Related Research Articles
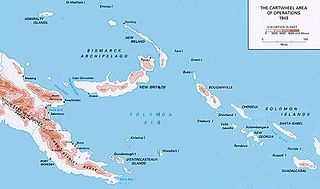
Operation Cartwheel (1943–1944) was a major military operation for the Allies in the Pacific theatre of World War II. Cartwheel was an operation aimed at neutralising the major Japanese base at Rabaul. The operation was directed by the Supreme Allied Commander in the South West Pacific Area (SWPA), General Douglas MacArthur, whose forces had advanced along the northeast coast of New Guinea and occupied nearby islands. Allied forces from the South Pacific Area, under Admiral William Halsey, advanced through the Solomon Islands toward Bougainville. The Allied forces involved were from Australia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, the US and various Pacific Islands.

The Battle of Rabaul, also known by the Japanese as Operation R, an instigating action of the New Guinea campaign, was fought on the island of New Britain in the Australian Territory of New Guinea, from 23 January into February 1942. It was a strategically significant defeat of Allied forces by Japan in the Pacific campaign of World War II, with the Japanese invasion force quickly overwhelming the small Australian garrison, the majority of which was either killed or captured. Hostilities on the neighbouring island of New Ireland are usually considered to be part of the same battle. Rabaul was significant because of its proximity to the Japanese territory of the Caroline Islands, site of a major Imperial Japanese Navy base on Truk.
Eric M. Hammel was a military historian, with a focus on the military campaigns of the United States Marine Corps in the Pacific War, and other military action in World War II as well as military conflicts including the Vietnam War and the Arab-Israeli Conflict. Hammel wrote a series of books about World War II Flying Aces but his most influential book was The Root : The Marines in Beirut, August 1982-February 1984 on the subject of the 1983 Beirut barracks bombings.

Tomitarō Horii was a lieutenant general in the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. After graduating from the Imperial Japanese Army Academy in 1911, Horii served in China before undertaking a variety of regimental appointments. Following Japan's entry into World War II, he commanded a division during the capture of Guam before commanding the Japanese force that had been given the task of capturing Port Moresby. In November 1942, in the retreat from Oivi–Gorari, Horii drowned while attempting to canoe down the Kumusi River to reach Japanese forces defending Buna–Gona. His canoe was swept out to sea and capsized.
Vunakanau Airfield was an aerodrome located near Vunakanau, East New Britain, Papua New Guinea. The airfield was constructed as a Royal Australian Air Force aerodrome and consisted of an unpaved single runway during World War II. The airfield was captured during the battle of Rabaul in 1942 by the Imperial Japanese and was extensively modified and expanded. Vunakanau was later neutralized by Allied air bombing from 1944.
Lark Force was an Australian Army formation established in March 1941 during World War II for service in New Britain and New Ireland. Under the command of Lieutenant Colonel John Scanlan, it was raised in Australia and deployed to Rabaul and Kavieng, aboard SS Katoomba, MV Neptuna and HMAT Zealandia, to defend their strategically important harbours and airfields.

The 2/22nd Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army. Raised as part of the Second Australian Imperial Force for service during World War II, the battalion formed part of the 23rd Brigade, attached to the 8th Division. It was captured by the Japanese during the Battle of Rabaul in 1942. After being captured, the battalion was not re-raised and a large number of its personnel died in captivity; those that did not were returned to Australia at the end of the war in 1945.

SS Westralia was a 2,884 GRT cargo and passenger ship. She served as a troopship in the First World War and was later converted into a hulk. She was sunk in the air raids on Rabaul on 20 January 1942.

The World War II Allied names for Japanese aircraft were reporting names, often described as codenames, given by Allied personnel to Imperial Japanese aircraft during the Pacific campaign of World War II. The names were used by Allied personnel to identify aircraft operated by the Japanese for reporting and descriptive purposes. Generally, Western men's names were given to fighter aircraft, women's names to bombers, transports, and reconnaissance aircraft, bird names to gliders, and tree names to trainer aircraft.

