Related Research Articles
In the United States, an interstate compact is a pact or agreement between two or more states, or between states and any foreign sub-national government.
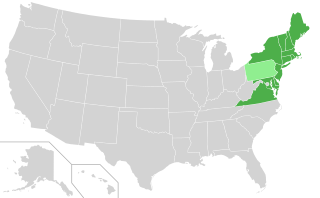
The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI, pronounced "Reggie") is the first mandatory market-based program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States. RGGI is a cooperative effort among the states of Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Virginia to cap and reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the power sector. RGGI compliance obligations apply to fossil-fueled power plants 25 megawatts (MW) and larger within the 11-state region. Pennsylvania's participation in the RGGI cooperative was ruled unconstitutional on November 1, 2023, although that decision has been appealed. North Carolina's entrance into RGGI has been blocked by the enactment of the state's fiscal year 2023–25 budget.

Conservation Law Foundation (CLF) is an environmental advocacy organization based in New England, United States. Since 1966, CLF's mission has been to advocate for New England's environment and its communities. CLF's advocacy work takes place across five integrated program areas: Clean Energy & Climate Change, Clean Air & Water, Healthy Oceans, People & Justice, and Healthy Communities. CLF's mission statement is to "use the law, science, and the market to create solutions that preserve natural resources, build healthy communities, and sustain a vibrant economy." CLF focuses on promoting renewable energy and fight air and water pollution; building sustainable fishing communities and protect marine habitat; promoting public transit and defend public health; achieving environmental justice; and sustaining a vibrant, equitable economy.
The Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006, or Assembly Bill (AB) 32, is a California state law that fights global warming by establishing a comprehensive program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from all sources throughout the state. AB32 was co-authored by Assemblymember Fran Pavley and Speaker of the California Assembly Fabian Nunez and signed into law by Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger on September 27, 2006.

Western Climate Initiative, Inc. (WCI) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit corporation which administers the shared emissions trading market between the American state of California and the Canadian province of Quebec as well as separately administering the individual emissions trading systems in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia and American state of Washington. It also provides administrative, technical and infrastructure services to support the implementation of cap-and-trade programs in other North American jurisdictions. The organization was originally founded in February 2007 by the governors of five western states with the goal of developing a multi-sector, market-based program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions; it was incorporated in its current form in 2011.

The Climate Registry (TCR) is a non-profit organization governed by U.S. states and Canadian provinces and territories. TCR designs and operates voluntary and compliance greenhouse gas (GHG) reporting programs globally, and assists organizations in measuring, reporting and verifying the carbon in their operations in order to manage and reduce it. TCR also consults with governments nationally and internationally on all aspects of GHG measurement, reporting, and verification.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person.
United States vehicle emission standards are set through a combination of legislative mandates enacted by Congress through Clean Air Act (CAA) amendments from 1970 onwards, and executive regulations managed nationally by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and more recently along with the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). These standard cover common motor vehicle air pollution, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate emissions, and newer versions have incorporated fuel economy standards.
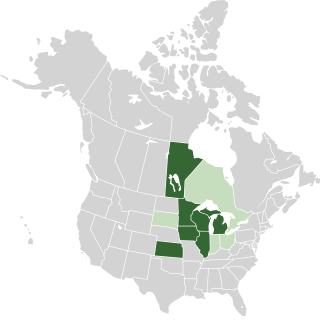
The Midwestern Greenhouse Gas Reduction Accord was a regional agreement by six governors of states in the US Midwest who are members of the Midwestern Governors Association (MGA), and the premier of one Canadian province, whose purpose is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to combat climate change. The accord has been inactive since March 2010, when an advisory group presented a plan for action to the association with a scheduled implementation date of January 2012. Signatories to the accord are the U.S. states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Illinois, Iowa, Michigan, Kansas, and the Canadian Province of Manitoba. Observers of the accord are Indiana, Ohio, and South Dakota, as well as the Canadian Province of Ontario.

The New England Governors and Eastern Canadian Premiers (NEG-ECP) Climate Change Action Plan 2001 is a resolution adopted on August 28, 2001, by the New England Governors and the Eastern Canadian Premiers. The resolution calls for a reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to 1990 levels by 2010, at least 10% below 1990 levels by 2020, 35-45% below 1990 levels by 2030, and a 75-85% reduction of 2001 levels by 2050.

Climate change in Massachusetts affects both urban and rural environments, including forestry, fisheries, agriculture, and coastal development. The Northeast is projected to warm faster than global average temperatures; by 2035, the Northeast is "projected to be more than 3.6°F (2°C) warmer on average than during the preindustrial era."

Greenhouse gas emissions by Australia totalled 533 million tonnes CO2-equivalent based on greenhouse gas national inventory report data for 2019; representing per capita CO2e emissions of 21 tons, three times the global average. Coal was responsible for 30% of emissions. The national Greenhouse Gas Inventory estimates for the year to March 2021 were 494.2 million tonnes, which is 27.8 million tonnes, or 5.3%, lower than the previous year. It is 20.8% lower than in 2005. According to the government, the result reflects the decrease in transport emissions due to COVID-19 pandemic restrictions, reduced fugitive emissions, and reductions in emissions from electricity; however, there were increased greenhouse gas emissions from the land and agriculture sectors.

