| Torok Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Cretaceous | |
| Type | Formation |
| Location | |
| Region | Alaska |
| Country | United States |
The Torok Formation is a geologic formation in the National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska (NPR-A). It preserves fossils dating back to the Cretaceous period.
The Torok Formation lies 2,000–4,000 feet deeper than the Nanushuk Formation. They form a huge wedge of sediment deposited in a deep water basin and stretch from north of the Brooks Range beneath the Alaska North Slope to the adjacent offshore. It contains reservoirs in turbidite sandstone and is very porous. The USGS found large-scale folds and faults in the South of the formation and evidence, that the rocks have been heated to temperatures at which oil is converted to natural gas. [1]
The Torok Formation was deposited on the floor of the Alaska North Slope basin. [1]
In 2016, oil discovery in the deeper Torok Formation of more than 1.0 billion barrels (160 million cubic meters) was announced at Smith Bay, less than 1 mile (1.6 km) offshore from the NPR-A. [1] It came at the same time as ConocoPhillips discovery of Willow project, which at 300 million barrels (48 million cubic meters) is less than a third of the size. [1]
The Campos Basin is one of 12 coastal sedimentary basins of Brazil. It spans both onshore and offshore parts of the South Atlantic with the onshore part located near Rio de Janeiro. The basin originated in Neocomian stage of the Cretaceous period 145–130 million years ago during the breakup of Gondwana. It has a total area of about 115,000 square kilometres (44,000 sq mi), with the onshore portion small at only 500 square kilometres (190 sq mi).

North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid petroleum and natural gas, produced from petroleum reservoirs beneath the North Sea.

The Denver Basin, variously referred to as the Julesburg Basin, Denver-Julesburg Basin, or the D-J Basin, is a geologic structural basin centered in eastern Colorado in the United States, but extending into southeast Wyoming, western Nebraska, and western Kansas. It underlies the Denver-Aurora Metropolitan Area on the eastern side of the Rocky Mountains.
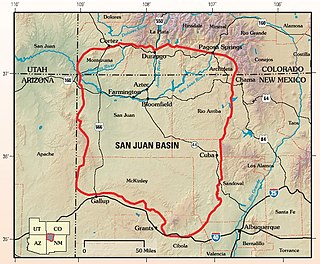
The San Juan Basin is a geologic structural basin located near the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. The basin covers 7,500 square miles and resides in northwestern New Mexico, southwestern Colorado, and parts of Utah and Arizona. Specifically, the basin occupies space in the San Juan, Rio Arriba, Sandoval, and McKinley counties in New Mexico, and La Plata and Archuleta counties in Colorado. The basin extends roughly 100 miles (160 km) N-S and 90 miles (140 km) E-W.
Umiat (OO-mee-yat) is an unincorporated community in North Slope Borough, Alaska, United States. It is located on the Colville River, 140 miles southwest of Deadhorse in the Arctic Circle. The town is not accessible by road or rail, only by air or river.
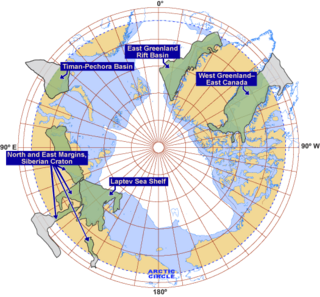
Exploration for petroleum in the Arctic is expensive and challenging both technically and logistically. In the offshore, sea ice can be a major factor. There have been many discoveries of oil and gas in the several Arctic basins that have seen extensive exploration over past decades but distance from existing infrastructure has often deterred development. Development and production operations in the Arctic offshore as a result of exploration have been limited, with the exception of the Barents and Norwegian seas. In Alaska, exploration subsequent to the discovery of the Prudhoe Bay oilfield has focussed on the onshore and shallow coastal waters.
Canada's early petroleum discoveries took place near population centres or along lines of penetration into the frontier.
Prudhoe Bay Oil Field is a large oil field on Alaska's North Slope. It is the largest oil field in North America, covering 213,543 acres (86,418 ha) and originally contained approximately 25 billion barrels (4.0×109 m3) of oil. The amount of recoverable oil in the field is more than double that of the next largest field in the United States by acreage (the East Texas Oil Field), while the largest by reserves is the Permian Basin (North America). The field was operated by BP; partners were ExxonMobil and ConocoPhillips until August 2019; when BP sold all its Alaska assets to Hilcorp.

The Sirte Basin is a late Mesozoic and Cenozoic triple junction continental rift along northern Africa that was initiated during the late Jurassic Period. It borders a relatively stable Paleozoic craton and cratonic sag basins along its southern margins. The province extends offshore into the Mediterranean Sea, with the northern boundary drawn at the 2,000 meter (m) bathymetric contour. It borders in the north on the Gulf of Sidra and extends south into northern Chad.

