
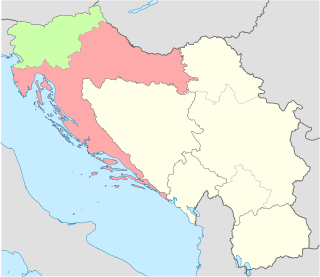
The Republic of Serbian Krajina or Serb Republic of Krajina, known as the Serbian Krajina or simply Krajina, was a self-proclaimed Serb proto-state, a territory within the newly independent Republic of Croatia, which it defied, and which was active during the Croatian War of Independence (1991–95). It was not recognized internationally. The name Krajina ("Frontier") was adopted from the historical Military Frontier of the Habsburg Monarchy and Austria-Hungary, which had a substantial Serb population and existed up to the late 19th century. The RSK government waged a war for ethnic Serb independence from Croatia and unification with FR Yugoslavia and Republika Srpska.
The Brioni Agreement or Brioni Declaration is a document signed by representatives of Slovenia, Croatia, and Yugoslavia under the political sponsorship of the European Community (EC) on the Brijuni Islands on 7 July 1991. The agreement sought to create an environment in which further negotiations on the future of Yugoslavia could take place. However, ultimately it isolated the federal prime minister Ante Marković in his efforts to preserve Yugoslavia, and effectively stopped any form of federal influence over Slovenia. This meant the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) would focus on combat in Croatia, creating a precedent of redrawing international borders and staking the EC's interest in resolving the Yugoslav crisis.

The Battle of Vukovar was an 87-day siege of Vukovar in eastern Croatia by the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA), supported by various paramilitary forces from Serbia, between August and November 1991. Before the Croatian War of Independence the Baroque town was a prosperous, mixed community of Croats, Serbs and other ethnic groups. As Yugoslavia began to break up, Serbia's President Slobodan Milošević and Croatia's President Franjo Tuđman began pursuing nationalist politics. In 1990, an armed insurrection was started by Croatian Serb militias, supported by the Serbian government and paramilitary groups, who seized control of Serb-populated areas of Croatia. The JNA began to intervene in favour of the rebellion, and conflict broke out in the eastern Croatian region of Slavonia in May 1991. In August, the JNA launched a full-scale attack against Croatian-held territory in eastern Slavonia, including Vukovar.

The Croatian War of Independence was fought from 1991 to 1995 between Croat forces loyal to the Government of Croatia—which had declared independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY)—and the Serb-controlled Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) and local Serb forces, with the JNA ending its combat operations in Croatia by 1992. In Croatia, the war is primarily referred to as the "Homeland War" and also as the "Greater-Serbian Aggression". In Serbian sources, "War in Croatia" and (rarely) "War in Krajina" are used.
The Vukovar massacre, also known as the Vukovar hospital massacre or the Ovčara massacre, was the killing of Croatian prisoners of war and civilians by Serb paramilitaries, to whom they had been turned over by the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA), at the Ovčara farm southeast of Vukovar on 20 November 1991, during the Croatian War of Independence. The massacre occurred shortly after Vukovar's capture by the JNA, Territorial Defence (TO), and paramilitaries from neighbouring Serbia. It was the largest massacre of the Croatian War of Independence.
Veljko Kadijević was a Serbian general of the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA). He was the Minister of Defence in the Yugoslav government from 1988 until his resignation in 1992, which made him de facto commander-in-chief of the JNA during the Ten-Day War in Slovenia and the initial stages of the Croatian War of Independence.

Veselin Šljivančanin is a former Montenegrin Serb officer in the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) who participated in the Battle of Vukovar and was subsequently convicted on a war crimes indictment by the International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia for his role in the Vukovar massacre. His prison sentence was changed twice, from five to seventeen to ten years. He has since been ordered released by the ICTY on time served and good behavior.

The Lovas killings involved the killing of 70 Croat civilian residents of the village of Lovas between 10–18 October 1991, during the Croatian War of Independence. The killings took place during and in the immediate aftermath of the occupation of the village by the Yugoslav People's Army supported by Croatian Serb forces and Dušan Silni paramilitaries on 10 October, two days after Croatia declared independence from Yugoslavia. The occupation occurred during the Battle of Vukovar, as the JNA sought to consolidate its control over the area surrounding the city of Vukovar. The killings and abuse of the civilian population continued until 18 October, when troops guarding a group of civilians forced them to walk into a minefield at gunpoint and then opened fire upon them.

