
Botulism is a rare and potentially fatal illness caused by a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The disease begins with weakness, blurred vision, feeling tired, and trouble speaking. This may then be followed by weakness of the arms, chest muscles, and legs. Vomiting, swelling of the abdomen, and diarrhea may also occur. The disease does not usually affect consciousness or cause a fever.

Botulinum toxin, or botulinum neurotoxin, is a highly potent neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum and related species. It prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from axon endings at the neuromuscular junction, thus causing flaccid paralysis. The toxin causes the disease botulism. The toxin is also used commercially for medical and cosmetic purposes.

Clostridium botulinum is a gram-positive, rod-shaped, anaerobic, spore-forming, motile bacterium with the ability to produce the neurotoxin botulinum.

Ribonuclease is a type of nuclease that catalyzes the degradation of RNA into smaller components. Ribonucleases can be divided into endoribonucleases and exoribonucleases, and comprise several sub-classes within the EC 2.7 and 3.1 classes of enzymes.

An antitoxin is an antibody with the ability to neutralize a specific toxin. Antitoxins are produced by certain animals, plants, and bacteria in response to toxin exposure. Although they are most effective in neutralizing toxins, they can also kill bacteria and other microorganisms. Antitoxins are made within organisms, and can be injected into other organisms, including humans, to treat an infectious disease. This procedure involves injecting an animal with a safe amount of a particular toxin. The animal's body then makes the antitoxin needed to neutralize the toxin. Later, blood is withdrawn from the animal. When the antitoxin is obtained from the blood, it is purified and injected into a human or other animal, inducing temporary passive immunity. To prevent serum sickness, it is often best to use an antitoxin obtained from the same species.
Addiction modules are toxin-antitoxin systems. Each consists of a pair of genes that specify two components: a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin that interferes with the lethal action of the toxin. Found first in Escherichia coli on low copy number plasmids, addiction modules are responsible for a process called the postsegregational killing effect. When bacteria lose these plasmid(s), the cured cells are selectively killed because the unstable antitoxin is degraded faster than the more stable toxin. The term "addiction" is used because the cell depends on the de novo synthesis of the antitoxin for cell survival. Thus, addiction modules are implicated in maintaining the stability of extrachromosomal elements.

The hok/sok system is a postsegregational killing mechanism employed by the R1 plasmid in Escherichia coli. It was the first type I toxin-antitoxin pair to be identified through characterisation of a plasmid-stabilising locus. It is a type I system because the toxin is neutralised by a complementary RNA, rather than a partnered protein.
In a screen of the Bacillus subtilis genome for genes encoding ncRNAs, Saito et al. focused on 123 intergenic regions (IGRs) over 500 base pairs in length, the authors analyzed expression from these regions. Seven IGRs termed bsrC, bsrD, bsrE, bsrF, bsrG, bsrH and bsrI expressed RNAs smaller than 380 nt. All the small RNAs except BsrD RNA were expressed in transformed Escherichia coli cells harboring a plasmid with PCR-amplified IGRs of B. subtilis, indicating that their own promoters independently express small RNAs. Under non-stressed condition, depletion of the genes for the small RNAs did not affect growth. Although their functions are unknown, gene expression profiles at several time points showed that most of the genes except for bsrD were expressed during the vegetative phase, but undetectable during the stationary phase. Mapping the 5' ends of the 6 small RNAs revealed that the genes for BsrE, BsrF, BsrG, BsrH, and BsrI RNAs are preceded by a recognition site for RNA polymerase sigma factor σA.
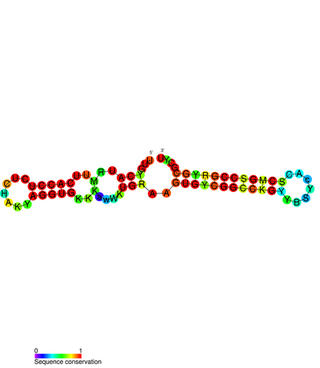
PtaRNA1 is a family of non-coding RNAs. Homologs of PtaRNA1 can be found in the bacterial families, Betaproteobacteria and Gammaproteobacteria. In all cases the PtaRNA1 is located anti-sense to a short protein-coding gene. In Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria, this gene is annotated as XCV2162 and is included in the plasmid toxin family of proteins.

A toxin-antitoxin system consists of a "toxin" and a corresponding "antitoxin", usually encoded by closely linked genes. The toxin is usually a protein while the antitoxin can be a protein or an RNA. Toxin-antitoxin systems are widely distributed in prokaryotes, and organisms often have them in multiple copies. When these systems are contained on plasmids – transferable genetic elements – they ensure that only the daughter cells that inherit the plasmid survive after cell division. If the plasmid is absent in a daughter cell, the unstable antitoxin is degraded and the stable toxic protein kills the new cell; this is known as 'post-segregational killing' (PSK).

