
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a method of gel electrophoresis used in biochemistry, molecular biology, genetics, and clinical chemistry to separate a mixed population of macromolecules such as DNA or proteins in a matrix of agarose, one of the two main components of agar. The proteins may be separated by charge and/or size, and the DNA and RNA fragments by length. Biomolecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the charged molecules through an agarose matrix, and the biomolecules are separated by size in the agarose gel matrix.

A rotaxane is a mechanically interlocked molecular architecture consisting of a dumbbell-shaped molecule which is threaded through a macrocycle. The two components of a rotaxane are kinetically trapped since the ends of the dumbbell are larger than the internal diameter of the ring and prevent dissociation (unthreading) of the components since this would require significant distortion of the covalent bonds.
DNA topoisomerases are enzymes that catalyze changes in the topological state of DNA, interconverting relaxed and supercoiled forms, linked (catenated) and unlinked species, and knotted and unknotted DNA. Topological issues in DNA arise due to the intertwined nature of its double-helical structure, which, for example, can lead to overwinding of the DNA duplex during DNA replication and transcription. If left unchanged, this torsion would eventually stop the DNA or RNA polymerases involved in these processes from continuing along the DNA helix. A second topological challenge results from the linking or tangling of DNA during replication. Left unresolved, links between replicated DNA will impede cell division. The DNA topoisomerases prevent and correct these types of topological problems. They do this by binding to DNA and cutting the sugar-phosphate backbone of either one or both of the DNA strands. This transient break allows the DNA to be untangled or unwound, and, at the end of these processes, the DNA backbone is resealed. Since the overall chemical composition and connectivity of the DNA do not change, the DNA substrate and product are chemical isomers, differing only in their topology.
Supramolecular chemistry refers to the branch of chemistry concerning chemical systems composed of a discrete number of molecules. The strength of the forces responsible for spatial organization of the system range from weak intermolecular forces, electrostatic charge, or hydrogen bonding to strong covalent bonding, provided that the electronic coupling strength remains small relative to the energy parameters of the component. While traditional chemistry concentrates on the covalent bond, supramolecular chemistry examines the weaker and reversible non-covalent interactions between molecules. These forces include hydrogen bonding, metal coordination, hydrophobic forces, van der Waals forces, pi–pi interactions and electrostatic effects.
A polycatenane is a chemical substance that, like polymers, is chemically constituted by a large number of units. These units are made up of concatenated rings into a chain-like structure.
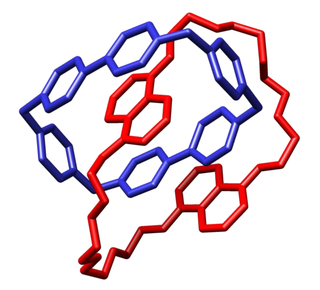
In macromolecular chemistry, a catenane is a mechanically interlocked molecular architecture consisting of two or more interlocked macrocycles, i.e. a molecule containing two or more intertwined rings. The interlocked rings cannot be separated without breaking the covalent bonds of the macrocycles. They are conceptually related to other mechanically interlocked molecular architectures, such as rotaxanes, molecular knots or molecular Borromean rings. Recently the terminology "mechanical bond" has been coined that describes the connection between the macrocycles of a catenane. Catenanes have been synthesised in two different ways: statistical synthesis and template-directed synthesis.
Interlock can refer to the following:

In chemistry, a molecular knot is a mechanically interlocked molecular architecture that is analogous to a macroscopic knot. Naturally-forming molecular knots are found in organic molecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins. It is not certain that naturally occurring knots are evolutionarily advantageous to nucleic acids or proteins, though knotting is thought to play a role in the structure, stability, and function of knotted biological molecules. The mechanism by which knots naturally form in molecules, and the mechanism by which a molecule is stabilized or improved by knotting, is ambiguous. The study of molecular knots involves the formation and applications of both naturally occurring and chemically synthesized molecular knots. Applying chemical topology and knot theory to molecular knots allows biologists to better understand the structures and synthesis of knotted organic molecules.

