Related Research Articles

The (Montreux) Convention regarding the Regime of the Straits, often known simply as the Montreux Convention, is an international agreement governing the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits in Turkey. Signed on 20 July 1936 at the Montreux Palace in Switzerland, it went into effect on 9 November 1936, addressing the long running Straits Question over who should control the strategically vital link between the Black and Mediterranean seas.

The Strait of Hormuz is a strait between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. It provides the only sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the open ocean and is one of the world's most strategically important choke points. On the north coast lies Iran, and on the south coast lies the Musandam peninsula, shared by the United Arab Emirates and the Musandam Governorate, an exclave of Oman. The strait is about 90 nautical miles (167 km) long, with a width varying from about 52 nmi (96 km) to 21 nmi (39 km).

The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international treaty that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. As of July 2024, 169 States and the European Union are parties.

A strait is a water body connecting two seas or two water basins. While the landform generally constricts the flow, the surface water still flows, for the most part, at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in both directions. In some straits there may be a dominant directional current through the strait. Most commonly, it is a narrowing channel that lies between two land masses. Some straits are not navigable, for example because they are either too narrow or too shallow, or because of an unnavigable reef or archipelago. Straits are also known to be loci for sediment accumulation. Usually, sand-size deposits occur on both the two opposite strait exits, forming subaqueous fans or deltas.

The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed regional seas and estuaries, rivers, lakes, groundwater systems (aquifers), and wetlands.
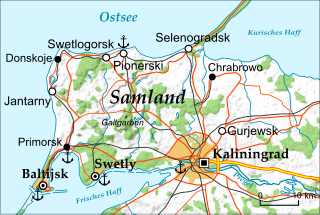
The Strait of Baltiysk is a strait enabling passage from the Baltic Sea into the brackish Vistula Lagoon, located in Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia. The constructed strait separates the Vistula Spit from the peninsula which was part of the Vistula Spit in the 15th century and now is part of Sambian Peninsula.

Law of the sea is a body of international law governing the rights and duties of states in maritime environments. It concerns matters such as navigational rights, sea mineral claims, and coastal waters jurisdiction. The connotation of ocean law is somewhat broader, but the law of the sea is so comprehensive that it covers all areas of ocean law as well.
Freedom of navigation (FON) is a principle of law of the sea that ships flying the flag of any sovereign state shall not suffer interference from other states when in international waters, apart from the exceptions provided for in international law. In the realm of international law, it has been defined as “freedom of movement for vessels, freedom to enter ports and to make use of plant and docks, to load and unload goods and to transport goods and passengers". This right is now also codified as Article 87(1)a of the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea.

Wetar Strait is an international strait in Southeast Asia. It separates the island of Wetar from the eastern part of the island of Timor. The strait is also the eastern portion of a pair of international straits, the other one being Ombai Strait; the two straits combine to link the Indian Ocean with the Pacific Ocean.
Innocent passage is a concept in the law of the sea that allows for a vessel to pass through the territorial sea of another state, subject to certain restrictions. The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea Article 19 defines innocent passage as:
- Passage is innocent so long as it is not prejudicial to the peace, good order or security of the coastal State. Such passage shall take place in conformity with this Convention and with other rules of international law.
- Passage of a foreign ship shall be considered to be prejudicial to the peace, good order or security of the coastal State if in the territorial sea it engages in any of the following activities:
In Canadian law, Canadian Internal Waters are the waters "on the landward side of the baselines of the territorial sea of Canada."

