
A cyst, also traditionally known from Old English as a wen, is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac ; however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location.

A ganglion cyst is a fluid-filled bump associated with a joint or tendon sheath. It most often occurs at the back of the wrist, followed by the front of the wrist.

Cysticercosis is a tissue infection caused by the young form of the pork tapeworm. People may have few or no symptoms for years. In some cases, particularly in Asia, solid lumps of between one and two centimetres may develop under the skin. After months or years these lumps can become painful and swollen and then resolve. A specific form called neurocysticercosis, which affects the brain, can cause neurological symptoms. In developing countries this is one of the most common causes of seizures.

An epidermoid cyst or epidermal inclusion cyst is a benign cyst usually found on the skin. The cyst develops out of ectodermal tissue. Histologically, it is made of a thin layer of squamous epithelium.

Cherubism is a rare genetic disorder that causes prominence in the lower portion in the face. The name is derived from the temporary chubby-cheeked resemblance to putti, the chubby-faced infants featured in Renaissance paintings, which were often mistakenly described as cherubs.

Lymphangiomas are malformations of the lymphatic system characterized by lesions that are thin-walled cysts; these cysts can be macroscopic, as in a cystic hygroma, or microscopic. The lymphatic system is the network of vessels responsible for returning to the venous system excess fluid from tissues as well as the lymph nodes that filter this fluid for signs of pathogens. These malformations can occur at any age and may involve any part of the body, but 90% occur in children less than 2 years of age and involve the head and neck. These malformations are either congenital or acquired. Congenital lymphangiomas are often associated with chromosomal abnormalities such as Turner syndrome, although they can also exist in isolation. Lymphangiomas are commonly diagnosed before birth using fetal ultrasonography. Acquired lymphangiomas may result from trauma, inflammation, or lymphatic obstruction.

A dentigerous cyst, also known as a follicular cyst, is an epithelial-lined developmental cyst formed by accumulation of fluid between the reduced enamel epithelium and the crown of an unerupted tooth. It is formed when there is an alteration in the reduced enamel epithelium and encloses the crown of an unerupted tooth at the cemento-enamel junction. Fluid is accumulated between reduced enamel epithelium and the crown of an unerupted tooth.
“Lateral periodontal cysts (LPCs) are defined as non-keratinised and non-inflammatory developmental cysts located adjacent or lateral to the root of a vital tooth.” LPCs are a rare form of jaw cysts, with the same histopathological characteristics as gingival cysts of adults (GCA). Hence LPCs are regarded as the intraosseous form of the extraosseous GCA. They are commonly found along the lateral periodontium or within the bone between the roots of vital teeth, around mandibular canines and premolars. Standish and Shafer reported the first well-documented case of LPCs in 1958, followed by Holder and Kunkel in the same year although it was called a periodontal cyst. Since then, there has been more than 270 well-documented cases of LPCs in literature.

Calcifying odontogenic cyst (COC) is a rare developmental lesion that comes from odontogenic epithelium. It is also known as a calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor, which is a proliferation of odontogenic epithelium and scattered nest of ghost cells and calcifications that may form the lining of a cyst, or present as a solid mass.

A glandular odontogenic cyst (GOC) is a rare and usually benign odontogenic cyst developed at the odontogenic epithelium of the mandible or maxilla. Originally, the cyst was labeled as "sialo-odontogenic cyst" in 1987. However, the World Health Organization (WHO) decided to adopt the medical expression "glandular odontogenic cyst". Following the initial classification, only 60 medically documented cases were present in the population by 2003. GOC was established as its own biological growth after differentiation from other jaw cysts such as the "central mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC)", a popular type of neoplasm at the salivary glands. GOC is usually misdiagnosed with other lesions developed at the glandular and salivary gland due to the shared clinical signs. The presence of osteodentin supports the concept of an odontogenic pathway. This odontogenic cyst is commonly described to be a slow and aggressive development. The inclination of GOC to be large and multilocular is associated with a greater chance of remission. GOC is an infrequent manifestation with a 0.2% diagnosis in jaw lesion cases. Reported cases show that GOC mainly impacts the mandible and male individuals. The presentation of GOC at the maxilla has a very low rate of incidence. The GOC development is more common in adults in their fifth and sixth decades.

Syringocystadenoma papilliferum is a rare non-malignant adnexal neoplasm that develops from apocrine or eccrine sweat glands and can be identified histologically by cystic, papillary, and ductal invaginations into the dermis lined by double-layered outer cuboidal and luminal high columnar epithelium and connected to the epidermis.

Ovarian torsion (OT) or adnexal torsion is an abnormal condition where an ovary twists on its attachment to other structures, such that blood flow is decreased. Symptoms typically include pelvic pain on one side. While classically the pain is sudden in onset, this is not always the case. Other symptoms may include nausea. Complications may include infection, bleeding, or infertility.

A bone cyst or geode is a cyst that forms in bone.
Eruptive vellus hair cysts are small lesions that occur most often in the chest wall, abdomen and extremities, often with a crusted surface. EVHC may occur randomly, or it can be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait; sporadic cases usually appear at 4–18 years of age. The cysts appear similar clinically to steatocystoma multiplex, as well as acneiform eruptions and milia. Histopathology is the basis of diagnosis. Retinoids, surgery, and lasers are used as treatment modalities.

Mucinous cystadenoma is a benign cystic tumor lined by a mucinous epithelium. It is a type of cystic adenoma (cystadenoma).
Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the lung (MCACL) is a very rare malignant mucus-producing neoplasm arising from the uncontrolled growth of transformed epithelial cells originating in lung tissue.
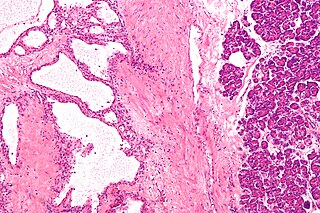
Pancreatic serous cystadenoma is a benign tumour of the pancreas. It is usually solitary and found in the body or tail of the pancreas, and may be associated with von Hippel–Lindau syndrome.
Odontogenic cyst are a group of jaw cysts that are formed from tissues involved in odontogenesis. Odontogenic cysts are closed sacs, and have a distinct membrane derived from rests of odontogenic epithelium. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. Intra-bony cysts are most common in the jaws, because the mandible and maxilla are the only bones with epithelial components. That odontogenic epithelium is critical in normal tooth development. However, epithelial rests may be the origin for the cyst lining later. Not all oral cysts are odontogenic cysts. For example, mucous cyst of the oral mucosa and nasolabial duct cyst are not of odontogenic origin.
Laryngeal cysts are cysts involving the larynx or more frequently supraglottic locations, such as epiglottis and vallecula. Usually they do not extend to the thyroid cartilage. They may be present congenitally or may develop eventually due to degenerative cause. They often interfere with phonation.
Tornwaldt's disease is the inflammation or abscess of the embryonic cyst of pharyngeal bursa. It is located in the midline of the posterior wall of the nasopharynx. It is covered anteriorly by mucosa in the adenoid mass. It is bounded posteriorly by longus muscle.