The Monterey Formation is an extensive Miocene oil-rich geological sedimentary formation in California, with outcrops of the formation in parts of the California Coast Ranges, Peninsular Ranges, and on some of California's off-shore islands. The type locality is near the city of Monterey, California. The Monterey Formation is the major source-rock for 37 to 38 billion barrels of oil in conventional traps such as sandstones. This is most of California's known oil resources. The Monterey has been extensively investigated and mapped for petroleum potential, and is of major importance for understanding the complex geological history of California. Its rocks are mostly highly siliceous strata that vary greatly in composition, stratigraphy, and tectono-stratigraphic history.
Safaniya Oil Field, operated and owned by Saudi Aramco, is the largest offshore oil field in the world. It is located about 265 kilometres (165 mi) north of the company headquarters in Dhahran on the coast of the Persian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Measuring 50 by 15 kilometres, the field has a producing capability of more than 1.2 million barrels per day.
The Weald Basin is a major topographic feature of the area that is now southern England and northern France from the Triassic to the Late Cretaceous. Its uplift in the Late Cretaceous marked the formation of the Wealden Anticline. The rock strata contain hydrocarbon deposits which have yielded coal, oil and gas.

The Vaca Muerta Formation, commonly known as Vaca Muerta, is a geologic formation of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous age, located in the Neuquén Basin in northern Patagonia, Argentina. It is well known as the host rock for major deposits of shale oil and shale gas.

The Bazhenov Formation or Bazhenov Shale is a geological stratum in the West Siberian basin. It was formed from sediment deposited in a deep-water sea in Tithonian–early Berriasian time. The sea covered more than one million square kilometers in the central basin area. Highly organic-rich siliceous shales were deposited during this time in anoxic conditions on the sea bottom. The sea was connected to the world's oceans and contains trace minerals derived from dissolved minerals and organic materials similar to sapropel sediments in the Black Sea.
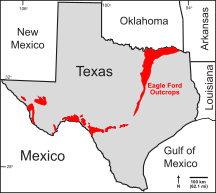
The Eagle Ford Group is a sedimentary rock formation deposited during the Cenomanian and Turonian ages of the Late Cretaceous over much of the modern-day state of Texas. The Eagle Ford is predominantly composed of organic matter-rich fossiliferous marine shales and marls with interbedded thin limestones. It derives its name from outcrops on the banks of the West Fork of the Trinity River near the old community of Eagle Ford, which is now a neighborhood within the city of Dallas. The Eagle Ford outcrop belt trends from the Oklahoma-Texas border southward to San Antonio, westward to the Rio Grande, Big Bend National Park, and the Quitman Mountains of West Texas. It also occurs in the subsurface of East Texas and South Texas, where it is the source rock for oil found in the Woodbine, Austin Chalk, and the Buda Limestone, and is produced unconventionally in South Texas and the "Eaglebine" play of East Texas.

The Nanushuk Formation or Nanushuk Group is a geologic group in Alaska in westernmost National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska (NPR-A). Petroleum in these rocks likely was generated beneath Western Alaska North Slope and migrated northeastward into NPR-A. The formation preserves fossils dating back to the Albian-Cenomanian ages of the Cretaceous period. Its thickness varies from about 1500 to about 250 meters. Underneath the Nanushuk lies the Torok Formation.

The West Siberian petroleum basin is the largest hydrocarbon basin in the world covering an area of about 2.2 million km2, and is also the largest oil and gas producing region in Russia.

Smith Bay is an estuary in the Beaufort Sea that supports a wide range of fish, birds, and marine mammals. It is located northeast of Point Barrow, Alaska. The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management recognizes the southeastern portion of Barrow Canyon, which covers some, but not all, of Smith Bay, as an Environmentally Important Area.

The Delta Field is located offshore from Nigeria on Oil Mining Leases (OML) 49 and 95. This is located within the Niger Delta Basin and sits in 12 feet of water. In 1965, the Delta 1 well was completed and the Delta Field opened in 1968 for production.

The Alaskan North Slope (ANS) is a foreland basin located on the northern edge of the Brooks Range. The Alaska North Slope is bounded on the north by the Beaufort Sea and runs from the Canadian border to the maritime boundary with Russia in the west. The western edge extends into the Chukchi Sea and Chukchi platform where the basin is at its widest. As the basin moves east it narrows towards the Canadian border. The basin is 1000 km long, 600 km at its widest, and covers a total area of 240,000 km2.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)