Molecular machines are a class of molecules typically described as an assembly of a discrete number of molecular components intended to produce mechanical movements in response to specific stimuli, mimicking macromolecular devices such as switches and motors. Naturally occurring or biological molecular machines are responsible for vital living processes such as DNA replication and ATP synthesis. Kinesins and ribosomes are examples of molecular machines, and they often take the form of multi-protein complexes. For the last several decades, scientists have attempted, with varying degrees of success, to miniaturize machines found in the macroscopic world. The first example of an artificial molecular machine (AMM) was reported in 1994, featuring a rotaxane with a ring and two different possible binding sites.

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA by James Watson.
Topoisomerase IV is one of two Type II topoisomerases in bacteria, the other being DNA gyrase. Like gyrase, topoisomerase IV is able to pass one double-strand of DNA through another double-strand of DNA, thereby changing the linking number of DNA by two in each enzymatic step. Both share a hetero-4-mer structure formed by a symmetric homodimer of A/B heterodimers, usually named ParC and ParE.

Jean-Pierre Sauvage is a French coordination chemist working at Strasbourg University. He graduated from the National School of Chemistry of Strasbourg, in 1967. He has specialized in supramolecular chemistry for which he has been awarded the 2016 Nobel Prize in Chemistry along with Sir J. Fraser Stoddart and Bernard L. Feringa.
In chemistry, mechanically interlocked molecular architectures (MIMAs) are molecules that are connected as a consequence of their topology. This connection of molecules is analogous to keys on a keychain loop. The keys are not directly connected to the keychain loop but they cannot be separated without breaking the loop. On the molecular level, the interlocked molecules cannot be separated without the breaking of the covalent bonds that comprise the conjoined molecules; this is referred to as a mechanical bond. Examples of mechanically interlocked molecular architectures include catenanes, rotaxanes, molecular knots, and molecular Borromean rings. Work in this area was recognized with the 2016 Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Bernard L. Feringa, Jean-Pierre Sauvage, and J. Fraser Stoddart.

Type II topoisomerases are topoisomerases that cut both strands of the DNA helix simultaneously in order to manage DNA tangles and supercoils. They use the hydrolysis of ATP, unlike Type I topoisomerase. In this process, these enzymes change the linking number of circular DNA by ±2. Topoisomerases are ubiquitous enzymes, found in all living organisms.

David Alan Leigh FRS FRSE FRSC is a British chemist, Royal Society Research Professor and, since 2014, the Sir Samuel Hall Chair of Chemistry in the Department of Chemistry at the University of Manchester. He was previously the Forbes Chair of Organic Chemistry at the University of Edinburgh (2001–2012) and Professor of Synthetic Chemistry at the University of Warwick (1998–2001).
A molecular switch is a molecule that can be reversibly shifted between two or more stable states. The molecules may be shifted between the states in response to environmental stimuli, such as changes in pH, light, temperature, an electric current, microenvironment, or in the presence of ions and other ligands. In some cases, a combination of stimuli is required. The oldest forms of synthetic molecular switches are pH indicators, which display distinct colors as a function of pH. Currently synthetic molecular switches are of interest in the field of nanotechnology for application in molecular computers or responsive drug delivery systems. Molecular switches are also important in biology because many biological functions are based on it, for instance allosteric regulation and vision. They are also one of the simplest examples of molecular machines.
Stephen Levene is an American biophysicist and professor of bioengineering, molecular biology, and physics at the University of Texas at Dallas.

Cyclobis(paraquat-p-phenylene) belongs to the class of cyclophanes, and consists of aromatic units connected by methylene bridges. It is able to incorporate small guest molecule and has played an important role in host–guest chemistry and supramolecular chemistry.

Polyrotaxane is a type of mechanically interlocked molecule consisting of strings and rings, in which multiple rings are threaded onto a molecular axle and prevented from dethreading by two bulky end groups. As oligomeric or polymeric species of rotaxanes, polyrotaxanes are also capable of converting energy input to molecular movements because the ring motions can be controlled by external stimulus. Polyrotaxanes have attracted much attention for decades, because they can help build functional molecular machines with complicated molecular structure.
When Topology Meets Chemistry: A Topological Look At Molecular Chirality is a book in chemical graph theory on the graph-theoretic analysis of chirality in molecular structures. It was written by Erica Flapan, based on a series of lectures she gave in 1996 at the Institut Henri Poincaré, and was published in 2000 by the Cambridge University Press and Mathematical Association of America as the first volume in their shared Outlooks book series.












