Related Research Articles

A geographic information system (GIS) consists of integrated computer hardware and software that store, manage, analyze, edit, output, and visualize geographic data. Much of this often happens within a spatial database, however, this is not essential to meet the definition of a GIS. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system also to include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, the body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations.

Geocaching is an outdoor recreational activity, in which participants use a Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver or mobile device and other navigational techniques to hide and seek containers, called geocaches or caches, at specific locations marked by coordinates all over the world. As of 2023, there are over 3 million active caches worldwide.

In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large-scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines, but historically using a variety of methods. Traditional definitions require a topographic map to show both natural and artificial features. A topographic survey is typically based upon a systematic observation and published as a map series, made up of two or more map sheets that combine to form the whole map. A topographic map series uses a common specification that includes the range of cartographic symbols employed, as well as a standard geodetic framework that defines the map projection, coordinate system, ellipsoid and geodetic datum. Official topographic maps also adopt a national grid referencing system.

DeLorme Publishing Company was a producer of personal satellite tracking, messaging, and navigation technology. In 2016, Garmin acquired the company's products and the DeLorme trademark. The company's main product, inReach, integrates GPS and satellite technologies. inReach provides the ability to send and receive text messages anywhere in the world by using the Iridium satellite constellation. By pairing with a smart phone, navigation is possible with access to free downloadable topographic maps and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) charts. On February 11, 2016, the company announced that it had been purchased by Garmin, a multinational producer of GPS products and services.

A geotagged photograph is a photograph which is associated with a geographic position by geotagging. Usually this is done by assigning at least a latitude and longitude to the image, and optionally elevation, compass bearing and other fields may also be included.

Geotagging, or GeoTagging, is the process of adding geographical identification metadata to various media such as a geotagged photograph or video, websites, SMS messages, QR Codes or RSS feeds and is a form of geospatial metadata. This data usually consists of latitude and longitude coordinates, though they can also include altitude, bearing, distance, accuracy data, and place names, and perhaps a time stamp.
Address geocoding, or simply geocoding, is the process of taking a text-based description of a location, such as an address or the name of a place, and returning geographic coordinates, frequently latitude/longitude pair, to identify a location on the Earth's surface. Reverse geocoding, on the other hand, converts geographic coordinates to a description of a location, usually the name of a place or an addressable location. Geocoding relies on a computer representation of address points, the street / road network, together with postal and administrative boundaries.

3D scanning is the process of analyzing a real-world object or environment to collect three dimensional data of its shape and possibly its appearance. The collected data can then be used to construct digital 3D models.

OpenStreetMap (OSM) is a free, open geographic database updated and maintained by a community of volunteers via open collaboration. Contributors collect data from surveys, trace from aerial imagery and also import from other freely licensed geodata sources. OpenStreetMap is freely licensed under the Open Database License and as a result commonly used to make electronic maps, inform turn-by-turn navigation, assist in humanitarian aid and data visualisation. OpenStreetMap uses its own topology to store geographical features which can then be exported into other GIS file formats. The OpenStreetMap website itself is an online map, geodata search engine and editor.

TomTom N.V. is a Dutch multinational developer and creator of location technology and consumer electronics. Founded in 1991 and headquartered in Amsterdam, TomTom released its first generation of satellite navigation devices to market in 2004. As of 2019 the company has over 4,500 employees worldwide and operations in 29 countries throughout Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Americas.

A point of interest (POI) is a specific point location that someone may find useful or interesting. An example is a point on the Earth representing the location of the Eiffel Tower, or a point on Mars representing the location of its highest mountain, Olympus Mons. Most consumers use the term when referring to hotels, campsites, fuel stations or any other categories used in modern automotive navigation systems.
Satellite navigation software or GNSS navigation software usually falls into one of the following two categories:
- Navigation with route calculation and directions from the software to the user of the route to take, based on a vector-based map, normally for motorized vehicles with some motorized forms added on as an afterthought.
- Navigation tracking, often with a map "picture" in the background, but showing where you have been, and allowing "routes" to be preprogrammed, giving a line you can follow on the screen. This type can also be used for geocaching.
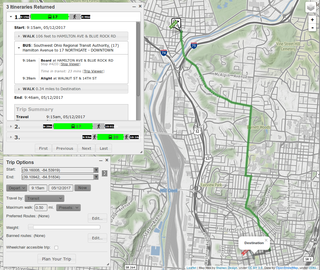
A journey planner, trip planner, or route planner is a specialized search engine used to find an optimal means of travelling between two or more given locations, sometimes using more than one transport mode. Searches may be optimized on different criteria, for example fastest, shortest, fewest changes, cheapest. They may be constrained, for example, to leave or arrive at a certain time, to avoid certain waypoints, etc. A single journey may use a sequence of several modes of transport, meaning the system may know about public transport services as well as transport networks for private transportation. Trip planning or journey planning is sometimes distinguished from route planning, which is typically thought of as using private modes of transportation such as cycling, driving, or walking, normally using a single mode at a time. Trip or journey planning, in contrast, would make use of at least one public transport mode which operates according to published schedules; given that public transport services only depart at specific times, an algorithm must therefore not only find a path to a destination, but seek to optimize it so as to minimize the waiting time incurred for each leg. In European Standards such as Transmodel, trip planning is used specifically to describe the planning of a route for a passenger, to avoid confusion with the completely separate process of planning the operational journeys to be made by public transport vehicles on which such trips are made.