Lakunai Airfield, later known as Rabaul Airport; was an aerodrome located near Rabaul, East New Britain, Papua New Guinea. It was located at the foot of Tavurvur volcano, near Matupit Island. The airport was destroyed by the 1994 eruption that destroyed the town of Rabaul and subsequently a new airport was built and opened at Tokua, on the opposite side of the Rabaul caldera. The former airport was located at 04°13′S152°11′E.
Praed Point Battery was a coastal-defence installation at Praed Point, East New Britain, Papua New Guinea during World War II. It was built in 1941 by Royal Australian Engineers of Lark Force, together with 'L' Coastal Defence Battery of the Royal Australian Artillery. The battery defended St. George's Channel and the approaches to Blanche Bay.
Rapopo Airfield was an aerodrome located at Lesson Point, Blanche Bay near Rabaul, East New Britain, Papua New Guinea. The airfield was constructed by the Imperial Japanese during World War II in December 1942. Rapopo was later neutralized by Allied air bombing from 1944. The airfield was abandoned after the cessation of hostilities.
Tobera airfield was an aerodrome located near Tobera, near Keravat, East New Britain, Papua New Guinea. The airfield was constructed by the imperial Japan during World War II. Tobera was later neutralized by Allied air bombing from 1944. The airfield was abandoned after the cessation of hostilities.
Borpop Airfield, also known as Huris Airfield, was an aerodrome located near Namatani, west of Borpop Harbour in New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea. The airfield was built by the Imperial Japanese during World War II.
Wallace Battery was an artillery battery located on the northern side of the entrance to the Hunter River at Stockton, New South Wales, Australia. The battery was part of Fortress Newcastle. Two 6 inch Mk VII guns were installed at Fort Wallace in 1913. In 1940 the 6 inch guns were replaced by two 9.2-inch Mk X guns in emplacements.

Ataliklikun Bay is a bay of East New Britain Province, Papua New Guinea, opening into the Bismarck Sea. It is located in the northern part of New Britain, south-west of Lassul Bay and to the west of Cape Lambert and Rabaul. Urara Island is located in the northern part of the bay. The Raulavat plantation lies in the eastern part of its 25-mile shoreline. The villagers along the shore reportedly speak the Minigir language and the Masava dialect of Tolai. The United States Hydrographic Office said "a reef awash, about 200 yards long east and west, with 15 and 19 fathoms around, on which the steamer Seestem struck in 1909, lies in the south-west part of Ataliklikun Bay."
Lassul Bay is a bay of East New Britain Province, Papua New Guinea, opening into the Bismarck Sea. It is located in the north-western part of New Britain, to the west of Ataliklikun Bay on the Gazelle Peninsula. The communities around Lassul Bay are incorporated into the twenty-one wards of the Lassul-Baining Local-Level Government (LLG) including the settlement of Lassul. The land around the shoreline is swampy and the area has a history of plantation cultivation. The area was invaded in February 1942 by the Japanese during the Battle of Rabaul.

The Warangoi River also known as the Adler River, is a river located in the eastern part of the Gazelle Peninsula in the north-eastern part of New Britain, Papua New Guinea. It flows past the village of Warangoi and out into the Warangoi Bay. It played a part in the Battle of Rabaul early in 1942. Lieutenant Colonel Ishiro Kuwada's men of the 3rd Infantry Battalion captured at least 200 Australian men between the Warangoi River and Vunakanau. Virgin rainforest lies along the river basin.

The neutralisation of Rabaul was an Allied campaign to render useless the Imperial Japanese base at Rabaul in eastern New Britain, Papua New Guinea. Japanese forces landed on Rabaul on 23 January 1942, capturing it by February 1942, after which the harbor and town were transformed into a major Japanese naval and air installation. The Japanese heavily relied on it, using it as a launching point for Japanese reinforcements to New Guinea and Guadalcanal. Throughout the Solomon Islands campaign, neutralizing Rabaul became the primary objective of the Allied effort in the Solomons.
Bruce Gamble is an American historian, an author, and United States Military veteran. As a historian, Gamble specializes in World War II in the Pacific, and has written seven books on this particular topic.
References
- ↑ Gamble, Bruce (16 May 2010). Fortress Rabaul: The Battle for the Southwest Pacific, January 1942-April 1943. Zenith Imprint. p. 57. ISBN 978-0-7603-2350-2 . Retrieved 1 November 2011.
- ↑ Gamble, Bruce (15 December 2006). Darkest Hour: The True Story of Lark Force at Rabaul - Australia's Worst Military Disaster of World War II. Zenith Imprint. p. 112. ISBN 978-0-7603-2349-6 . Retrieved 1 November 2011.