Climate change in Canada has had large impacts on the country's environment and landscapes. These events are likely to become even more frequent and severe in the future due to the continued release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The number of climate change–related events, such as the 2021 British Columbia Floods and an increasing number of forest fires, has become an increasing concern over time. Canada's annual average temperature over land has warmed by 1.7 degrees Celsius since 1948. The rate of warming is even higher in Canada's north, the Prairies, and northern British Columbia. The country's precipitation has increased in recent years and extreme weather events have become more common.
The International Carbon Action Partnership (ICAP) is an international cooperative forum founded in 2007 by more than 15 government representatives. It brings together states and sub-national jurisdictions that have implemented or are planning to implement emissions trading systems (ETS). Then-Governor of California, Arnold Schwarzenegger, expressed at ICAP's founding ceremony:
"This first-of-its-kind partnership will provide more incentives for clean-tech investment and economic growth while not letting polluters off the hook. And it will help renew the health of our planet."
The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China, and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. Cumulatively, the United States has emitted over a trillion metric tons of greenhouse gases, more than any country in the world.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) began regulating greenhouse gases (GHGs) under the Clean Air Act from mobile and stationary sources of air pollution for the first time on January 2, 2011. Standards for mobile sources have been established pursuant to Section 202 of the CAA, and GHGs from stationary sources are currently controlled under the authority of Part C of Title I of the Act. The basis for regulations was upheld in the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia in June 2012.
The Ozone Transport Commission (OTC) is a multi-state organization founded in 1991 and created under the Clean Air Act. It is responsible for advising EPA on air pollution transport issues and for developing and implementing regional solutions to the ground-level ozone problem in the Northeast and Mid-Atlantic regions, collectively called the Ozone Transport Region (OTR). OTC has no regulatory authority, but assists its members in developing model regulations for implementation at the state level. OTC also manages a regional planning organization MANE-VU, which is charged with regional multi-pollutant air quality planning. In January 2020, operations of OTC were placed under new management by the Northeast States for Coordinated Air Use Management (NESCAUM) and Washington, DC operations were closed.

The Under2 Coalition is a coalition of subnational governments that aims to achieve greenhouse gases emissions mitigation. It started as a memorandum of understanding, which was signed by twelve founding jurisdictions on May 19, 2015 in Sacramento, California. Although it was originally called the Under2 MOU, it became known as the Under2 Coalition in 2017. As of June 2024, the coalition represents 178 individual states, regions, provinces and subnational governments along with several other national and subnational entities. The list of signatories has grown to 270 governments, representing over 1.75 billion people and 50% of the world economy. The Under2 MOU was conceived through a partnership between the governments of California and Baden-Wurttemberg, with Climate Group acting as secretariat.

Climate change in Rhode Island encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. state of Rhode Island.
Carbon pricing in Canada is implemented either as a regulatory fee or tax levied on the carbon content of fuels at the Canadian provincial, territorial or federal level. Provinces and territories of Canada are allowed to create their own system of carbon pricing as long as they comply with the minimum requirements set by the federal government; individual provinces and territories thus may have a higher tax than the federally mandated one but not a lower one. Currently, all provinces and territories are subject to a carbon pricing mechanism, either by an in-province program or by one of two federal programs. As of April 2023 the federal minimum tax is set at CA$65 per tonne of CO2 equivalent, set to increase to CA$170 in 2030.
References
- ↑ "The Transportation and Climate Initiative - An Agenda for Progress" (PDF). Retrieved 2024-06-20.
- 1 2 Mass. Part Of Regional Effort To Drive Down Emissions From Gas And Diesel
- ↑ "The Northeast Climate Pact Implodes". The Wall Street Journal . 19 November 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
Their problem is that consumers don't want to pay more for energy, and as the latest proof behold Connecticut Gov. Ned Lamont's retreat this week from a Northeast state climate pact
- ↑ David Abel (18 November 2021). "Baker pulls support for regional pact that would address climate change". The Boston Globe . Retrieved 21 November 2021.
Gas prices were expected to rise 5 to 9 cents a gallon when the rules took effect in 2023, with some estimates suggesting it could add as much as 24 cents
- ↑ "Rising gas prices are fueling opposition to Transportation Climate Initiative". 17 November 2021.
- ↑ Gov. Baker pulling Massachusetts out of Transportation Climate Initiative compact - "At the same time, the new federal infrastructure funding package, American Rescue Plan investments, as well as tax revenue surpluses generated by Massachusetts' strong economic recovery make the Commonwealth better positioned to upgrade its roads, bridges and public transportation systems"
- ↑ Amy Sokolow (20 November 2021). "Rhode Island, the final state, pulls out of TCI". The Boston Herald . Retrieved 21 November 2021.
After both Massachusetts and Connecticut's governors pulled out of the Transportation and Climate Initiative, citing waning support and higher gas prices, Rhode Island has also has left, putting the nail in the coffin on the multi-state partnership