 2011.
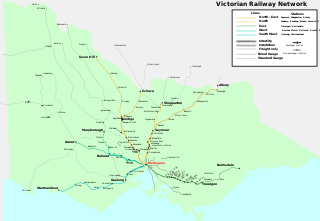
Rail transport in the Australian state of Victoria is provided by a number of railway operators who operate over the government-owned railway lines. The network consists of 2,357 km of Victorian broad gauge lines, and 1,912 km of standard gauge freight and interstate lines; the latter increasing with gauge conversion of the former. Historically, a few experimental 762 mm gauge lines were built, along with various private logging, mining and industrial railways. The rail network radiates from the state capital, Melbourne, with main interstate links to Sydney and to Adelaide, as well as major lines running to regional centres, upgraded as part of the Regional Fast Rail project.

Tallarook railway station is located on the North East line in Victoria, Australia. It serves the town of Tallarook, and it opened on 18 April 1872.

Seymour railway station is located on the North East line in Victoria, Australia. It serves the town of Seymour, and opened on 20 November 1872. The station is the terminus for V/Line's Seymour line services.

Benalla railway station is located on the North East line in Victoria, Australia. It serves the town of Benalla, and it opened on 18 August 1873.

Wangaratta railway station is located on the North East line in Victoria, Australia. It serves the town of the same name, and opened on 28 October 1873.
The North East railway line is a railway line in Victoria, Australia. The line runs from Southern Cross railway station on the western edge of the Melbourne central business district to Albury railway station in the border settlement of Albury–Wodonga, serving the cities of Wangaratta and Seymour, and smaller towns in northeastern Victoria. The line is owned by VicTrack, but the standard gauge section leased to, and maintained by, the Australian Rail Track Corporation.

Shepparton railway station is located on the Tocumwal line in Victoria, Australia. It serves the city of Shepparton, and it opened on 13 January 1880.
The Tocumwal railway line is a 1,600 mm gauge railway line in Victoria, Australia. The line runs between the border town of Tocumwal in New South Wales to Southern Cross, Melbourne. The line is utilised by various passenger and freight trains serving the northern suburbs of Melbourne and northern regions of Victoria.

Albury railway station is a heritage-listed railway station at Railway Place, Albury, New South Wales, Australia, adjacent to the border with Victoria, in Australia. It was designed under the direction of John Whitton and built from 1880 to 1881. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register in 1999.

The N Class are a class of diesel locomotives built by Clyde Engineering, Somerton for V/Line between 1985 and 1987.

The B class are a class of diesel locomotives built by Clyde Engineering, Granville for the Victorian Railways in 1952–1953. Ordered and operated by the Victorian Railways, they initiated the dieselisation of the system and saw use on both passenger and freight services, with many remaining in service today, both in preserved and revenue service. Some were rebuilt as the V/Line A class, while others have been scrapped.

The rail network of Melbourne, Australia, has a significant number of railway lines and yards serving freight traffic. Rail transport in Victoria is heavily focused on Melbourne, and, as a consequence, much of the state's rail freight passes through the metropolitan network.

Numurkah is a closed railway station on the Goulburn Valley railway line, which once served the town of the same name, in Victoria, Australia.

Strathmerton is a closed railway station on the Goulburn Valley railway in the town of Strathmerton, Victoria, Australia. The station opened at the same time as the railway from Shepparton to Cobram on 1 October 1888, with the line to Tocumwal not opening until 28 February 1905, ending at a temporary terminus on the south side of the Murray River, the line not completed into Tocumwal until July 1908. The junction between the lines was to the north of the station, facing down trains.
The 1922 Border Railways Acts, were Acts passed by the Parliaments of both Victoria and New South Wales, which authorised the construction of cross border railways in the Riverina region of Australia. Despite being located in New South Wales, the region was closer economically to Victoria and its railway network, operated by Victorian Railways. Another complication was that Victorian Railways used the 1,600 mm broad gauge, while the New South Wales Government Railways used 1,435 mm standard gauge.

The Toolamba–Echuca railway is a broad-gauge cross-country rail link between the towns of Toolamba and Echuca in Victoria, Australia. As a railway route to and from Echuca, it provides an alternative to the usual route via Bendigo. The line has not been used for passenger services since 1981, and goods movements on the line are intermittent, with it being booked out of service at times. The line was re-opened for goods traffic while there was track work on the Shepparton line between Seymour and Shepparton. On 3 October 2013 the line was re-opened after an upgrade.
The Cobram railway line was a short branch of the Tocumwal line in the north-eastern region of the Victorian railway network.

