According to the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, a nation's internal waters include waters on the side of the baseline of a nation's territorial waters that is facing toward the land, except in archipelagic states. It includes waterways such as rivers and canals, and sometimes the water within small bays.
In 1989 the USA and USSR issued a Joint Statement on Uniform Acceptance of Rules of International Law Governing Innocent Passage. It made it clear that the text of the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) reflected customary international law, and every ship, regardless of cargo, does not need permission to enter another state's territorial sea so long as it adheres to the definition of innocent passage in Article 19 of UNCLOS.
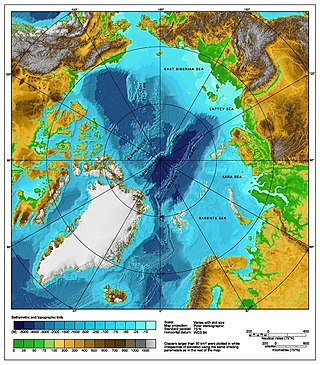
The Arctic consists of land, internal waters, territorial seas, exclusive economic zones (EEZs) and international waters above the Arctic Circle. All land, internal waters, territorial seas and EEZs in the Arctic are under the jurisdiction of one of the eight Arctic coastal states: Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States. International law regulates this area as with other portions of Earth.
Maritime Security Regimes are codes and conventions of behavior agreed upon by coastal states to provide a degree of security within territorial waters and on the high seas.

The Black Sea bumping incident of 12 February 1988 occurred when American cruiser USS Yorktown tried to exercise the right of innocent passage through Soviet territorial waters in the Black Sea during the Cold War. The cruiser was bumped by the Soviet frigate Bezzavetny with the intention of pushing Yorktown into international waters. This incident also involved the destroyer USS Caron, sailing in company with USS Yorktown and claiming the right of innocent passage, which was intentionally shouldered by a Soviet Mirka-class frigate SKR-6. Yorktown reported minor damage to its hull, with no holing or risk of flooding. Caron was undamaged.

On March 13, 1986, the American cruiser USS Yorktown and the destroyer USS Caron tried to exercise the right of innocent passage under international law through Soviet territorial waters in the Black Sea near the southern Crimean Peninsula. They were confronted by Soviet frigate Ladny and border guard vessels Dozorny and Izmail.
International piracy law is international law that is meant to protect against piracy. Throughout history and legal precedents, pirates have been defined as hostis humani generis, Latin for "the enemy of all mankind". The United Nations has codified much of the law in the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which defines different types of piracy and ways to combat it.
A coastal state is a term found in the law of the sea. Although widely used in the legal documents, including the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), this term lacks a precise definition. The "essential idea" of a coastal state is having an open sea coast and asserting the sovereignty or jurisdiction in the areas of the sea adjacent to this coast. Norway, Canada, and Chile are examples of the coastal states, Churchill counts up a total of 150 of such states.
An international strait is a narrow natural waterway connecting two parts of the high seas or exclusive economic zones, used for international navigation. Per the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), a transit passage regime prevails in such straits for both ships and aircraft with few exceptions, even when the territorial waters of bordering country or countries overlap. Worldwide, more than 200 straits might satisfy the criteria of an international strait. Notable international straits include Bosporus and Dardanelles, Strait of Magellan, Strait of Gibraltar, Strait of Dover, and Danish straits, with the most famous being probably the Strait of Hormuz.
References
- 1 2 Bugajski, Dariusz R. (2021). Navigational rights and freedoms in the international law and practice. Polish Naval Academy. pp. 146, 305–308. ISBN 978-83-961549-1-0. OCLC 1267382284.
- 1 2 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, Part III, Article 38
- ↑ "Chronological lists of ratifications of, accessions and successions to the Convention and the related Agreements as at 3 June 2011". Division for Ocean Affairs and the Law of the Sea. UN. Retrieved 2 January 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Jon M. Van Dyke (2 October 2008). "Transit Passage Through International Straits" (PDF). The Future of Ocean Regime-Building. University of Hawaii. pp. 178, 179, 186–187, 194–197. doi:10.1163/ej.9789004172678.i-786.50. ISBN 9789004172678. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-11-05. Retrieved 6 July 2019.
- ↑ Reagan, Ronald (10 March 1983). "Presidential Proclamation 5030" (PDF). United States Department of State . Retrieved 2 January 2011.
- ↑ Bugajski, Dariusz (2006). "The special status of the Strait of the Aland Islands as an exception of the transit passage principle (Art. 35 of the Convention on the Law of the Sea)". Prawo Morskie (12). The Gdańsk Branch of the Polish Academy of Sciences: 81–97. ISSN 0860-7338 . Retrieved 28 May 2024.
- ↑ López Martín 2010, p. xv, Foreword by Luis Ignacio Sánchez .
- ↑ Priestnall 1997, p. 10.