Related Research Articles

A telephone switchboard is a device used to connect circuits of telephones to establish telephone calls between users or other switchboards. The switchboard is an essential component of a manual telephone exchange, and is operated by switchboard operators who use electrical cords or switches to establish the connections.
Direct distance dialing (DDD) is a telecommunications service feature in North America by which a caller may, without operator assistance, call any other user outside the local calling area. Direct dialing by subscribers typically requires extra digits to be dialed as prefixes to the directory telephone number of the destination. International Direct Distance Dialing (IDDD) extends the system beyond the geographic boundaries of the North American Numbering Plan (NANP).
Telephony is the field of technology involving the development, application, and deployment of telecommunications services for the purpose of electronic transmission of voice, fax, or data, between distant parties. The history of telephony is intimately linked to the invention and development of the telephone.

An emergency telephone number is a number that allows a caller to contact local emergency services for assistance. The emergency number differs from country to country; it is typically a three-digit number so that it can be easily remembered and dialed quickly. Some countries have a different emergency number for each of the different emergency services; these often differ only by the last digit.

A blue box is an electronic device that produces tones used to generate the in-band signaling tones formerly used within the North American long-distance telephone network to send line status and called number information over voice circuits. During that period, charges associated with long-distance calling were commonplace and could be significant, depending on the time, duration and destination of the call. A blue box device allowed for circumventing these charges by enabling an illicit user, referred to as a "phreaker" to place long-distance calls, without using the network's user facilities, that would be billed to another number or dismissed entirely by the telecom company's billing system as an incomplete call. A number of similar "color boxes" were also created to control other aspects of the phone network.

The North American Numbering Plan (NANP) is a telephone numbering plan for twenty-five regions in twenty countries, primarily in North America and the Caribbean. This group is historically known as World Zone 1 and has the telephone country code 1. Some North American countries, most notably Mexico, do not participate with the NANP.
Subscriber trunk dialling (STD), also known as subscriber toll dialing, is a telephone numbering plan feature and telecommunications technology in the United Kingdom and various Commonwealth countries for the dialling of trunk calls by telephone subscribers without the assistance of switchboard operators.
Routing in the PSTN is the process of forwarding telephone calls between the constituent telephone networks that comprise the public switched telephone network (PSTN).

A business telephone system is a telephone system typically used in business environments, encompassing the range of technology from the key telephone system (KTS) to the private branch exchange (PBX).
The Traffic Service Position System (TSPS) was developed by Bell Labs in Columbus, Ohio to replace traditional cord switchboards. The first TSPS was deployed in Morristown, New Jersey in 1969 and used the Stored Program Control-1A CPU, "Piggyback" twistor memory and Insulated Gate Field Effect Transistor solid state memory devices similar to dynamic random access memory.
In telecommunications, a long-distance call (U.S.) or trunk call is a telephone call made to a location outside a defined local calling area. Long-distance calls are typically charged a higher billing rate than local calls. The term is not necessarily synonymous with placing calls to another telephone area code.
The Number Five Crossbar Switching System is a telephone switch for telephone exchanges designed by Bell Labs and manufactured by Western Electric starting in 1947. It was used in the Bell System principally as a Class 5 telephone switch in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) until the early 1990s, when it was replaced with electronic switching systems. Variants were used as combined Class 4 and Class 5 systems in rural areas, and as a TWX switch.
A class-4, or tandem, telephone switch is a U.S. telephone company central office telephone exchange used to interconnect local exchange carrier offices for long distance communications in the public switched telephone network.
The Number One Crossbar Switching System (1XB), was the primary technology for urban telephone exchanges served by the Bell System in the mid-20th century. Its switch fabric used the electromechanical crossbar switch to implement the topology of the panel switching system of the 1920s. The first No. 1 Crossbar was installed in the PResident-2 central office at Troy Avenue in Brooklyn, New York which became operational in February 1938.
The original North American area codes were established by the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1947, after the demonstration of regional Operator Toll Dialing during the World War II period. The program had the goal of speeding the connecting times for long-distance calling by eliminating intermediary telephone operators. Expanding this technology for national use required a comprehensive and universal, continent-wide telephone numbering plan.
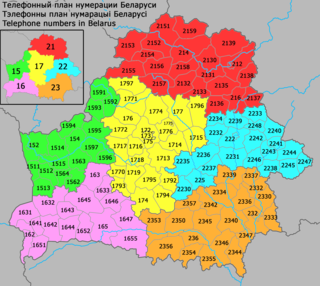
Belarus began using its own country code +375 in 1995, replacing the +7 international country code inherited from the Soviet Union. The local numbering plan was inherited from the Soviet Union and remains with few changes.

PSTN network topology is the switching network topology of a telephone network connected to the public switched telephone network (PSTN).

A telephone exchange, also known as a telephone switch or central office, is a crucial component in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or large enterprise telecommunications systems. It facilitates the interconnection of telephone subscriber lines or digital system virtual circuits, enabling telephone calls between subscribers.
In conventional landline telephony, a non-dialable toll point or toll station was a lone station or line serving a rural subscriber many miles from the nearest central office. As it had no home telephone exchange and therefore no local calling area, no customer could dial its number; all connections to it had to be obtained manually by the long distance operator.
Operator Toll Dialing was a telephone call routing and toll-switching system for the Bell System and the independent telephone companies in the United States and Canada that was developed in the 1940s. It automated the switching and billing of long-distance calls. The concept and technology evolved from the General Toll Switching Plan of 1929, and gained technical merits by the cutover of a new type of crossbar switching system in Philadelphia to commercial service in August 1943. This was the first system of its kind for automated forwarding of calls between toll switching centers, but it served customers only for regional toll traffic. It established initial experience with automatic toll switching for the design of a nationwide effort that was sometimes referred to as Nationwide Operator Toll Dialing.
References
- ↑ The Digital Future, 1979 Toll connecting trunk
- ↑ "4A Toll Switching System" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
 This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).