The Škabrnja massacre was the killing of 62 Croatian civilians and five prisoners of war by Serbian Autonomous Oblast Krajina Territorial Defence troops and the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) in the villages of Škabrnja and Nadin northeast of Zadar on 18–19 November 1991, during the Croatian War of Independence. The massacre occurred shortly after an agreement to evacuate Zadar's JNA garrison following an increase in fighting between the Croatian National Guard and the JNA. Most of the killings were committed by SAO Krajina troops which followed the leading armoured JNA units fighting their way into Škabrnja on 18 November. During the initial attack, the attacking force employed a human shield of captured civilians forced to walk in front of armoured vehicles. Most of the civilian population fled the village and about 120–130 were captured by the JNA and detained in the village school and kindergarten. However, others who took shelter in basements were killed in or just outside their homes. A portion of those killed in the massacre were buried in a mass grave in Škabrnja, while dozens of bodies were turned over to Croatian authorities.
Blagoje Adžić was a Serbian politician who served as an acting Minister of Defence of the Yugoslavia government.
Dragoljub Ojdanić was the Chief of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of Yugoslavia and Minister of Defence of Yugoslavia. Odjanic commanded the Uzice corps during the Bosnian War and was tried and convicted of the deportation and forcible transfer of Kosovo Albanians during the Kosovo War by the ICTY.

The Velepromet camp was a detention facility established in the final days of the Battle of Vukovar during the Croatian War of Independence. The camp was set up by the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA), which shared control of the facility with Croatian Serb rebels. The facility, originally an industrial storage site, was located on the southern outskirts of the city of Vukovar, in close proximity to the JNA barracks. It consisted of eight warehouses surrounded by a wire fence, and was established on 16 November 1991, when the first detainees were brought there.
The 1992 Yugoslav People's Army column incident in Tuzla was an attack on the 92nd Motorized Brigade of the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) in the Bosnian city of Tuzla on 15 May 1992. The incident occurred at the road junction of Brčanska Malta. At least 92 soldiers of the JNA were killed and 33 wounded during the attacks, with estimates reaching 200 killed. What started off as a peaceful retreat by agreement with local authorities but ended in an ambush when Patriotic League, Green Berets and Bosniaks from local police attacked the column. It was a repeat of a similar incident that occurred in Sarajevo a week prior.

Serbia was involved in the Yugoslav Wars in the period between 1991 and 1999—the war in Slovenia, the war in Croatia, the war in Bosnia and the war in Kosovo. During this period from 1991 to 1997, Slobodan Milošević was the President of Serbia, Serbia was part of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, the International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia (ICTY) has established that Milošević was in control of Serb forces in Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia during the wars which were fought there from 1991 to 1995.

The Bijeljina massacre involved the killing of civilians by Serb paramilitary groups in Bijeljina on 1–2 April 1992 during the Bosnian War. The majority of those killed were Bosniaks. Members of other ethnicities were also killed, such as Serbs deemed disloyal by the local authorities. The killing was committed by a local paramilitary group known as Mirko's Chetniks and by the Serb Volunteer Guard, a Serbia-based paramilitary group led by Željko Ražnatović. The SDG were under the command of the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA), which was controlled by Serbian President Slobodan Milošević.

The Erdut killings were a series of murders of 37 Hungarian and Croat civilians in the village of Erdut, Croatia committed by Croatian Serb forces and Serb Volunteer Guard paramilitaries between November 1991 and June 1992, during the Croatian War of Independence. Twenty-two Hungarians and 15 Croats were killed. The first killings occurred on 10 November 1991, when twelve civilians died. Eight more were killed over the following several days. Five more civilians were killed on 10 December, and another seven on 16 December. Four others were killed on 21 February 1992 and the final one was killed on 3 June. The bodies of these victims were either buried in mass graves or thrown into nearby wells.

The Vance plan was a peace plan negotiated by the former United States Secretary of State Cyrus Vance in November 1991 during the Croatian War of Independence. At that time, Vance was the Special Envoy of the Secretary-General of the United Nations; he was assisted by United States diplomat Herbert Okun during the negotiations. The plan was designed to implement a ceasefire, demilitarize parts of Croatia that were under the control of Croatian Serbs and the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA), allow the return of refugees, and create favourable conditions for negotiations on a permanent political settlement of the conflict resulting from the breakup of Yugoslavia.
Vladimir Lazarević is a Serbian colonel general of the Third Army Corps, and later the commander of the Priština Corps of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. He was indicted by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia 2003 and was convicted in 2009 of command responsibility for war crimes against Kosovo Albanians during the Kosovo War.

The 1991 siege of Kijevo was one of the earliest conflicts in the Croatian War of Independence. The 9th Corps of the Yugoslav People's Army led by Colonel Ratko Mladić and the forces of the Serbian Autonomous Oblast (region) of Krajina under Knin police chief Milan Martić besieged the Croat-inhabited village of Kijevo in late April and early May 1991. The initial siege was lifted after negotiations that followed major protests in Split against the JNA.
The RAM Plan, also known as Operation RAM, Brana Plan, or Rampart-91, was a military plan developed over the course of 1990 and finalized in Belgrade, Serbia during a military strategy meeting in August 1991 by a group of senior Serb officers of the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) and experts from the JNA's Psychological Operations Department. Its purpose was organizing Serbs outside Serbia, consolidating control of the Serbian Democratic Parties (SDS), and preparing arms and ammunition in an effort of establishing a country where "all Serbs with their territories would live together in the same state." A separate group of undercover operatives and military officers was charged with the implementation of the plan. These people then undertook numerous actions during the Yugoslav Wars that were later described as ethnic cleansing, extermination and genocide.








