Related Research Articles

Cologne is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 million people in the urban region. Centered on the left (west) bank of the Rhine, Cologne is about 35 km (22 mi) southeast of NRW's state capital Düsseldorf and 25 km (16 mi) northwest of Bonn.

The prince-electors, or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.

The Rhineland is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.

Adolf was the count of Nassau from about 1276 and the elected king of Germany from 1292 until his deposition by the prince-electors in 1298. He was never crowned by the pope, which would have secured him the imperial title. He was the first physically and mentally healthy ruler of the Holy Roman Empire ever to be deposed without a papal excommunication. Adolf died shortly afterwards in the Battle of Göllheim fighting against his successor Albert of Habsburg.

The Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen — not to be confused with the modern Archdiocese of Hamburg, founded in 1994 — was an ecclesiastical principality (787–1566/1648) of the Holy Roman Empire and the Catholic Church that after its definitive secularization in 1648 became the hereditary Duchy of Bremen. The prince-archbishopric, which was under the secular rule of the archbishop, consisted of about a third of the diocesan territory. The city of Bremen was de facto and de jure not part of the prince-archbishopric. Most of the prince-archbishopric lay rather in the area to the north of the city of Bremen, between the Weser and Elbe rivers. Even more confusingly, parts of the prince-archbishopric belonged in religious respect to the neighbouring Diocese of Verden, making up 10% of its diocesan territory.

The Battle of Worringen was fought on 5 June 1288 near the town of Worringen, which is now the northernmost borough of Cologne. It was the decisive battle of the War of the Limburg Succession, fought for the possession of the Duchy of Limburg between on one side the Archbishop Siegfried II of Cologne and Count Henry VI of Luxembourg, and on the other side, Duke John I of Brabant. It was one of the largest battles in Europe in the Middle Ages.
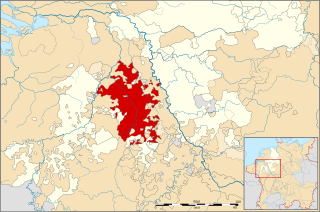
The Duchy of Jülich comprised a state within the Holy Roman Empire from the 11th to the 18th centuries. The duchy lay west of the Rhine river and was bordered by the Electorate of Cologne to the east and the Duchy of Limburg to the west. It had territories on both sides of the river Rur, around its capital Jülich – the former Roman Iuliacum – in the lower Rhineland. The duchy amalgamated with the County of Berg beyond the Rhine in 1423, and from then on also became known as Jülich-Berg. Later it became part of the United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg.

Count Engelbert II of Berg, also known as Saint Engelbert, Engelbert of Cologne, Engelbert I, Archbishop of Cologne or Engelbert I of Berg, Archbishop of Cologne was archbishop of Cologne and a saint; he was notoriously murdered by a member of his own family.
Adolf of Altena, Adolf of Berg or Adolf of Cologne, was Archbishop of Cologne from 1193 to 1205.

Maximilian Henry of Bavaria was the third son and fourth child of Albert VI, landgrave of Leuchtenberg and his wife, Mechthilde von Leuchtenberg. In 1650, he was named Archbishop-Elector of Cologne, Bishop of Hildesheim and Bishop of Liège succeeding his uncle, Ferdinand of Bavaria. He worked throughout his career with the French to limit the authority of the Holy Roman Emperor, and participated in the Franco-Dutch War on the opposite side from the Empire.

SiegfriedII of Westerburg was Archbishop of Cologne from 1275 to 1297.

Walram of Jülich was Archbishop of Cologne from 1332 to his death in 1349.

Henry VII, also known as Henry of Luxembourg, was Count of Luxembourg, King of Germany from 1308 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1312. He was the first emperor of the House of Luxembourg. During his brief career he reinvigorated the imperial cause in Italy, which was racked with the partisan struggles between the divided Guelf and Ghibelline factions, and inspired the praise of Dino Compagni and Dante Alighieri. He was the first emperor since the death of Frederick II in 1250, ending the Great Interregnum of the Holy Roman Empire; however, his premature death threatened to undo his life's work. His son, John of Bohemia, failed to be elected as his successor, and there was briefly another anti-king, Frederick the Fair, contesting the rule of Louis IV.
Adolf VII of Berg was the eldest son of Henry IV, Duke of Limburg and Irmgard of Berg.

Henry I of Nassau-Siegen, German: Heinrich I. von Nassau-Siegen was Count of Nassau-Siegen, a part of the County of Nassau, and ancestor of the House of Nassau-Siegen. He comes from the Ottonian branch of the House of Nassau.
The Free Imperial City of Aachen, also known in English by its French name of Aix-la-Chapelle and today known simply as Aachen, was a Free Imperial City and spa of the Holy Roman Empire west of Cologne and southeast of the Low Countries, in the Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle. The pilgrimages, the Coronation of the Holy Roman Emperor, flourishing industries and the privileges conferred by various emperors made it one of the most prosperous market towns of the Holy Roman Empire.
Simon I, Count of Tecklenburg was Count of Tecklenburg from 1156 until his death.
The German throne dispute or German throne controversy was a political conflict in the Holy Roman Empire from 1198 to 1215. This dispute between the House of Hohenstaufen and House of Welf was over the successor to Emperor Henry VI who had just died. After a conflict lasting 17 years the Hohenstaufen Frederick II prevailed.
The imperial election of 1653 was an imperial election held to select the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire. It took place in Augsburg on May 31.
The imperial election of 1292 was an imperial election held to select the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire. It took place in Frankfurt on May 5. Emperor Rudolf I of Germany had died on 15 July 1291.
References
- ↑ "Yes, I Can! By Robin Nixon | You can do it if you put your mind to it". Archived from the original on 2013-02-04. Retrieved 2009-11-25.
- ↑ The New Cambridge Medieval History: c. 1300-c. 1415 / edited by Michael Jones P516