
The Dongfeng series, typically abbreviated as "DF missiles", are a family of short, medium, intermediate-range and intercontinental ballistic missiles operated by the Chinese People's Liberation Army Rocket Force.

The SY, and HY series were early anti-ship cruise missiles (ASCM) developed by the People's Republic of China from the Soviet P-15 Termit missile. They entered service in the late 1960s and remained the main ASCMs deployed by the People's Liberation Army Navy through the 1980s. The missiles were used by the PRC and export customers to develop land-attack missiles.

The Shahab-3 is a family of liquid-fueled ballistic missiles developed by Iran, under the IRGC, and based upon the North Korean Nodong-1/A and Nodong-B missiles. The Shahab-3 family has a range of 800-1,000 kilometres (620 mi). It was tested from 1998 to 2003 and added to the military arsenal on 7 July 2003, with an official unveiling by Ayatollah Khamenei on July 20. It has an estimated accuracy of about 2,500m CEP. According to the IAEA, Iran in the early 2000s may have explored various fuzing, arming and firing systems to make the Shahab-3 more capable of reliably delivering a nuclear warhead.

The People's Republic of China has developed and possesses weapons of mass destruction, including chemical and nuclear weapons. The first of China's nuclear weapons tests took place in 1964, and its first hydrogen bomb test occurred in 1966 at Lop Nur. Tests continued until 1996, when the country signed the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT), but did not ratify it. China acceded to the Biological Weapons Convention (BWC) in 1984 and ratified the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC) in 1997. Since 2020, China has been wielding a nuclear triad, alongside four other countries.
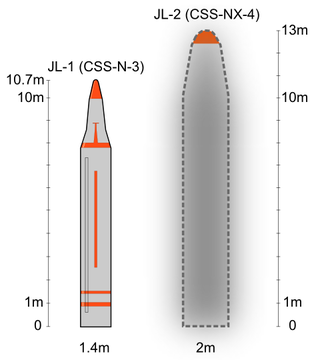
The JL-2 is a Chinese second-generation intercontinental-range submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) deployed on the People's Liberation Army Navy's (PLAN) Type 094 submarines. It succeeds the JL-1 SLBM deployed on the Type 092 submarine.
A theatre ballistic missile (TBM) is any ballistic missile with a range less than 3,500 kilometres (2,200 mi), used against targets "in-theatre". Its range is thus between that of tactical and intermediate-range ballistic missiles. The term is a relatively new one, encompassing the former categories of short-range ballistic missile and medium-range ballistic missile. Examples of this type of in-theatre missile are the Soviet RT-15, TR-1 Temp and American PGM-19 Jupiter missile, both from the 1960s.

The 9K120 Svir, 9K119 Refleks, 9K119M Refleks-M are laser beam riding, guided anti-tank missile systems developed in the Soviet Union. Both are designed to be fired from smoothbore 125 mm tank and anti-tank guns. The name Svir comes from the River Svir, while Refleks means reflex.

The Fateh-110, also known as NP-110 is an Iranian solid-fueled surface-to-surface ballistic missile produced by Iran's Aerospace Industries Organization since 2002. It is single-stage, road-mobile and can carry a high-explosive warhead of up to 500 kg. Four different versions, the Fateh-110A, 110B, 110D-1 and Fateh-E Mobin were developed with varying accuracy. The latest version, first shown to the public in August 2018 reportedly has a range of 300 km is reportedly more accurate than previous versions.

The Dong-Feng 15 is a short-range ballistic missile developed by China. The U.S. Department of Defense estimated in 2008 that China had 315–355 DF-15 missiles and 90–110 launchers.

The Dong Feng 31 is a third-generation long-range, road-mobile, three stage, solid-fuel rocket intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) in the Dongfeng missile series developed by the People's Republic of China. It is designed to carry a single 1-megaton thermonuclear weapon. It is a land-based variant of the submarine-launched JL-2. It is operated by the People's Liberation Army Rocket Force (PLARF). In 2009, the Chinese inventory was estimated as under 15 DF-31 missiles and under 15 DF-31A missiles. US Air Force National Air and Space Intelligence Center estimates that as of June 2017, five to ten Mod 1 and over fifteen Mod 2 launchers were operationally deployed.

The Agni missile is a family of medium to intercontinental range ballistic missiles developed by India, named after one of the five elements of nature. Agni missiles are long-range, nuclear weapons capable, surface-to-surface ballistic missiles. The first missile of the series, Agni-I was developed under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (lGMDP) and tested in 1989. After its success, the Agni missile programme was separated from the GMDP upon realizing its strategic importance. It was designated as a special programme in India's defence budget and provided adequate funds for subsequent development. As of November 2019, the missiles in the Agni series are being inducted into service. The family comprises the following:

The DF-3A is a Chinese liquid-fueled, single-stage, nuclear intermediate-range ballistic missile that entered service in 1971.

Saudi Arabia is not known to have a nuclear weapons program. From an official and public standpoint, Saudi Arabia has been an opponent of nuclear weapons in the Middle East, having signed the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, and is a member of the coalition of countries demanding a Nuclear-weapon-free zone in the Middle East. Studies of nuclear proliferation have not identified Saudi Arabia as a country of concern. Nuclear technology company IP3 International was formed in June 2016 to transfer nuclear technology from the United States to Saudi Arabia.
The Dongfeng-41 or DF-41 is a fourth-generation Chinese solid-fuelled road-mobile intercontinental ballistic missile operated by the People's Liberation Army Rocket Force. DF-41 is the fourth and the latest generation of the Dongfeng series strategic missiles developed by China. The missile was officially unveiled at the China National Day military parade on 1 October 2019.

Sejil, or Sejjil, is a family of Iranian solid-fueled medium range ballistic missiles. The Sejil are replacements for the Shahab liquid-fueled ballistic missiles. According to US Pentagon sources, the missile profile of the Sejil closely matches those of the Ashura, Ghadr-110 and the Samen.

The Hwasong-6 is a North Korean tactical ballistic missile. It is derived from the Hwasong-5, itself a derivative of the Soviet R-17 Elbrus. It carries the NATO reporting name Scud.

Ra'ad is an Iranian designed and built subsonic anti-ship cruise missile. The missile is a reverse engineered and upgraded variant of China's Silkworm anti-ship missile. The missile was developed by the state-run Iran Aviation Industries Organization (IAIO). Iran reportedly began full production of the Ra’ad in January 2004 and went into service in 2007. The missile is equipped for ground and ship-launched platforms.

The Dong-Feng 11 is a short-range ballistic missile developed by the People's Republic of China.

The Tondar is a hovercraft designed and manufactured by Iran. The Islamic Republic of Iran Navy is equipped with two variants of this craft, one for combat and one for transport missions, of which the Tondar is the combat type. General Ahmad Vahidi unveiled it in a ceremony in November 2012. According to the Fars news agency, the Tondar can be used with different types of weapons, including rockets, guns and can also launch UAVs.

The Tondar class consists of ten fast attack crafts operated by Navy of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps of Iran.

