A satellite navigation device, satnav device or satellite navigation receiver is a user equipment that uses one or more of several global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) to calculate the device's geographical position and provide navigational advice. Depending on the software used, the satnav device may display the position on a map, as geographic coordinates, or may offer routing directions.

Here Technologies is a Dutch multinational group specialized in mapping technologies, location data and related automotive services to individuals and companies. It is majority-owned by a consortium of German automotive companies and American semiconductor company Intel whilst other companies also own minority stakes. Its roots date back to U.S.-based Navteq in 1985, which was acquired by Finland-based Nokia in 2007. Here is currently based in The Netherlands.
The Ricoh 500SE digital compact camera is suitable for outdoor photography and networkability. Capability includes external information such as GPS position or barcode numbers within the image headers. External vendors sell hardware and software for workflows involving GPS positioning or barcode scanning. Most NMEA compliant bluetooth GPS receivers can be used with this camera through its built in bluetooth communication capability. The body is resistant to dust and water, making it robust for many environments.

Google Fusion Tables was a web service provided by Google for data management. Fusion tables was used for gathering, visualising and sharing data tables. Data are stored in multiple tables that Internet users can view and download.
In geographic information systems, toponym resolution is the relationship process between a toponym, i.e. the mention of a place, and an unambiguous spatial footprint of the same place.
Wikiloc is a website, launched in 2006, containing GPS trails and waypoints that members have uploaded. This mashup shows the routes in frames showing Google Maps. The service is also available in Google Earth. There are mobile apps for Android and iPhone. The product has more than 11M members, is offered in many languages and has more than 37.9M tracks of dozens of activities in many countries and territories. Wikiloc began as a worldwide online reference for hiking. Additionally, photographs on Wikiloc enabled automated content analysis to characterize the landscape in the Ebro Delta Natural Park, Spain.

Locus Map is a multi-functional Android navigation app. Primarily it is designed and used for leisure time outdoor activities like hiking, biking, or geocaching. The app is also used by professionals e.g. by S&R teams or for collecting geospatial data.
References
- 1 2 3 Lauer, Johannes; Zipf, Alexander (2010-05-11). Painho, Marco; Santos, Maribel Yasmina; Pundt, Hardy (eds.). A workflow for improving the availability of routable data (OSM) for logistics in agriculture - using data from Telematics-systems and community-based quality management (PDF). The 13th AGILE International Conference on Geographic Information Science. Guimarães, Portugal. ISBN 978-989-20-1953-6. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-10-28. Retrieved 2018-10-28.
- 1 2 "TopoFusion download page". TopoFusion. Archived from the original on 2007-01-07. Retrieved 2018-10-27.
- 1 2 "The Complete Route Planning Guide: Get out of the ether". BIKEPACKING LLC. 16 June 2016. Topofusion. Archived from the original on 2018-03-07. Retrieved 27 October 2018.
- ↑ Scott Morris. GPS Driven Trail Simulation and Network Production (PhD).
- ↑ Morris, S.; Morris, A.; Barnard, K. (2004-06-07). "Digital trail libraries". In Chen, Hsinchun; Wactlar, Howard; Chen, Ching-chih; Lim, Ee-Peng; Christel, Mike (eds.). Proceedings of the 2004 Joint ACM/IEEE Conference on Digital Libraries. JCDL '04 ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on Digital Libraries 2004. Tucson, Arizona, United States: IEEE. pp. 63−71. doi:10.1109/JCDL.2004.1336099. ISBN 1-58113-832-6. Archived from the original on 2018-10-29. Retrieved 2018-10-29.
- ↑ "TopoFusion Pro Revision History". TopoFusion. Archived from the original on 2018-10-29. Retrieved 2018-10-29.
- 1 2 3 "About TopoFusion". TopoFusion. Archived from the original on 2018-08-17. Retrieved 2018-10-27.
- ↑ Gardiner, Geoff (2009-12-31). "Gadget Guy – TopoFusion Pro" (PDF). The Dog House (11th ed.). susark9. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-10-28. Retrieved 2018-10-28.
- ↑ McNamara, Joel (10 Oct 2008). GPS for Dummies. John Wiley & Sons. p. 254. ISBN 978-0470156230.
- ↑ "Frequently Asked Questions". TopoFusion. Archived from the original on 2018-08-17. Retrieved 2018-10-27.
- ↑ McNamara, Joel (10 October 2008). Geocaching for Dummies. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118054383. TopoFusion.
- ↑ Hallo, Jeffrey C.; Manning, Robert E.; Valliere, William; Budruk, Megha (2005). "A Case Study Comparison of Visitor Self Reported and GPS Recorded Travel Routes" (PDF). In Bricker, Kelly (ed.). Proceedings of the 2004 Northeastern Recreation Research Symposium. Northeastern Recreation Research Symposium. Gen. Tech. Rep. NE-326. Newtown Square, PA: Northern Research Station, Forest Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture. pp. 174−176. doi:10.2737/NE-GTR-326. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-06-30. Retrieved 27 October 2018.
{{cite conference}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ↑ Erle, Schuyler; Gibson, Rich; Walsh, Jo (19 Jun 2005). Mapping Hacks: Tips & Tools for Electronic Cartography (1st ed.). O'Reilly Media. p. 34. ISBN 978-0596007034.