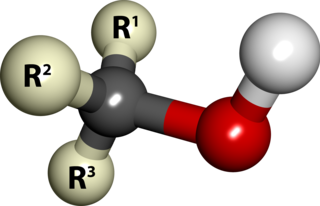
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol, which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula CnH2n+1OH. Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.

In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.

In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula R−O−R′, where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether". Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin.
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis.

In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)–. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula CH3C(O)CH3. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

In organic chemistry, a ketene is an organic compound of the form RR'C=C=O, where R and R' are two arbitrary monovalent chemical groups. The name may also refer to the specific compound ethenone H2C=C=O, the simplest ketene.

In organic chemistry, an aldehyde is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure R−CH=O. The functional group itself can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are common and play important roles in the technology and biological spheres.

In organic chemistry, a thiol, or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form R−SH, where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The −SH functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols, and the word is a blend of "thio-" with "alcohol".
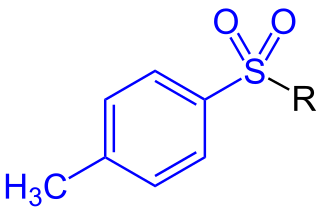
In organic chemistry, a toluenesulfonyl group is a univalent functional group with the chemical formula H3CC6H4SO2–. It consists of a tolyl group, H3CC6H4–, joined to a sulfonyl group, –SO2–, with the open valence on sulfur. This group is usually derived from the compound tosyl chloride, H3CC6H4SO2Cl, which forms esters and amides of toluenesulfonic acid, H3CC6H4SO2OH. The para orientation illustrated (p-toluenesulfonyl) is most common, and by convention tosyl without a prefix refers to the p-toluenesulfonyl group.

In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula R2NC(O)OR and structure >N−C(=O)−O−, which are formally derived from carbamic acid. The term includes organic compounds, formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion H2NCOO−.

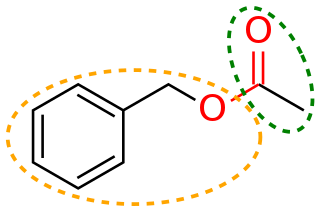
In organic chemistry, benzyl is the substituent or molecular fragment possessing the structure R−CH2−C6H5. Benzyl features a benzene ring attached to a methylene group group.

Organoborane or organoboron compounds are chemical compounds of boron and carbon that are organic derivatives of BH3, for example trialkyl boranes. Organoboron chemistry or organoborane chemistry is the chemistry of these compounds.
The Barton–McCombie deoxygenation is an organic reaction in which a hydroxy functional group in an organic compound is replaced by a hydrogen to give an alkyl group. It is named after British chemists Sir Derek Harold Richard Barton and Stuart W. McCombie.
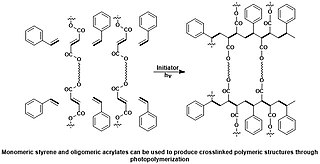
A photopolymer or light-activated resin is a polymer that changes its properties when exposed to light, often in the ultraviolet or visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These changes are often manifested structurally, for example hardening of the material occurs as a result of cross-linking when exposed to light. An example is shown below depicting a mixture of monomers, oligomers, and photoinitiators that conform into a hardened polymeric material through a process called curing.

Organozinc compounds in organic chemistry contain carbon (C) to zinc (Zn) chemical bonds. Organozinc chemistry is the science of organozinc compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis and reactions.
The Hofmann–Löffler reaction (also referred to as Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Freytag reaction, Löffler–Hofmann reaction, as well as Löffler's method) is an organic reaction in which a cyclic amine 2 (pyrrolidine or, in some cases, piperidine) is generated by thermal or photochemical decomposition of N-halogenated amine 1 in the presence of a strong acid (concentrated sulfuric acid or concentrated CF3CO2H). The Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag reaction proceeds via an intramolecular hydrogen atom transfer to a nitrogen-centered radical and is an example of a remote intramolecular free radical C–H functionalization.
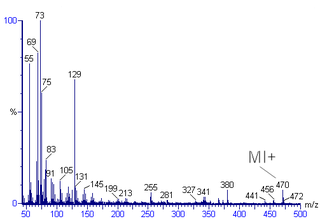
Mass spectral interpretation is the method employed to identify the chemical formula, characteristic fragment patterns and possible fragment ions from the mass spectra. Mass spectra is a plot of relative abundance against mass-to-charge ratio. It is commonly used for the identification of organic compounds from electron ionization mass spectrometry. Organic chemists obtain mass spectra of chemical compounds as part of structure elucidation and the analysis is part of many organic chemistry curricula.

In mass spectrometry, fragmentation is the dissociation of energetically unstable molecular ions formed from passing the molecules in the ionization chamber of a mass spectrometer. The fragments of a molecule cause a unique pattern in the mass spectrum. These reactions are well documented over the decades and fragmentation pattern is useful to determine the molar weight and structural information of the unknown molecule. Fragmentation that occurs in tandem mass spectrometry experiments has been a recent focus of research, because this data helps facilitate the identification of molecules.

The Shvo catalyst is an organoruthenium compound that catalyzes the hydrogenation of polar functional groups including aldehydes, ketones and imines. The compound is of academic interest as an early example of a catalyst for transfer hydrogenation that operates by an "outer sphere mechanism". Related derivatives are known where p-tolyl replaces some of the phenyl groups. Shvo's catalyst represents a subset of homogeneous hydrogenation catalysts that involves both metal and ligand in its mechanism.
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of photochemistry that uses single-electron transfer. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes, and semiconductors. While organic photoredox catalysts were dominant throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, soluble transition-metal complexes are more commonly used today.


