RdlD RNA is a family of small non-coding RNAs which repress the protein LdrD in a type I toxin-antitoxin system. It was discovered in Escherichia coli strain K-12 in a long direct repeat (LDR) named LDR-D. This locus encodes two products: a 35 amino acid peptide toxin (ldrD) and a 60 nucleotide RNA antitoxin. The 374nt toxin mRNA has a half-life of around 30 minutes while rdlD RNA has a half-life of only 2 minutes. This is in keeping with other type I toxin-antitoxin systems.
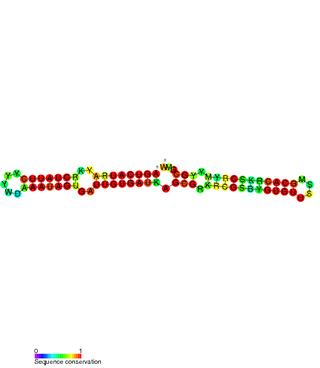
The SymE-SymR toxin-antitoxin system consists of a small symbiotic endonuclease toxin, SymE, and a non-coding RNA symbiotic RNA antitoxin, SymR, which inhibits SymE translation. SymE-SymR is a type I toxin-antitoxin system, and is under regulation by the antitoxin, SymR. The SymE-SymR complex is believed to play an important role in recycling damaged RNA and DNA. The relationship and corresponding structures of SymE and SymR provide insight into the mechanism of toxicity and overall role in prokaryotic systems.
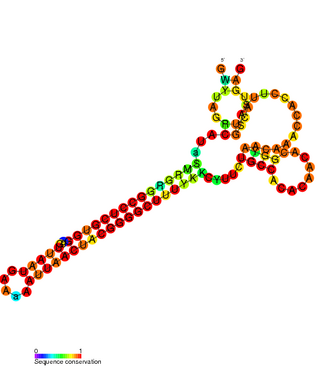
The FlmA-FlmB toxin-antitoxin system consists of FlmB RNA, a family of non-coding RNAs and the protein toxin FlmA. The FlmB RNA transcript is 100 nucleotides in length and is homologous to sok RNA from the hok/sok system and fulfills the identical function as a post-segregational killing (PSK) mechanism.

The TxpA/RatA toxin-antitoxin system was first identified in Bacillus subtilis. It consists of a non-coding 222nt sRNA called RatA and a protein toxin named TxpA.
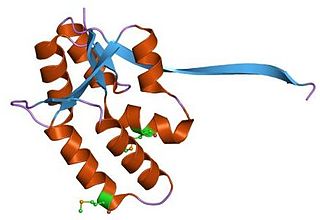
In molecular biology the PIN domain is a protein domain that is about 130 amino acids in length. PIN domains function as nuclease enzymes that cleave single stranded RNA in a sequence- or structure-dependent manner.

VapBC is the largest family of type II toxin-antitoxin system genetic loci in prokaryotes. VapBC operons consist of two genes: VapC encodes a toxic PilT N-terminus (PIN) domain, and VapB encodes a matching antitoxin. The toxins in this family are thought to perform RNA cleavage, which is inhibited by the co-expression of the antitoxin, in a manner analogous to a poison and antidote.
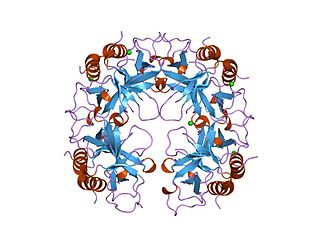
The CcdA/CcdB Type II Toxin-antitoxin system is one example of the bacterial toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems that encode two proteins, one a potent inhibitor of cell proliferation (toxin) and the other its specific antidote (antitoxin). These systems preferentially guarantee growth of plasmid-carrying daughter cells in a bacterial population by killing newborn bacteria that have not inherited a plasmid copy at cell division.
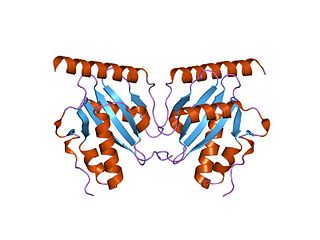
The parDE type II toxin-antitoxin system is one example of the bacterial toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems that encode two proteins, one a potent inhibitor of cell proliferation (toxin) and the other its specific antidote (antitoxin). These systems preferentially guarantee growth of plasmid-carrying daughter cells in a bacterial population by killing newborn bacteria that have not inherited a plasmid copy at cell division.
The Botulism Antitoxin Heptavalent - (Equine) – BAT, made by Emergent BioSolutions Canada Inc. – is a licensed, commercially available botulism anti-toxin that effectively neutralizes all seven known botulinum nerve toxin serotypes. It is indicated for sporadic cases of life-threatening botulism and is also stockpiled for the eventuality of botulinum nerve toxins being used in a future bioterrorist attack.
SR6 is a 100 nucleotide long antisense RNA antitoxin that overlaps 2 toxins: 3' end of yonT and yoyJ at its 5'end. In type I toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems the antitoxin is a small RNA that neutralizes a toxin protein. Several type I TA systems have been described in B. subtilis. YonT/SR6 system is located on the SPβ prophage of the B. subtilis chromosome and it was shown to be multi-stress responsive. SR6 acts by promoting yonT mRNA degradation. It may regulate the second toxin, yoyJ by a different mechanism.














