Verano azul is a well-known Spanish television drama series directed by Antonio Mercero. It was first broadcast on La Primera Cadena of Televisión Española from October 11, 1981 to February 14, 1982.

Fernando José Torres Sanz is a Spanish professional footballer who plays as a striker for J1 League club Sagan Tosu and the Spain national team.

Chiclana de la Frontera is a town and municipality in southwestern Spain, in the province of Cádiz, Andalucía, near the Gulf of Cádiz. It belongs to the association of municipalities of the Bay of Cádiz, the provincial capital of Cádiz, Jerez de la Frontera, San Fernando, El Puerto de Santa María, Puerto Real and Rota which form the third largest metropolitan area in Andalusia, behind Seville and Málaga, and the twelfth largest in Spain. It is located 20 kilometres south-east from Cádiz, and borders the municipalities of San Fernando and Puerto Real to the north. In 1877, the municipality's population was 11,677; in 2012, it was 81,473. It has a surface area is 203 square kilometres (78 sq mi) and a population density of 401 inhabitants / km². The average elevation is 11 metres (36 ft) above sea level. The economy depends largely upon modern industry, especially salt processing and tourism, and the municipality is known for its beaches such as the 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) long Playa de la Barrosa, hotels and golf courses in the resort of Novo Sancti Petri. The municipality contains the largest number of hotel beds in the Province of Cádiz and the Costa de la Luz. The town's newspaper, Chiclana Información, is distributed on Saturday mornings.

Sierra de Cádiz is a comarca province of Cádiz.
Rancho Bolsa del Potrero y Moro Cojo was a 6,916-acre (27.99 km2) Mexican land grant in the northern Salinas Valley, in present-day Monterey County, California. It was given in 1822 by Governor Pablo Vicente de Solá to Joaquín de la Torre.
Rancho Arroyo Seco was a 16,523-acre (66.87 km2) Mexican land grant in the Salinas Valley, in present-day Monterey County, California. It was given in 1840 by Governor Juan B. Alvarado to Joaquín de la Torre.
Torre de Santa María is a municipality located in the province of Cáceres and autonomous community of Extremadura, Spain. The municipality covers an area of 19.07 square kilometres (7.36 sq mi) and as of 2011 had a population of 642 people.

Hotel Sevilla is a historic hotel in Algeciras, Spain. Its construction took place between 1922 and 1925 by the Madrid-based architect Emilio Antón. It is built in the neo-baroque style, with four floors. The balconies and balusters contain decorative floral motifs.

The Chapel of the Charity (Spanish: Capilla de la Caridad is a Roman Catholic chapel in Villa Nueva, Algeciras, Spain.

Capilla del Cristo de la Alameda is a chapel in Algeciras, Spain. It was built in 1776 at the initiative of the priest Domingo Perez. The building was then situated along one of Algeciras's main streets of the time, Calle Alameda, and was attended by many sailors entering the port. In 1931 the church was assaulted and in subsequent years was converted into a storehouse and then an auto repair shop until the late 1990s when the city recovered it and it became the headquarters of the Municipal Museum of Sacred Art. The chapel consists of a single room and a small sacristy, and has a Baroque gabled facade.

Torre del Arroyo del Lobo is a ruined medieval defensive tower near Algeciras, Spain. It is located in the cove of Getares, and monitored the stretch of coast from Punta Carnero to Punta de San García between the cities of Algeciras and Tarifa as part of the defensive system of the Strait of Gibraltar in the Middle Ages.

The Torre de los Adalides was a rectangular medieval look-out tower of Islamic design located in the vicinity of Algeciras, Spain. It was situated roughly 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) from the coast on a hill some 100 metres (330 ft) above sea level in the area which is now covered by the city's northern suburbs. The tower was demolished by the Spaniards during the Spanish–American War as they thought the Americans might use it as a base of their own. The ruins of the tower are within military limits and cannot be approached without a formal permit.
The Río Palmones is a river of the Province of Cádiz in Southeastern coastal Spain. Its source is in Lomas del Castaño, Sierra Blanquilla, and it flows for some 37 kilometres (23 mi) into the Bay of Gibraltar, North of the city of Algeciras, in the neighborhood of Palmones. The Battle of Río Palmones took place here in 1342.
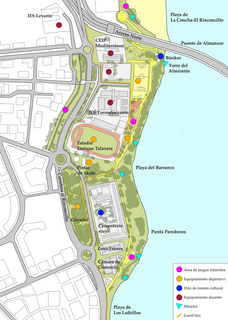
Paseo Cornisa is a park in Algeciras, Spain. It was inaugurated in May 2007. It stretches for just over a kilometre between Punta del Cementerio and Punta del Almirante in the north of the city near the old cemetery and parallel to the Playa del Barranco and Playa de El Rinconcillo. The park has an area of over 20,000 square metres (220,000 sq ft). Within the park is the Torre del Almirante or Admiral's Tower which dates from the 14th century.
Hotel AC Algeciras is a hotel on Carretera del Rinconcillo in southern Algeciras, in the Province of Cádiz in southeastern Spain. It is located in close proximity to the Playa de Los Ladrillos. It is located in a modern, angular-looking, dark grey building, and is one of the newest and modern hotels in the city, built in 2005–06, operated by AC Hotels and Marriott Hotels. Frommer's said of it "The most contemporary hotel in town, this AC stands in front of the Puerto Marítimo, only 1km from the city center. The rooms are modern minimalist yet very comfortable, and the hotel is well maintained."

Fuerte de San García was a fort in Algeciras, Spain, It was built in the 1730s and destroyed in 1811 to deny it to the French. Today all that remains are the foundation and base ruins, in the Parque del Centenario, but it is a registered Bien de Interés Cultural landmark

Iglesia de San Mateo is the main church of Tarifa in the Province of Cadiz, Spain. It was supposed to have been built in 1506 on the remains of an old mosque, although worship at the church has only been mentioned in documents since 1534, another date given for its inauguration. Numerous alterations have been made to the church over the centuries. The main Baroque facade was designed by architect Torcuato Cayon de la Vega in 1774, and the work was completed four years later under the direction of maestro Carlos Hermida. The bell tower has a square, robust base, and is topped with a fluted dome. The Capilla del Sagrario was restored in 1899, a magnificent dome on scallops that extends to the ground forming three semicircular chapels.

The Palacio Haedo is a 19th-century building on the Avenida Santa Fe in Buenos Aires, Argentina. It is located to the south of the Torre de Los Ingleses and the Plaza San Martín and Monument del libertador Jose de Plaza San Martín, in close proximity to the Consulate of Colombia and the Gran Hotel Buenos Aires. It was built in the late 19th century as a residence for the Haedo family by architects Passeroni and Brizuela in the Neo-Gothic style.

















