
Tic-tac-toe, noughts and crosses, or Xs and Os is a paper-and-pencil game for two players who take turns marking the spaces in a three-by-three grid with X or O. The player who succeeds in placing three of their marks in a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal row first is the winner. It is a solved game, with a forced draw assuming best play from both players.
Three men's morris is an abstract strategy game played on a three by three board that is similar to tic-tac-toe. It is also related to six men's morris and nine men's morris. A player wins by forming a mill, that is, three of their own pieces in a row.

Combinatorial game theory is a branch of mathematics and theoretical computer science that typically studies sequential games with perfect information. Study has been largely confined to two-player games that have a position that the players take turns changing in defined ways or moves to achieve a defined winning condition. Combinatorial game theory has not traditionally studied games of chance or those that use imperfect or incomplete information, favoring games that offer perfect information in which the state of the game and the set of available moves is always known by both players. However, as mathematical techniques advance, the types of game that can be mathematically analyzed expands, thus the boundaries of the field are ever changing. Scholars will generally define what they mean by a "game" at the beginning of a paper, and these definitions often vary as they are specific to the game being analyzed and are not meant to represent the entire scope of the field.
Combinatorial game theory measures game complexity in several ways:
- State-space complexity
- Game tree size
- Decision complexity
- Game-tree complexity
- Computational complexity

3D tic-tac-toe, also known by the trade name Qubic, is an abstract strategy board game, generally for two players. It is similar in concept to traditional tic-tac-toe but is played in a cubical array of cells, usually 4×4×4. Players take turns placing their markers in blank cells in the array. The first player to achieve four of their own markers in a row wins. The winning row can be horizontal, vertical, or diagonal on a single board as in regular tic-tac-toe, or vertically in a column, or a diagonal line through four boards.
In mathematics, the Hales–Jewett theorem is a fundamental combinatorial result of Ramsey theory named after Alfred W. Hales and Robert I. Jewett, concerning the degree to which high-dimensional objects must necessarily exhibit some combinatorial structure.
In combinatorial game theory, the strategy-stealing argument is a general argument that shows, for many two-player games, that the second player cannot have a guaranteed winning strategy. The strategy-stealing argument applies to any symmetric game in which an extra move can never be a disadvantage. A key property of a strategy-stealing argument is that it proves that the first player can win the game without actually constructing such a strategy. So, although it might prove the existence of a winning strategy, the proof gives no information about what that strategy is.

Score four is a "three dimensional" abstract strategy game, similar to Connect Four. It was first sold under the name "Score Four" by Funtastic in 1968. Lakeside issued 4 different versions in the 1970s. Later Hasbro sold the game as "Connect Four Advanced" in the UK.
Harary's generalized tic-tac-toe or animal tic-tac-toe is a generalization of the game tic-tac-toe, defining the game as a race to complete a particular polyomino on a square grid of varying size, rather than being limited to "in a row" constructions. It was devised by Frank Harary in March 1977, and is a broader definition than that of an m,n,k-game.
Nine holes is a two-player abstract strategy game from different parts of the world and is centuries old. It was very popular in England. It is related to tic-tac-toe, but even more related to three men's morris, achi, tant fant, shisima, picaria, and dara, because pieces are moved on the board to create the 3 in a row. It is an alignment game.

Picaria is a two-player abstract strategy game from the Zuni Native American Indians or the Pueblo Indians of the American Southwest. It is related to tic-tac-toe, but more related to three men's morris, Nine Holes, Achi, Tant Fant, and Shisima, because pieces can be moved to create the three-in-a-row. Picaria is an alignment game.
Tsoro yematatu is a two-player abstract strategy game from Zimbabwe. Players first drop their three pieces onto the board, and then move them to create a 3 in-a-row which wins the game. It is similar to games like Tapatan, Achi, Nine holes, Shisima, and Tant Fant. However, what makes this game unique is that pieces can jump over each other which adds an extra dimension in the maneuverability of the pieces.

Zillions of Games is a commercial general game playing system developed by Jeff Mallett and Mark Lefler in 1998. The game rules are specified with S-expressions, Zillions rule language. It was designed to handle mostly abstract strategy board games or puzzles. After parsing the rules of the game, the system's artificial intelligence can automatically play one or more players. It treats puzzles as solitaire games and its AI can be used to solve them.
A positional game is a kind of a combinatorial game for two players. It is described by:
Order and Chaos is a variant of the game tic-tac-toe on a 6×6 gameboard. It was invented by Stephen Sniderman and introduced by him in Games magazine in 1981. The player Order strives to create a five-in-a-row of either Xs or Os. The opponent Chaos endeavors to prevent this.
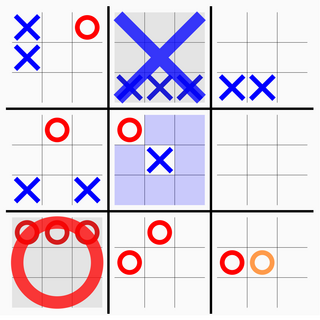
Ultimate tic-tac-toe is a board game composed of nine tic-tac-toe boards arranged in a 3 × 3 grid. Players take turns playing on the smaller tic-tac-toe boards until one of them wins on the larger board. Compared to traditional tic-tac-toe, strategy in this game is conceptually more difficult and has proven more challenging for computers.

Notakto is a tic-tac-toe variant, also known as neutral or impartial tic-tac-toe. The game is a combination of the games tic-tac-toe and Nim, played across one or several boards with both of the players playing the same piece. The game ends when all the boards contain a three-in-a-row of Xs, at which point the player to have made the last move loses the game. However, in this game, unlike tic-tac-toe, there will always be a player who wins any game of Notakto.

Wild tic-tac-toe is an impartial game similar to tic-tac-toe. However, in this game players can choose to place either X or O on each move. This game can also be played in its misere form where if a player creates a three-in-a-row of marks, that player loses the game.

Tic-tac-toe is an instance of an m,n,k-game, where two players alternate taking turns on an m×n board until one of them gets k in a row. Harary's generalized tic-tac-toe is an even broader generalization. The game can also be generalized as a nd game. The game can be generalised even further from the above variants by playing on an arbitrary hypergraph where rows are hyperedges and cells are vertices.
A nd game (or nk game) is a generalization of the combinatorial game tic-tac-toe to higher dimensions. It is a game played on a nd hypercube with 2 players. If one player creates a line of length n of their symbol (X or O) they win the game. However, if all nd spaces are filled then the game is a draw. Tic-tac-toe is the game where n equals 3 and d equals 2 (3, 2). Qubic is the (4, 3) game. The (n > 0, 0) or (1, 1) games are trivially won by the first player as there is only one space (n0 = 1 and 11 = 1). A game with d = 1 and n > 1 cannot be won if both players are playing well as an opponent's piece will block the one-dimensional line.











